Basicity of amines, effect of substituents on basicity, and synthetic
uses of aryl diazonium salts
Session Objectives
By the end of this session, students will be able to:
Ø Discuss
the Basicity of amines.
Amines.
Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3.
Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the
amine both basic and nucleophilic
Amines Nomenclature
alkylamines arylamines
Amines are classified according to the degree of nitrogen
substitution: 1° (RNH2), 2° (R2NH), 3°
(R3N) and 4° (R4N+)
primary (1°)
amines secondary (2°) amines tertiary (3°) amines quarternary (4°) ammonium ion
Structure and bonding. The nitrogen of alkylamines is sp3
hybridized and tetrahedral.
The nitrogen of arylamines (aniline) is slightly flatten,
reflecting resonance interactions with the aromatic ring.
Physical Properties
Basicity of Amines. The basicity is reflective of and is expressed
as the pKa of the conjugate acid.
The conjugate base of a weak acid is a strong base:
Higher pKa
= weaker acid = stronger conjugate base
The conjugate base of a strong acid is a weak base
Lower pKa
= stronger acid = weaker conjugate base
pKa values of ammonium ions
Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X–,
have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+
X–, has a pKa ~ 9.3)
The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic
amines are considerably more acidic than alkyl amines (pKa <
5). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic
if it is in an sp2 hybridized orbital (versus an sp3)
NH4+ pKa= 9.3
(H3CH2C)NH3+
10.8
(H3CH2C)2NH2+ 11.1
(H3CH2C)3NH+ 10.8
Arylamines are
much less basic than alkylamines. The
lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen of aniline are conjugated to the p-electrons of the aromatic
ring and are therefore less available for acid-base chemistry. Protonation disrupts the conjugation.
Substitutents can greatly influence the basicity of the
aniline. The effect is dependent upon the nature and position of the
substitutent.
Electron-donating substituents (-CH3, -OH, -OCH3)
make the substituted aniline more basic than aniline itself (the pKa
of the anilinium ion is higher than 4.6)
Electron-withdrawing substituents (-Cl, -NO2)
make the substituted aniline less basic than aniline itself (the pKa of
the anilinium ion is lower than 4.6)
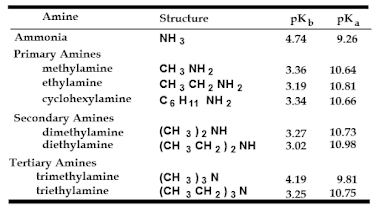
Basicity-Aliphatic Amines
Diazonium Salts
• Diazonium: there are 2 nitrogen
atoms joined together in the positive ion.
• In French, nitrogen is still called
by its old name ‘azote’ which means unable to support life.
• Notice the triple bond between the
nitrogen atoms
• The positive charge is on the
nitrogen that is attached to the benzene ring
Why are
they important? They look pretty weird!
• They are essential in the dye
industry.
• A Diazonium salt is produced then
reacted with a phenol. If the correct phenol is used, almost any colour can be
produced.
Formation
of the Diazonium salt.
• Formed by reacting phenylamine with
sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid.
• These reagents form in situ nitrous
acid HONO.
• The Diazonium salt is unstable above
10°C, so the reaction is normally carried out in ice.
• An aliphatic Diazonium salt is very
unstable, so only aromatics are used.
• The lone pairs present in the salt
can participate in the benzene ring, making it more stable. More correctly this
is due to overlap of p-orbitals in the diazo group with the p-system in the
ring.
• So phenylamine would give
benzenediazonium chloride.
• The conditions are 5°C and remember
the HONO (nitrous acid) is prepared in situ by reacting sodium nitrite with
hydrochloric acid.
• The diazonium salt can ten do one of
two things depending on the temperature
Reactions
of aromatic diazonium salts
Summary
• Triacylglycerols
undergo stepwise enzymatic hydrolysis to finally liberate free fatty acids and
glycerol
• Hydrolysis
of triacylglycerols by alkali to produce glycerol and soaps is known as
saponification
• Rancidity
is the term used to represent the deterioration of fats and oils resulting in
an unpleasant taste
• Oils
which on exposure to air, change into hard solids e.g., linseed oil