Rotameter
Variable area meter
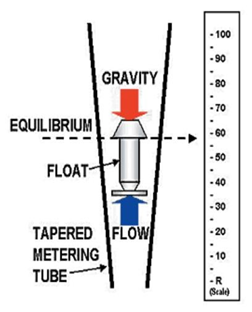
• A device used to measure fluid flow, in which a float rises in a tapered vertical tube to a height dependent on the rate of flow through the tube
• It is a variable area meter which works on the principle of upthurst force exerted by fluid and force of gravity
Construction
• It consists of vertically tampered and transparent tube in which a plummet is placed
• During the flow the plummet rise due to variation in flow
• The upper edge of the plummet is used as an index to note the reading
• Graduated tapered metering glass tube
• Float
Float:
• Floats may be constructed of metals of various densities from lead to aluminum or from glass or plastic.
• Stainless-steel floats are common ones
• Float shapes and proportions are also varied for different applications
• For small flows floats are spherical in shape
Working
• As the flow is upward through the tapered tube the plummet rises and falls depend on the flow rate
• Greater the flow rate higher the rise
Fluid enters the tapered tube, some of the fluid strikes directly the float. Some of the fluid passes from sides
Two forces are acting in this case:
· Upthurst Force (Buoyancy)
· Weight of the float
Annular space increases due to increase in area of the tube
When equilibrium is established the float comes to rest
Measurement of flow rate
The flowrate is measured directly from calibrated scale.
The reading is noted generally from ending point of cap of the float.
Advantages:
• No external power or fuel
• Manufactured of cheap materials
• Since the area of the flow passage increases as the float moves up the tube, the scale is approximately linear.
Disadvantages:
• Accuracy of rotameter
• Uncertainty of the measurement
• Impact of gravity