Quality by
Design (QbD) in Product Development
v Systematic,
holistic and proactive approach to pharmaceutical development.
v Begins
with predefined objectives
v Emphasizes
product and process understanding and process control
v Based
on sound science and quality risk management
Ref.: ICH Q8 (R2)
Generic industry business model: Regulator’s perspective
v File
first, learn later
v Major
amendments during review process
– Exhibit batch stability
failure, formulation revision
v Longer
time for generic product approval
v Approved
product may not be marketed
v Post
approval changes – prior approval supplements
How QbD will help improve?
v Ensure
higher level of assurance of product quality for patient
Ø Improved
product and process design & understanding
Ø Monitoring,
tracking & trending of product & process.
v More
efficient regulatory oversight
v Efficiency
and cost saving for industry
Ø Increase
efficiency of manufacturing process
Ø Minimize
/ eliminate potential compliance actions
Overview of QbD
Quality Target Product
Profile à Product Design and Understanding à Process Design and Understanding à Control Strategy à Continuous Improvement
v Quality
Target Product Profile (QTPP)
v Define
Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
v Perform
risk assessment
v Link
raw material attributes and process parameters to CQAs
v Design
and implement a control strategy
v Manage
product lifecycle, including continuous improvement
Quality Target Product Profile-QTPP
What is QTPP?
• A
set of elements that defines the drug product
• The
target or goal set in advance
• A
guide to Drug Product development
What forms the basis for QTPP?
• The
RLD and its label
• Applicable
regulatory guidelines
When to define QTPP?
• At
the start of development
• Knowledge
gained in development may change some elements
Components of QTPP
Components related to safety, efficacy, identity, purity and
potency
Critical and non-critical components, e.g.
• Critical:
Assay, content uniformity
• Non-critical:
Appearance
Fixed and variable components
• Fixed
elements must be present
e.g. Dosage form, strength
• Variable
elements may have a range of acceptable values
e.g. Tablet weight, assay
QTPP components for IR tablet – Example
Dosage Form |
Route of administration |
Strength |
Weight |
Pharmacokinetics |
Appearance |
Identity |
Assay |
Impurities |
Content uniformity |
Friability |
Dissolution |
Residual solvents |
Specific requirements in QTPP
v Scored
tablets
Ø Weight
variation between two halves
Ø Dissolution
of half tablet
v Orally
Disintegrating tablets
Ø Hardness
Ø Disintegration
time
Ø Container
closure
v Extended
Release products
Ø Alcohol
induced dose dumping
Critical Quality Attributes – CQAs
v CQAs
are a subset of the QTPP
v Include
critical parameters that are likely to change based upon variations in raw
materials and processes
-Identity
test for dosage form – Not a CQA
-Assay,
Content uniformity – CQAs
v CQAs
are monitored throughout the DP development.
v CQAs
ensure that DP remains within safe and effective levels.
QTPP and CQAs
QTPP components |
Dosage Form |
Route of administration |
Strength |
Weight |
Pharmacokinetics |
Appearance |
Identity |
Assay |
Impurities |
Content uniformity |
Friability |
Dissolution |
Residual solvents |
â
CQAs |
Assay (efficacy) |
Impurities (safety) |
C.U. (efficacy) |
Dissolution (efficacy) |
QTPP and Specifications
QTPP
• Desired
target for developmental work
• Components
of QTPP may or may not be in specification
–
Not in spec – Dosage form, strength
–
In spec – Assay, impurities
• Does
not include acceptance criteria
Specifications
• Includes
all of the CQAs
• Specification
is a list of
–
tests,
–
references to analytical procedures
–
acceptance criteria
• Establishes
the set of criteria to which DP should conform to be considered acceptable for
its intended use
• Defining
a QTPP does not mean setting all acceptance criteria
• or
the product specifications before development work begins.
QbD Tools – Risk Assessment
Why risk assessment in product development?
v To
identify relative risk levels at the beginning of product development
v To
prioritize limited development resources
v To
document the decision making process throughout development
v To
assess the needs of additional studies for scale up and technology transfer
v To
identify appropriate specifications, critical process parameters and
manufacturing controls
v To
decrease variability of critical quality attributes
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment for
• Formulation
– starting material properties, levels of components
• Manufacturing
process
Steps for risk assessment
• List
out all components / processes
• Prepare
the process flow chart
• Identify
all potential failure modes for each item with risk query (what might go
wrong?)
• Risk
analysis
• Risk
evaluation
Various formal methodologies available for risk assessment
v Failure
Mode Effects Analysis & Failure Mode Effects & Criticality Analysis
v Hazard
& Operability Analysis
v Supporting
statistical tools
• It
is neither always appropriate nor always necessary to use a formal risk management
process….. The use of informal risk assessment processes can also be considered
acceptable. – ICH Q9
• A
risk-based justification based on experience and data is always necessary!
Quality by Design for ANDAs:
An Example for Immediate-Release Dosage Forms
v Generic
product development for Acetriptan Tablets, 20 mg.
v Acetriptan
is a BCS Class II compound displaying poor aqueous solubility (less than 0.015
mg/mL) across the physiological pH range.
v It
exists in three different polymorphic forms which may affect dissolution.
v Polymorph
III is the most stable polymorph.
v Drug
product is prepared with roller compaction process.
Risk assessment for formulation components
Drug Product CQA | Formulation Variables | ||||
Drug Substance PSD | MCC/Lactose Ratio | CCS Level | Talc Level | Magnesium Stearate Level | |
Assay | MEDIUM | MEDIUM | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Content Uniformity | HIGH | HIGH | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Dissolution | HIGH | MEDIUM | HIGH | LOW | HIGH |
Degradation Products | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | MEDIUM |
Risk assessment of DP manufacturing process
Drug Product CQAs | Process Steps | ||||
Pre-RC* Blending and Lubrication | Roller Compaction | Milling | Final Blending and Lubrication | Compression | |
Assay | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM |
Content Uniformity | HIGH | HIGH | HIGH | LOW | HIGH |
Dissolution | MEDIUM | HIGH | MEDIUM | HIGH | HIGH |
Degradation Products | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Justification for assigned risks
Process Steps | Drug Product CQAs | Assigned Risk | Justification |
Pre-Roller Compaction Blending and Lubrication | Assay | MEDIUM | Suboptimal pre-roller compaction blending and |
Content Uniformity | HIGH | The PSD and cohesiveness of the drug substance | |
Dissolution | MEDIUM | Blending process variables may impact the distribution | |
Degradation Products | LOW | Blending process variables are unrelated to the |
CMAs, CPPs and CQAs
What factors affect drug product CQAs?
v Properties
of Input Materials- Identify Critical Material Attributes (CMAs)
v Properties
of in-process materials- CQAs of one step become CMAs for a downstream unit operation
v Manufacturing
process parameters- Identify Critical Process Parameters (CPPs)
Critical Material Attributes (CMAs)
Risk Assessment of the drug substance attributes
Drug Product CQAs | Drug Substance Attributes | |||||
Solid State Form | Hygroscopicity | Particle Size | Residual Solvents | Process Impurities | Chemical Stability | |
Physical Attributes (size and splitability) | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Assay | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Content Uniformity | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Drug Release | HIGH | LOW | HIGH | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Solid state form and particle size of DS are CMAs
CPPs
• Risk
assessment of manufacturing process
• Identify
high risk steps (unit operation) that affect the CQAs of DP.
Drug Product CQAs | Process Steps | ||||
Pre-RC* Blending and Lubrication | Roller Compaction | Milling | Final Blending and Lubrication | Compression | |
Assay | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM | LOW | MEDIUM |
Content Uniformity | HIGH | HIGH | HIGH | LOW | HIGH |
Dissolution | MEDIUM | HIGH | MEDIUM | HIGH | HIGH |
Degradation Products | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW | LOW |
Process Step: Compression
CPPs | DP CQAs | Risk Assessment | Justification and Strategy |
Main compression force | Content Uniformity | LOW | CU is dominated by BU and flowability and is unrelated to |
Dissolution | HIGH | Suboptimal compression force may affect tablet hardness | |
Press speed (dwell time) | Content Uniformity | HIGH | A faster than optimal press speed may cause inconsistent |
Dissolution | HIGH |
Control Strategy
“A planned set of controls, derived from current product and
process understanding that ensures process performance and product quality…..”
ICH Q8 (R2) & Q10
Control Strategy includes following elements (but not
limited to):
• Input
material attributes (e.g. drug substance, excipients, container closure)
• Equipment
operating conditions (process parameters)
• In-process
controls
• Finished
product specifications
• Controls
for each unit operations
• Methods
and frequency of monitoring and control.
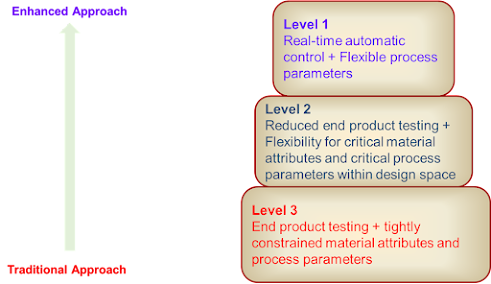
Control Strategy Implementation Options
QbD Tools – DoE
Design of experiments (DoE)
• Useful
for screening of variables with significant impact on DP CQAs
• Classical
approach uses OFAT (One Factor At A Time)
• Limited
number of experiments gives limited information.
• DoE
helps study effects of interaction of multiple factors at a time
• Used
in optimization studies, enables creation of “design space”
• “Design
space” is proposed by the applicant and subject to regulatory assessment and
approval.
• “Design
space” developed at lab or pilot scale can be proposed for commercial scale,
but needs to be verified at production scale for scale dependant parameters.
Process Analytical Technology (PAT)
Ø Timely
measurements during processing
v Critical
quality and performance attributes
v Raw
and in-process materials
Ø At-line,
on-line or in-line measurements
• Founded
on “Process Understanding”
Opportunities for improvement
• More
reliable and consistent processes (& product)
• Less
failures, less reworks, less recalls
• Flexibility
w.r.t. scale and equipment
• Better
/ faster Quality Systems
• Process
Enhancement Opportunities
PAT in Tablet manufacturing
Stage | Technique | Measurement |
Dispensing | NIR / Raman | Identification of raw materials |
Wet Granulation | NIR | Moisture distribution |
Drying | NIR | Moisture content |
Blending | NIR | Blend Uniformity |
Compression | Strain gauges | Compression force |
NIR | Content Uniformity |
PAT Examples
Spectral Probe NIR Analyzer installed on viewing window of
Glatt FBD without any dryer modification.
Real-time Blend
Uniformity by using TruProcess™ Analyzer
QbD: Required or Optional?
Required
• Quality
target product profile (QTPP) including critical quality attributes (CQAs) of
the drug product and including Product design and understanding
• Product
design and understanding
• Critical
material attributes (CMAs) of the drug substance and excipients
• Process
design and understanding
• Critical
process parameters (CPPs)
• Control
strategy, including justification
Optional
• Design
Space
• Process
Analytical Technology
References for QbD
- Guidance
for Industry: Q8(R2) Pharmaceutical Development - Guidance
for Industry: Q9 Quality Risk Management - Guidance
for Industry: Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System - Guidance
for Industry PAT: A Framework for Innovative Pharmaceutical Development,
Manufacturing, and Quality Assurance - Quality
by Design for ANDAs: An Example for Modified Release Dosage Forms - Quality
by Design for ANDAs: An Example for Immediate Release Dosage Forms - GPhA
presentations - Draft
QbR updated