Energy flow in an Ecosystem
Intended Learning Outcomes
At the end of this Lecture, students will be able to
• Explain energy flow in the ecosystem
• Draw models of energy flow in the ecosystem
• Explain Food chain
• Explain types of food chain
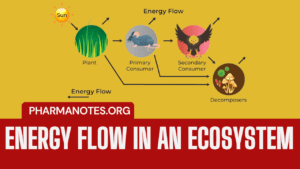
Energy flow in an Ecosystem
• Biological activities requires energy which ultimately comes from the sun. Solar energy is transformed into chemical energy by a process of photosynthesis this energy is stored in plant tissue and then transformed into heat energy during metabolic activities.
• Thus in biological world the energy flows from the sun to plants and then to all heterotrophic organisms the flow of energy is unidirectional and non-cyclic. This one way flow of energy is governed by laws of thermodynamics which states that:
(a) Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but may be transformed from one form to another.
(b) During the energy transfer there is degradation of energy from a concentrated form (mechanical, chemical, or electrical etc.) to a dispersed form (heat).
• No energy transformation is 100 % efficient, it is always accompanied by some dispersion or loss of energy in the form heat. Therefore, biological systems

Single Channel Energy Flow Model
The flow of energy takes place in a unidirectional manner through a single channel of producers to herbivores and carnivores. The energy captured by autotrophs does not revert back to solar input but passes to herbivores; and that which passes to herbivores does not go back to autotrophs but passes to consumers.
Due to one way flow of energy, the entire system would collapse if primary source of energy were cut off. At each tropic level there occurs progressive decrease in energy which is mainly due to loss of energy as heat in metabolic reactions and also some of the energy is utilized at each tropic level

Y- Shaped or Double Channel Energy Flow Model
• Y- shaped model shows a common boundary, light and heat flow as well as import , export and storage of organic matter . Decomposers are placed in separate box to partially separate the grazing and detritus food chains. In terms of energy levels decomposers are in fact a mixed group.

• Y- shaped energy flow is more realistic and practical than the single channel energy flow model because:
• It conforms to the basic stratified structure of ecosystems
• It separates the two chains i.e. grazing & detritus food chain in both time and space.
• Micro consumers (bacteria & fungi) and the macro consumers (animals) differ greatly in size- metabolism relations in two models. Model Y- Shaped or Double Channel Energy Flow
Universal Energy Flow Model
As the flow of energy takes place, there is gradual loss of energy at each level there by resulting in less energy available at the next tropic level as indicated by narrower pipes (energy flow) and smaller boxes (stored energy in biomass).
The loss of energy is mainly the energy which is not utilized (U). This is the energy loss in locomotion, excretion etc. or it the energy lost in respiration (CR) which is for maintenance. The remaining energy is used for production (P).

Food Chain & Food Web
• Food Chain: In food chain each organism eats the smaller organisms and is eaten by the larger one. All those organisms which are interlinked with each other through food to gather constitute the ecosystem.
• The different levels in a food chain are called tropic levels, Each food chain has three main tropic levels:- Producer level, Consumer level, and decomposer level.
• If any of the intermediate stage of the food chain is removed, the succeeding links of the food chain will be affected.
• The arrangement in a food chain can be depicted as:
Types of Food Chains
Grazing Food Chain: This type of food chain starts from living green plants goes to grazing herbivores and onto carnivores. Ecosystem with such type of food chain directly depends upon the solar energy for their food requirements. Most of the ecosystem in nature follow this type of food chain.
Detritus food Chain: This type of food chain goes from dead organic matter onto microorganisms and then to the organisms feeding on detritus and their predators. Such ecosystem are less dependent on direct solar energy.
Parasitic Food Chain: This type of food chain starts from big hosts and ends with parasitic organisms.
Grazing Food Chain

Detritus Food Chain

Food Web
• Food Web: The interconnected, interlocking pattern of food chain is known as food web.
• Under natural condition of the linear arrangement of food chain hardly occurs and they remain interconnected with each other through different types of organisms at different levels Such a interconnected and interlocking pattern of food chain is known as food web.

Summary
• Biological activities requires energy which ultimately comes from the sun.
• Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed but may be transformed from one form to another.
• During the energy transfer there is degradation of energy from a concentrated form (mechanical, chemical, or electrical etc.) to a dispersed form (heat).
• In food chain each organism eats the smaller organisms and is eaten by the larger one
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf