Blood Clotting and Transfusion
Objectives
At the end of this
lecture, student will be able to
• Describe blood clotting
• Explain the ABO and Rh blood groups
• Outline the concept of blood transfusion
• Explain ABO blood group interactions
• Explain Erythroblastosis Foetalis
Content
• Blood clotting
• Concept of blood grouping
• Blood grouping interactions
Blood
Clotting (Coagulation)
Blood
Clotting
• Extrinsic pathway and the intrinsic pathway lead to the
formation of prothrombinase
• Prothrombinase converts prothrombin (a plasma protein
formed by the liver) into the enzyme thrombin
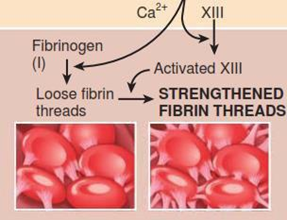
• Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen (another plasma
protein formed by the liver) into insoluble fibrin
• Fibrin forms the threads of the clot
Role of
Clotting Factors
Clotting Factors
Fibrinolysis
• Dissolution of clot
• Mechanism
– Plasminogen (a plasma protein) is activated by many
factors & becomes Plasmin
– Plasmin then breaks down fibrin meshwork
– Phagocytic WBCs remove products of clot dissolution
Haemostatic
Mechanism Overview
Thrombus
and Embolus
• Thrombus – clot formed in an intact vessel, possibly due
to:
Roughened vessel walls
Slow-moving blood (e.g. in varicose veins)
Blood
Groups
Antigens
(Agglutinogens)
• The surfaces of RBC contain a genetically determined
assortment of antigens
• Composed of glycoproteins and glycolipids
• 24 blood groups
• ABO and Rh
• The Lewis, Kell, Kidd & Duffy systems
Significance
of Antigen
• Based on the presence or absence of various antigens,
blood is categorized into different blood group
• A, B, AB and O
Antigens and
Antibodies of ABO Blood Types
ABO Blood
Group Interactions
Concept of
Blood Transfusion
Rh Blood
Group
• Rh – Antigen was discovered in the blood of the Rhesus
monkey
• Rh antigens present – Rh positive and vice versa
• Normally blood plasma dose not cantain anti-Rh antibodies
• To a Rh- person if Rh+ blood is given – Immune system
starts to make anti-Rh antibodies that will remain in the blood
• A second transfusion of Rh+ blood is given later
• The previously formed anti Rh antibodies will cause
agglutination and hemolysis of the RBCs in the donated blood
Blood
Grouping
Erythroblastosis
Foetalis
Summary
• Extrinsic pathway and the intrinsic pathway lead to the
formation of prothrombinase in blood clotting
• The ABO blood
grouping – Based
on antigen (A
or B) and antibody ( A or B) type
• Rh blood type – Based on another surface antigen called
either Rh or D
• Erythroblastosis Foetalis: Rh incompatibility between
mother and foetus