Ketone bodies and their utilization

Ketone bodies and their utilization
Objective
• At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
– Explain ketogenesis and Ketolysis
– Describe the disorders associated with ketone bodies
Ketone bodies
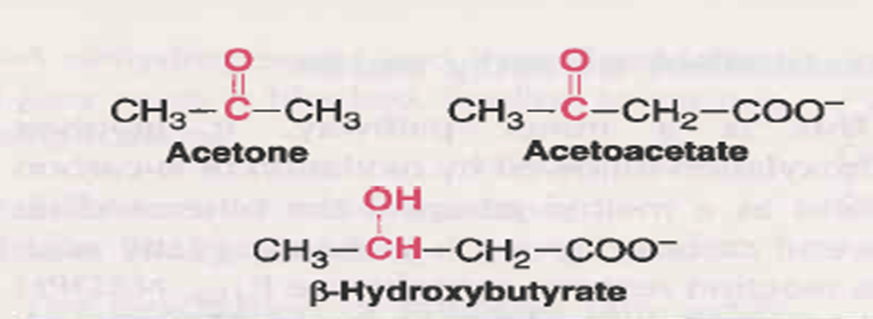
• Acetone, Acetoacetate & β-hydroxybutyrate are known as ketone bodies
• Only the first two are true ketones while β-hydroxybutyrate does not possess a keto (C=O)group
• Ketone bodies are water-soluble and energy yielding
• Acetone, however, is an exception, since it cannot be metabolized
Ketogenesis
• Synthesis of ketone bodies is known as Ketogenesis
• Occurs in Iiver
• Enzymes are Located in mitochondrial matrix
• Acetyl CoA, formed by oxidation of fatty acids, pyruvate or some amino acids, is the precursor for ketone bodies
• The main purpose of ketogenesis in the liver is to distribute excess fuel (Acetyl-CoA) to other tissues.
Ketogenesis occurs through the following reactions
1. Two moles of acetyl CoA condense to form acetoacetyl CoA, This reaction is catalysed by thiolase, an enzyme involved in the final step of β-oxidation
2. Acetoacetyl CoA combines with another molecule of acetyl CoA to produce β-hydroxy β-methyl glutaryl CoA (HMG CoA), catalysed by HMG CoA synthase
3. HMG CoA lyase cleaves HMG CoA to produce acetoacetate and acetyl CoA
4. Acetoacetate can undergo spontaneous decarboxylation to form acetone
5. Acetoacetate can be reduced by a dehydrogenease to β-hydroxybutyrate
Ketolysis
• Degradation of ketone bodies
• Ketone bodies produced in the liver reach peripheral tissues through circulation
• Heart, kidney, cortex, brain and to a certain extent skeletal muscle uses ketone bodies for energy
Biological significance
• Heart, kidney and cortex prefer to use ketone bodies rather than glucose.
• During prolonged starvation, brain derives most of the energy from ketone bodies
• Liver is unable to use ketone bodies due to lack of enzymes.
Utilization of Ketone bodies
• Ketone bodies, being water-soluble, are easily transported from the liver to various tissues
• Acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate serve as important sources of energy for the peripheral tissues such as skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle/ renal cortex etc
• During prolonged starvation, ketone bodies are the major fuel source for the brain and other parts of central nervous system
• The production of ketone bodies and their utilization become more significant when glucose is in short supply to the tissues, as observed in starvation, and diabetes mellitus
Disorders
• The concentration of ketone bodies in blood is maintained around 1 mg/dl
• Their excretoin in urine is very low and undetectable by routine tests (Rothera’s test)
• When the rate of synthesis of ketone bodies exceeds the rate of utilization, increased concentration in blood known as ketonemia
• Ketonuria represents the excretion of ketone bodies in urine
• Hyper ketonemia and ketonuria gives rise to ketosis (Smell of acetone in breath is a common feature in ketosis)
• Ketosis is most commonly associated with starvation and severe uncontrolled diabetes mellitus,
• The hormone glucagon stimulates ketogenesis whereas insulin inhibits it
• Ketoacidosis: Both acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate are strong acids. Increase in their concentration in blood would cause acidosis
• Diabetic ketoacidosis is dangerous, may result in coma and even death if not treated
Summary of ketone bodies synthesis, Utilization and excretion
Summary
• Ketogenesis is synthesis of ketone bodies
• Take place in liver and major source of energy
• Acetone, Acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate are 3 ketone bodies
• Increased concentration in blood known as ketonemia
• Ketonuria represents the excretion of ketone bodies in urine
• The overall picture of ketonemia and ketonuria is commonly referred to as ketosis
• The hormone glucagon stimulates ketogenesis whereas insulin inhibits it.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf