Beckmann Rearrangement

Beckmann Rearrangement
Session Objectives
By the end of this session, students will be able to:
• Steps involved in Beckmann rearrangement
• Mechanism of Beckmann rearrangement
Beckmann Rearrangement
The Beckmann Rearrangement is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of an oxime into an amide.
An oxime is a functional group consisting of a nitrogen atom (-N=O) attached to a carbon atom, typically in an aldehyde or ketone.
This transformation is achieved by using various reagents and conditions, and it leads to the rearrangement of the molecule, resulting in the formation of an amide.
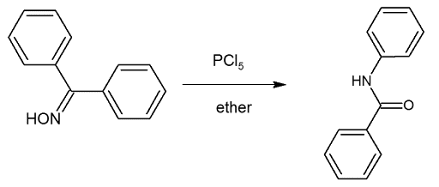
PREPARATION OF BENZANILIDE FROM BENZOPHENONE (BECKMANN REARRANGEMENT)
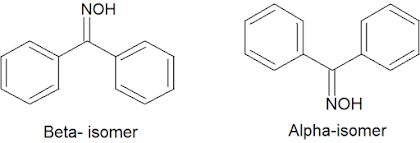
• Aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxyl amines in the presence of sodium hydroxide to give an Oxime of low melting point (alpha or syn aldoxime).
• It rapidly rearranges to give an isomeric Oxime of higher melting point by acids-(beta or anti aldoxime).
• Oximes of ketones undergo Beckmann rearrangement to substituted amides under the influence of variety of acidic reagents e.g HCOOH, PCl5, H2SO4, SOCl2, etc.
• In this rearrangement, the migrating group is always anti- to –OH group and thus this reaction is stereo specific.
• Here benzophenone oxime in presence of PCl5 rearranges to benzanilide.
Step involved in Beckmann Rearrangement Reaction:
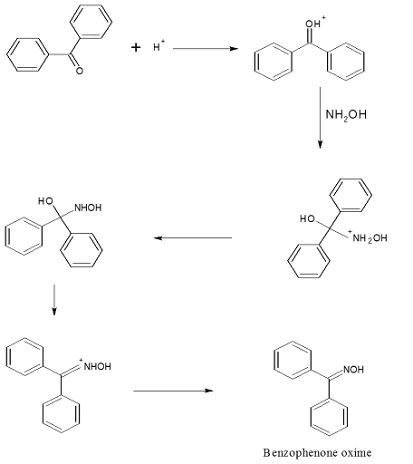
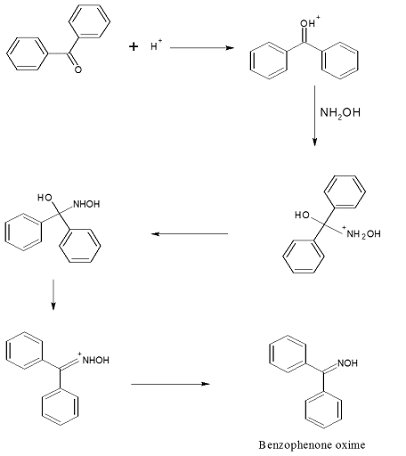
Step-I: Preparation of benzophenone oxime
Step-II: Preparation of benzanilide from benzophenone oxime
Mechanism of Beckmann Rearrangement
The mechanism of the Beckmann Rearrangement involves the acid-catalyzed migration of a group from the nitrogen atom to the adjacent carbonyl carbon.
The process proceeds via a series of intermediates, with the oxime undergoing rearrangement to form an amide.
The reaction is highly regioselective, and the choice of reaction conditions can influence the outcome.
MECHANISM: – Step-I: Preparation of benzophenone oxime
Step-II: Preparation of benzanilide:
Summary
• Aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxyl amines in the presence of sodium hydroxide to give an Oxime of low melting point (alpha or syn aldoxime).
• This is stable in alkali but rapidly rearranges to give an isomeric Oxime of higher melting point by acids-(beta or anti aldoxime).
• Oximes of ketones undergo Beckmann rearrangement to substituted amides under the influence of variety of acidic reagents e.g HCOOH, PCl5, H2SO4, SOCl2, etc.
• In this rearrangement, the migrating group is always anti- to –OH group and thus this reaction is stereo specific.
• Here benzophenone oxime in presence of PCl5 rearranges to benzanilide.
FAQs about Beckmann Rearrangement
1. What are the key features of the Beckmann Rearrangement?
The Beckmann Rearrangement is a chemical reaction that converts oximes into amides, often used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and materials.
2. Who discovered the Beckmann Rearrangement?
German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann is credited with the discovery of this rearrangement.
3. Can the Beckmann Rearrangement be used in the synthesis of polymers?
Yes, it plays a crucial role in the production of nylon-6, a widely used polymer.
4. What safety precautions should be taken when working with the Beckmann Rearrangement?
Safety measures should include the use of protective equipment, proper handling of reagents, and a well-ventilated workspace.
5. How is the regioselectivity of the Beckmann Rearrangement controlled?
Regioselectivity can be influenced by the choice of reagents and reaction conditions, and it varies based on the specific substrate.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf