Dakin Reaction & Oppenauer Oxidation
Session Objectives
By the end of this session, students will be able to:
• Dakin Reaction
• Mechanism of Dakin Reaction
• Oppenauer Oxidation
• Mechanism ofbOppenauer Oxidation
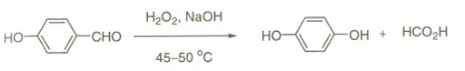
Dakin Reaction
• Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho– or para-hydroxylatedbphenyl aldehyde (2 hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate.
• Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
Reaction Mechanism of Dakin Reaction
• The Dakin reaction starts with nucleophilic addition of a hydroperoxide anion to the carbonyl carbon forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
• The intermediate collapses causing [1,2]-aryl migration, hydroxide elimination, and formation of a phenyl ester.
• The phenyl ester is subsequently hydrolyzed: nucleophilic addition of hydroxide from solution to the ester carbonyl carbon forms a second tetrahedral intermediate, which collapses, eliminating a phenoxide and forming a carboxylic acid.
• Finally, the phenoxide extracts the acidic hydrogen from the carboxylic acid, yielding the collected products
Dakin Reaction
Reaction Mechanism of Dakin Reaction
Synthetic applications of Dakin reaction
• The Dakin reaction is most commonly used to synthesize benzenediols and alkoxyphenols.
• Catechol, for example, is synthesized from o-hydroxy and o-alkoxy phenyl aldehydes and ketones, and is used as the starting material for synthesis of several compounds, including the catecholamines, catecholamine derivatives, and 4-tert-butylcatechol, a common antioxidant and polymerization inhibitor.
• Other synthetically useful products of the Dakin reaction include guaiacol (2-Methoxyphenol (a precursor of several flavorants; hydroquinone (benzene-1,4-diol or quinol) a common photograph-developing agent; and 2-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and 3-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole, two antioxidants commonly used to preserve packaged food.
• In addition, the Dakin reaction is useful in the synthesis of indolequinones, naturally occurring compounds that exhibit high anti-biotic, anti fungal, and anti-tumor activities.
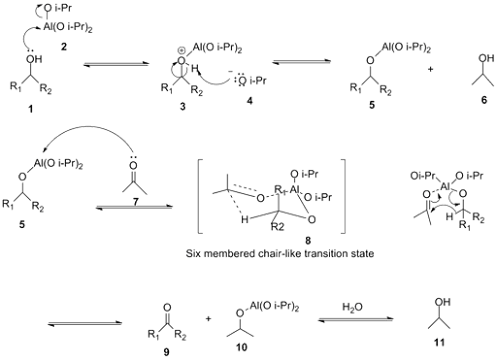
Oppenauer Oxidation
• Oppenauer oxidation, named after Rupert Viktor Oppenauer,is a gentle method for selectively oxidizing secondary alcohols to ketones.
• Alcohols on refluxing with aluminium isopropoxide in acetone are oxidisied to aldehydes or ketones.
• Acetone acts as hydrogen acceptor and it is converted into isopropyl alcohol.
• The presence of excess of acetone drives the reaction towards the oxidation product.
Reaction Mechanism of Oppenauer Oxidation
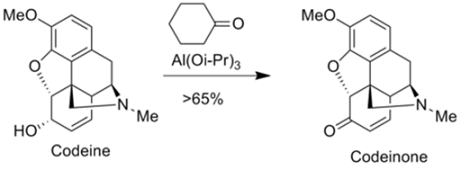
Synthetic applications of Oppenauer Oxidation
• The Oppenauer oxidation is used to prepare analgesics in
the pharmaceutical industry such as morphine and codeine.
• For instance, codeinone is prepared by the Oppenauer
oxidation of codeine.
• The Oppenauer oxidation is also used to synthesize hormones.
• Progesterone is prepared by the Oppenauer oxidation of pregnenolone.
Summary
• Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho– or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate.
• Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidized, and the hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
• Oppenauer oxidation, named after Rupert Viktor Oppenauer, is a gentle method for selectively oxidizing secondary alcohols to ketones.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf