Suspension Culture
Content
• Suspension Culture
• Definition
• Types
• Apparatus used
Objective
At the end of the lecture the student will able to:
• Discuss the technique of suspension culture
• Discuss the various suspension culture apparatus
Suspension
Culture
• Type of culture –
single cell or small aggregates of cells multiply while suspended in agitated
liquid medium under aseptic conditions
• Cell suspension –
friable callus cells – liquid medium – agiated – rotary shaker
• Agitation of medium
is very important, it helps in two ways
i. Prevent the clumping or settling of cells – dispersion –
auxins or pectinase or cellulase enzyme
ii. Gaseous exchange, aeration
• Mainly of two types
Batch suspension culture and Continuous suspension culture
Batch suspension culture:
• Cell material or inoculums grow – finite volume of
agitated liquid medium
Continuous suspension
culture:
• Process in which spent medium is continuously replaced by
fresh medium in order to maintain steady growth
• Depletion of nutrients does not occur due to continuous
flow of fresh medium
Suspension culture apparatus:
i) Agitated liquid
culture apparatus
a. Shake
culture
b. Slowly
rotating culture (Auxophytons) – Tumble tube Nipple flask Spin culture
ii) Stationary liquid
culture apparatus – Chemostat and Turbidostat
Shake Culture:
• Agitation is provided by moving the liquid medium
• Consists a metal platform and number of clamps
• Clamps are used to hold container
• When platform shakes, it provides circular motion to
medium and leads to gaseous exchange or aeration
• Shaker speed – 30 – 150 rpm
Advantages: Large
amount of cells can be grown, various sized flasks can be used
Disadvantage: Sometimes
evaporation of medium due to high speed
Tumble tube:
• Consists of glass tube of capacity 10 ml with a neck at
the centre
• Neck is plugged with cotton (gaseous exchange)
• 24 such tubes are placed on a circular disc, 5-6 circular
discs are placed on a shaft
• When shaft rotates, tubes tumble, medium flows from one
end to another
• As the tube tumbles, explant alternatively exposed to
medium and air, which helps in gaseous exchange
• Large amount of cells cannot be grown
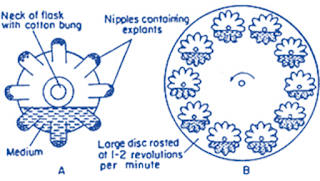
Nipple flask:
• Modified form of tumble tube
• Available in 2 sizes, 250 ml with 8 nipples and 1000 ml
with 10 nipples
• About 10 nipple flasks are placed on a circular disc
• When disc rotates, medium enters and leaves the
projection, explant alternatively exposed to medium and air Speed of rotation –
1-2 rpm
• Large amount of cells can be grown
Spin culture:
• Consists of bottle of capacity 10 Liter
• Mounted at an angle 450 in the spin
• Bottle spins because of the inclined angle
• As a result there is a movement of medium
• Movement leads to gaseous exchange
• Large amount of cells can be grown compare to tumble tube
and nipple flask
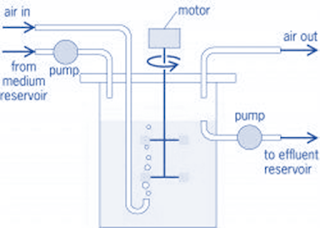
Chemostat:
• It is a continuous suspension culture
• Consists air inlet, air outlet, provision for continuous supply
of medium and removal of spent medium, and magnetic stirrer
• There is a fixed rate of media input and it is time
programmed
• A steady state is achieved by the addition of the medium
Turbidostat:
• It is also a continuous suspension culture
• Consists similar apparatus as that of chemostat along with
densitometer
• Turbidity of suspension culture medium increases with
increase in number of cells
• Turbidity is measured by measuring optical density using
densitometer
• Once turbidity reaches maximum level spent medium is
removed and fresh medium enters
Growth measurement:
• Cell count/cell number
• Cell viability
Packed cell volume:
• Suspension culture medium with cells is subjected to Centrifugation
at 2000 rpm for 10-15 min
• Cells settled down at the bottom
• Volume of these settled cells is measured – Packed cell
volume
Summary
• Tissue culture is growing of tissues or cells on a
suitable nutrient medium under aseptic conditions in vitro, may be plant or
animal tissue culture
• Types include callus, suspension, hairy root, single cell,
haploid, organogenesis, embryo culture etc
• Suspension culture is growing of cells/cell aggregates in
liquid media, batch or continuous
• Agitation is essential, helps in gaseous exchange
• Initiated using friable callus cells, sterile seedling,
embryo etc
• Agitated liquid apparatus like shake culture, tumble tube,
nipple flask, spin culture and stationary liquid culture like chemostat and
turbidostat
• Large amount of cells can be grown compare to callus
culture