Tranquilizers
• A tranquilizer is a drug which
is designed for the treatment of anxiety, fear, tension, agitation, and
disturbances of the mind, specifically to reduce states of anxiety and tension.
• Psychoses mean mental condition raised
by disturbance in mental function.
• Mental disease has always been
puzzling and frightening things.
• They are quite different from other
disease of mankind.
Psychoses
may be:
1. Organic psychoses where there is
memory distrurnace clouding of consciousness due to endocrinal abnormalities of
head injury.
2. Functional psychoses may be:
a) Manic: disturbance of mood.
b) Schizophrenia in which there is
disordered of thoughts emotions
c) Hallucinations
d) Anxiety where feeling of fear.
Classifications of Tranquilizers:
1. Phenothiazine
derivatives and related tricyclic compound:
a) Phenothiazine
derivatives: e.g. chlorpromazine, Prochlorperazine trifluoroperazine.
b) Thioxanthenes
derivatives: e.g. chlorprothixene ,flupenthixol
2. Butyrophenones: e.g. haloperidol,
trifluoperidol (Triperidol)
3. Dibenzodiazepines: e.g. clozapine
4. Benzamides and salicylamides e.g.
Sulpiride
5. Diphenyl butyl piperidine
derivatives: e.g. pimozide
6. Miscellaneous: e.g. Reserpine.
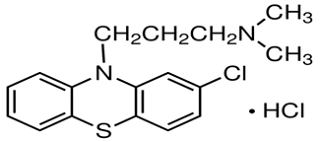
Chlorpromazine
Structure of Chlorpromazine:
Chemical
name: 2-chloro, 10
(dimethyl amino propyl) phenothiazine.
Physical properties of Chlorpromazine:
• It is hydrochloride salt is white or
cream coloured powder.
• It has slight odour.
• It is very soluble in water
• It is freely soluble in alcohol
• It is decomposed on exposure to light,
becoming yellow to pink and finally violet.
Chemical properties of Chlorpromazine:
• When it is oxidised with conc.
sulphuric acid it gives red colour.
• When it is treated with conc. Nitric acid,
it oxides to give red coloured substance which on standing to becomes yellowish.
• It is also oxidised by ceric ammonium
sulphtae solution.
Stability and storage of Chlorpromazine:
• It is
discolored when exposed to light and hence it is stored in well closed light
resistant containers.
Uses of Chlorpromazine:
It is used to treat:
• Schizophrenia
• Mania and
hypomania
• Used to
control nausea and vomiting.
• Used to
produce pre and post-operative sedation, which enhance the effect of
barbiturates and analgesics.
• It acts as
vasodilators.
• It reduces
the salivary and gastric secretion.
• It has local anesthetics property.
Pharmaceutical formulations: Chlorpromazine elixir, injection, tablets, suppositories
Brand names: Largactil, Chorozine, Copamide
Prochlorperazine
Physical properties of Prochlorperazine:
• It is
official as maleate salt which is white to yellow crystalline powder.
• It is
odourless
• It has
slightly bitter taste.
• It is very
soluble in water and alcohol.
Stability and storage of Prochlorperazine:
• It is
affected by light hence it is stored in well closed light resistant containers.
Uses of Prochlorperazine:
• As under
chlorpromazine
• It is less
sedative and more effective as antiemetic
Pharmaceutical formulations: Prochlorperazine tablets, capsules
Brand names: Mentil, Stemetil
Trifluoperazine
Physical properties of Trifluoperazine:
• It is
official as a hydrochloride salt which is white or pale yellow crystalline powder.
• It is odorless.
• It has
bitter taste.
• It is hygroscopic.
• It is freely
soluble in water.
Stability and storage of Trifluoperazine:
• It is
hygroscopic .it is oxidised by oxygen in presence of moisture and sunlight.
Hence it is stored in well closed light resistant containers.
Uses of Trifluoperazine:
• As under
chlorpromazine.
Pharmaceutical formulations: Trifluoperazine tablets, capsules, injections
Brand names: Stelabid, Eskazine, Siquil
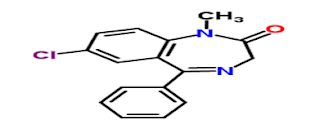
Haloperiodol
Structure of Haloperiodol:
Chemical names: 4-[4-(p- chlorophenyl),
4 –hydroxy piperidine] 4’ –florobutyroohenone.
Physical properties of Haloperiodol:
• It is white
to faint yellowish, amorphous or microcrystalline powder.
• It has
odourless
• It has tasteless.
• It is
practically insoluble in water
• It is
sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Storage: stored in well closed containers.
Uses of Haloperiodol:
• Acute
schizophrenia
• Mania and
hypomania
• Behavioral
disturbance
• Severe
anxiety
• Childhood
development disordered
• It is used
as an antiemetic
• It
potentiates the cation of CNS depressant like analgesic barbiturates,
anesthetics
Pharmaceutical formulations: Haloperiodol
tablets, injections,
capsules, elixir
Brand names: Halidol, Tarncodol
Triperiodol
Physical properties of Triperiodol:
• It is white
or yellowish crystalline powder
• It is
odorless
• It is
tastless
• It is
practically insoluble in water.
Stability, storage, and uses as under
haloperidol
Pharmaceutical formulations: Triperiodol
tablets
Brand names: Triperidol
Chlordizepoxide
Physical properties of Chlordizepoxide:
• It is
official as hydrochloride salt
• It is white
crystalline powder.
• It has
slightly odor
• It has very
bitter taste.
• It is
soluble in water.
Chemical properties of Chlordizepoxide:
• When it is hydrolysed
it is converted to demoxepam with the removal of methyl amino group.
• On further
degradation it is converted to 2-amino, 5-chloro benzoquinone in which 4, 5
azeomethine linkage is ruptured.
Stability and storage of Chlordizepoxide:
• It is
affected by air, moisture and sunlight hence it is stored in well closed light
resistant containers.
Uses of Chlordizepoxide:
It is used to treat:
• Symptoms of
anxiety
• Psychosomatic
disordered
• Insomnia
associated with anxiety
• Muscle spasm
• It is also
used in premedication in anesthesia
Pharmaceutical formulations: Chlordizepoxide tablets, injections
Brand names: Tropium, Librium
Diazepam
Structure of Diazepam:
Chemical name: 7 Chloro, 2, 3 dihydro, 1 methyl 5 phenyl 1H-1 4 benzodizepine -2-one.
Physical properties of Diazepam:
• It is white
pale yellow crystalline powder
• It is
odorless
• It is
tasteless first followed by bitter taste
• It is
sparingly soluble in water
• It is
soluble in alcohol,
Stability and storage of Diazepam:
• It is
degraded by moisture and light.
• Hence it is
stored in tightly closed light resistant containers
Uses of Diazepam:
• For
management of anxiety and tension state.
• For
management of acute alcoholic withdrawal.
• To relief
from skeletal muscle spasm.
• To treat
epilepsy
• To produce
sedations
• To treat
excitation state.
• As
premedication for surgical dressing
Pharmaceutical formulations: Diazepam tablets, capsules,
injections, elixir.
Brand names: Calmpose, sedanite
Lorazepam
Physical properties of Lorazepam:
• It is white
to off white powder
• It is
odorless
• It is
practically insoluble in water
• It is
slightly soluble in alcohol
Storage of Lorazepam:
• It is
degraded by moisture and light. Hence it is stored in tightly closed light
resistant containers
Treatment of Lorazepam:
It is used to treat:
• For
management of anxiety and tension state.
• Insomnia
associated with anxiety
• Epileptic
seizures (IV)
• As
premedication for surgical dressing
Pharmaceutical formulations: Lorazepam tablets,
injection
Brand names: Ativen,
Lorapam, Alzapam
Meprobamate
Physical properties of Meprobamate:
• It is white
crystalline powder or granular crystalline aggregates.
• It is
odorless
• It has
bitter characteristic state.
• It is
slightly soluble in water
• Freely
soluble in alcohol
Chemical properties of Meprobamate:
• When it is
treated with dimethyl amino benzaldehyde solution in sulphuric acid a yellow
colour is produced with changes to orange on standing.
Stability and storage: it is stored in well closed containers.
Uses of Meprobamate:
• For
management of anxiety and tension state.
• Muscle
skeletal relaxant
• Petit mal
type of epilepsy
Pharmaceutical formulations: Meprobamte tablets, capsules, injection, oral suspensions
Brand names: Equanil, Cadiporm, PMT