Cardiovascular, Antimicrobial, Anti-inflammatory and Antibiotic agents of marine origin

Cardiovascular antimicrobial antiinflammatory and antibiotic agents of marine origin
Objective
At the end of this
lecture, students will be able to:
• Discuss the different sources of Cardiovascular, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and antibiotic agents of marine origin
Marine Cardiovascular drugs
• Cardiotonics
• Marine peptides
• Marine glycosides
Laminin
• Obtained from marine algae Laminaria angustata
• Belongs to the family heterotrimeric glycopoteins composed of heavy chain, designated as alpha and 2 light chains, designated as beta and gamma which are linked by disulphide bonds to form and symmetrical cross shaped structure
• Shows hypotensive effect
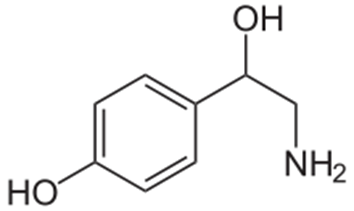
Octapamine
• Found in the salivary glands of Octapus vulgaris, O. macropus and Eledone moschata
• Produces cardiovascular adrenergic response
• As neurotransmitter in invertebrates
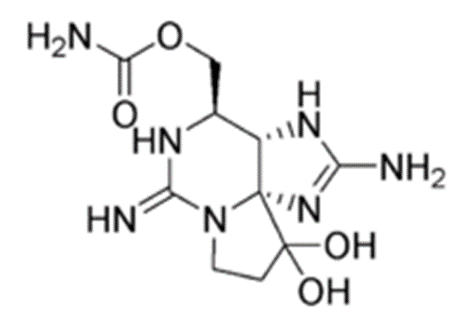
Saxitoxin (Mussel poison, Clam poison, Paralytic shellfish poison, STX)
• Obtained from the dinoflagellates, Gonyaulax catenella or G. tamarensis
• Exhibits hypotensive effect
Autonomium chloride
• Obtained from Verongia fistularis
• Exerts both α and β adrenergic effects
• Also exhibits cholinergic action
• Shows CNS stimulant activity
• Polypeptides obtained from marine sources (Sea anemones) includes a polypeptide with 147 aminoacids from Actinia equine exhibiting bradycardia, rapid hypotension and respiratory arrest
• Other polypeptides are obtained from Condylactis gigantean, Parasicyonis action stoloides exhibiting haemolytic and neurotoxic Action
Marine glycosdies – Holothurins and astrosaponins
Holothurins
• Obtained from the family, Holothuroidae and phylum Echinodermata possessing steroidal moiety resembling digitalis
Astrosaponins
• From fishes of family Asteroidae
Eledoisin
• Obtained from the posterior salivary glands of Eledone moschata
• Stimulates extravascular smooth muscle, lacrimal secretion
• Potent vasodilator, hypotensive agent
Hypotensive compounds
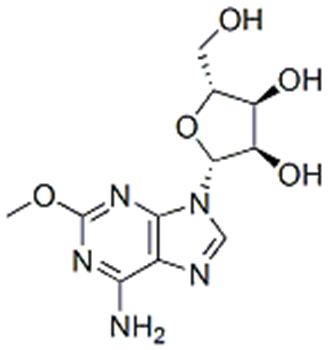
Spongosine
• Nucleoside and a methoxy derivative of adenosine
• Obtained from Caribbean sponge, Cryptotetheia crypta
• Exhibits various coronary vasodilation and negative inotropy
• Acts as hypotensive agent
• Reduces force and rate of contraction of heart
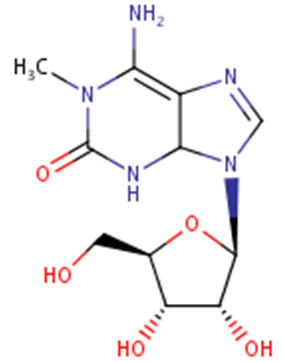
Doridosine
• Obtained from nudibranch Anisodoris nobilis
• Most potent hypotensive marine nucleoside
• Exerts hypothermic activity
Hypotensive peptides and other compounds
Aaptamine
• Obtained from Aaptos asptos
• Used as α adrenergic blocking agent
• Causes hypotension
Hymenin
• Obtained from Hymeniacidon aldis
• Used as α adrenergic blocking agent
• Causes hypotension
Urotensins I and II
• Obtained from specific caudal neurosecretory system of Giltichthys miralilis and from Catostomus commersoni
• Exerts vasodilation and hence hypotension
Marine Antimicrobial agents
Chemical compound | Organism | Uses |
| Istamycins | Streptomyces tenimariensis | Effective against gram +ve and – ve organisms |
| Bromopyrones Fimbrolides Laurene | Ptilonia austrulasica Delisea fimbriata Laurencia | Have halogen in particular bromine, hence toxic |
| Holotoxin A, B, C (Steroidal glycoside) | Sea cucumber, Stichopus japonicas | Antifungal |
| Zonarol and isozonarol | Dictyopteris zonaroides (Brown algae) | Antimicrobial |
| Tetrabromoheptanone | Bonnemaisonia hemifera (Red algae) | Antimicrobial
|
| Aeropolysnin | Verongia aerophola (Sponge) | Antimicrobial |
| Prepacifenol | Laurencia pacifia, L.filiformis (Red algae) | Antimicrobial |
| Thelphin | Thelepsus setosul (Annelida) | Antimicrobial |
| Eunicin | Eucinia mammosa (Gorgonian corals) | Antimicrobial |
| Acanthelin | Acanthella acuta | Against mycobacterium |
Marine Antiinflammatory compounds
• A novel bi indoles was isolated from the marine cyanobacterium, Rivularia firma
• The major compound was (+)-7’-mtheoxy -2,3,5,5’ tetrabromo-3, 4’-bi-1H indole; Active against carrageenan & kaolin induced paw edema
• Palaulol, a sesqueterpene from the sponge, Fascaplysinopsis species
• A sesqueterpene furan form the coelenterate, Sinularia species
Other anti-inflammatory compound includes
• Dendalone-3-hydroxybutyrate from the sponge, Phyllospongia dendyi
• Flustramine A and B from the Swedish marine moss Flustra foliaceae
• Tetradotoxin form the globe fish Spheroides rubripes
• 6-n-tridecyl salicylic acid from the brown algae Caulocystis cephalornithos
• Flexibilide from the soft coral, Sinularia flexibilis
• Monalide from the sponge Luffariella variabilis
Marine Antibiotic agents
The naturally occurring antibiotics includes
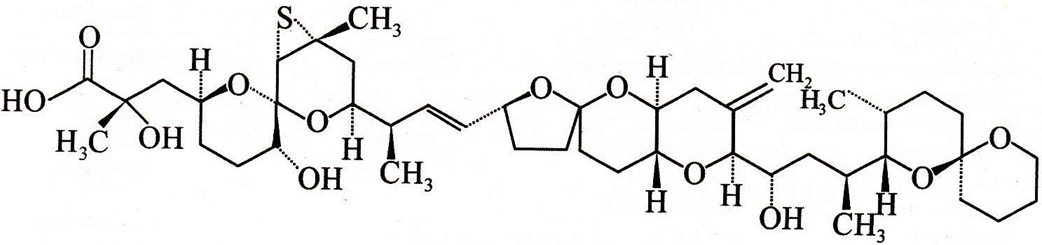
Okadaic acid (Halochondrine A)
• Obtained from Halichondria sps (Marine black sponge)
• First ionophoric polyether identified in marine organism
Acanthifolicin
• Obtained from the sponge, Pandoras acanthifolium
• Possess antibacterial activity and cytotoxic activity
The other antibiotic agents include
• 2,4 dibromo-6-(3,4,5 tribromo pyrrole-2-yl)-phenol obtained from the Marine bacterium, Pseudomonas bromutilis
• Cycloeudesmol obtained from the red algae Chondria oppsiticlada
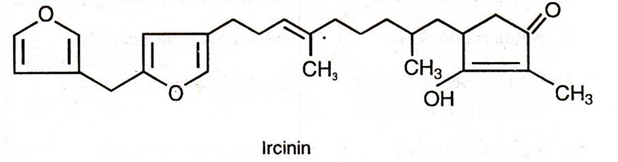
• Variablin and ircinin obtained from the sponge Ircinia strobilina & I. oros
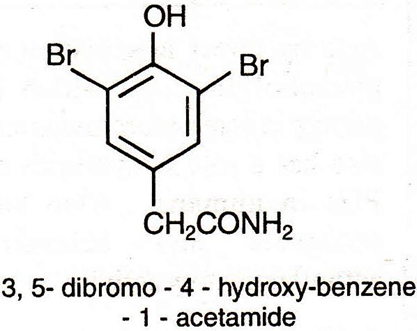
• 3,5 dibromo 4 hydroxy benzene-1 acetamide obtained form the sponge, Verongia archeri
Cardiovascular antimicrobial antiinflammatory and antibiotic agents of marine origin Summary
• Compounds used in cardiovascular system – laminin, octapamine, saxitoxin, autonomium chloride, astrosaponins, eledoisin, spongosine, doridosine, aaptamine, hymenin, urotensins etc
• Antimicorbial compounds – Istamycins, Bromopyrones, Fimbrolides, Laurene, Holotoxin A, B, C (Steroidal glycoside), Zonarol and isozonarol, Tetrabromoheptanone, Aeropolysnin, Prepacifenol, Thelphin, Eunicin, Acanthelin
• Anti-inflammatory drugs include novel bi indoles, (+)-7’-mtheoxy – 2,3,5,5’ tetrabromo-3, 4’-bi-1H indole etc
• The various antibiotics compounds are okadaic acid, acanthifolicin, 2,4 dibromo-6-(3,4,5 tribromo pyrrole-2-yl)-phenol, Cycloeudesmol, Variablin and ircinin, 3,5 dibromo 4 hydroxy benzene-1 acetamide etc