Fermentation Process of Penicillin
Fermentation Process of Penicillin
Objectives
At the end of the lecture, student will be able to
• Discuss the mechanism of action and adverse effects of Penicillin
• Explain the fermentation process of Penicillin
Penicillin
• First antibiotic – scottish scientist – Alexander Fleming – 1928
• PCN – isolated from fungus – Penicillium notatum
• ß-lactum antibiotics
• Active against – Gram +ve bacteria (Staphylococci and Streptococci) not against gram –ve except at high dose
Mechanism of Action
• Interferes with the cell wall synthesis of bacteria
• Inhibit the formation – peptidoglycan cross links in bacterial cell wall – binding of ß-lactum ring of penicillin to enzyme DD-transpeptidase
• DD-transpeptidase – cannot catalyze – formation of cross links – imbalance in cell wall production – degrades – rapid cell death
Adverse effects
• 10 % people – allergic reactions
• ≥ 1% of people – diarrhoea, hypersensivity, nausea, rashes, neurotoxicity and urticaria
• Pain and inflammation at the site of injection
• 0.1- 1% – fever, vomiting, erythema, dermatitis, seizures
Route of Administration:
• Oral
• IV
Use:
• Otitis Media
• Meningitis
• Sore Throat
• Pneumonia & Respiratory Infection
• Septicemia
• Peritonitis
• Gonorrhea
• UTI
Known Issues
• Resistance (B-lactmase & other mechanisms) Allergic rxns
• Cross-hypersensitivity (1-3% w/cephalosporins)
Classification of Penicillin
Production of Penicillin
• Stationary mat culture
• Medium – sterilized – shallow layers – bottles, flasks, trays or pans – glass or metal
• Wet or dry spores – added – medium or blown on its surface
• Incubated – 24 – 28˚C for six or seven days
• Equipment and labor required
• Harvest – pooling all the broths – but contaminated (penicillinase enzyme) – separated and discarded
• Problems –Low yield
– Oxygen penetration is low
– Portion of mycelium submerged – medium – deficient in O2
– Aerial hyphae – poor access to nutrients
• If not – penicillinase – will destroy all the pooled penicillin
• Deep tank aerated fermentation – World War II
Fermentation Process
• Several different fungi are used
• Principal organism used – commercial production – Mutated strains – Penicillium chrysogenum
Media Composition (Jackson, 1958)
Trade secrets
• Cornsteep liquor solids – 3.5 %
• Lactose – 3.5 %
• Glucose – 1 %
• Calcium carbonate – 1 %
• Potassium dihydrogen phosphate – 0.4 %
• Edible oil – 0.25 %
• Penicillin precursor
Production media: (Sylvester and Coghill, 1954)
• Corn steep liquor solids – 30 gm
• Lactose – 30 gm
• Glucose – 5 gm
• Sodium nitrate – 3 gm
• Magnesium sulphate – 0.25 gm
• Zinc sulphate – 0.044 gm
• Calcium carbonate – 3 gm
• Penicillin precursor
Step 1: Stock culture Maintenance
• High yielding strains of Penicillium chrysogenum
• Agar media – minimum vegetative growth and rapid sporulation of entire culture
• Media – inoculated – spores
This primary stock can maintained as
• Well-sporulated agar slants – frozen
• Soil stocks are prepared and stored at 2-4˚C
• Lyophilized
Step 2: Inoculum preparation
• Spores – heavily sporulated working stock – suspended in water or dil solution of non-toxic wetting agent, 1:10,000 SLS
• Added to bottles or flasks – wheat bran + nutrient (Inoculum media – similar to production media – except lactose and precursor not added)
• Incubated – 24 ˚C for 5-7 days – to provide heavy sporulation
• Spores – used – inoculate inoculum tanks
• Inoculum tanks – incubated – 24-48 hrs – agitation and aeration – production tank
• Contamination – inoculum tanks – microscopically observations and sub culturing in broth medium
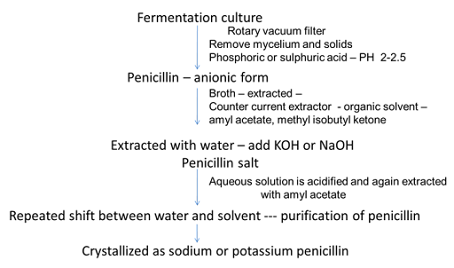
Production of penicillin
• Penicillin fermentation – 25-26
• 3-5 days
• Exact duration depends on
– Fungal strain
– Type of production media
– Aeration and agitation conditions
• Periodic samples – penicillin yield and contamination check – sensitive to penicillinase producing organisms
Course of Penicillin Production
Harvest and Recovery
Summary
• Principal organism used – commercial production – Mutated strains – Penicillium chrysogenum
• Penicillin fermentation – 25-26
• 3-5 days
• Exact duration depends on
– Fungal strain
– Type of production media
– Aeration and agitation conditions
• Periodic samples – penicillin yield and contamination check – sensitive to penicillinase producing organisms
Also, Visit: Biotechnology Notes