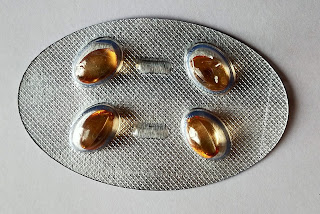
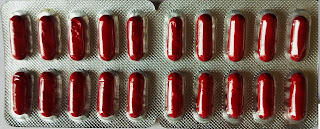
PHARMACEUTICAL CAPSULE

Pharmaceutical Capsule
Capsule is solid dosage forms in which one or more medicinal and or inert substances are enclosed within a small shell or container generally prepared from a suitable form of gelatin. Depending upon their formulation, the gelatin capsule shells may be hard or soft.
Characteristics:
- May be swallowed whole by the patient.
- May be inserted into the rectum for drug release and absorption from the site.
- The contents may be removed from the gelatin shell and employed as a pre measured medicinal powder, the capsule shell being use to contain a dose of the medicinal substance.
- Elegance.
- Ease of use.
- Portability.
- Tasteless shell to mask the unpleasant taste/odor of the drug.
- Permits physician to prescribe the exact medication needed by the patient.
- Conveniently carried.
- Readily identified.
- Easily taken.
- tasteless when swallowed.
- Commonly embossed or imprinted on their surface the manufacturer’s name and product code readily identified.
Components of Capsules
- Gelatin.
- FD & C and D & C colorant.
- Sugar.
- Water – 12 to 16 % but may vary depending on the storage condition.
- Sulfur dioxide (.15%) – prevent decomposition during manufacture.
- Opaquants/Opacifying agent – titanium dioxide.
Type of capsule
The two main types of capsules are-
1-Soft gel encapsulation
In 1834, Mothes and Dublanc were granted a patent for a method to produce a single-piece gelatin capsule that was sealed with a drop of gelatin solution.
They used individual iron moulds for their process, filling the capsules individually with a medicine dropper.
Modern soft-gel encapsulation uses variations of a process developed by R.P. Scherer in 1933.
His innovation was to use a rotary die to produce the capsules, with the filling taking place by blow molding.
This method reduced wastage, and was the first process to yield capsules with highly repeatable dosage.
2. HARD GELATIN CAPSULES
Two-part hard gelatin capsule
Also referred to as “DFC” Dry Filled Capsule.
Manufactured into two sections, the capsule body and a shorter cap.
A recent innovation in capsule shell design is the Snap-Fit, Coni-Snap, and Coni Snap Supro hard gelatin capsules.
Capsule size
|
Empty Hard |
||||
|
Size |
Outer Diameter (mm) |
Height or Locked Length (mm) |
Actual Vol. (mL) |
Typical Fill Weights (mg) 0.70 Powder Density |
|
000 |
9.91 |
26.14 |
1.37 |
960 |
|
00 |
8.53 |
23.30 |
0.95 |
665 |
|
0 |
7.65 |
21.70 |
0.68 |
475 |
|
1 |
6.91 |
19.40 |
0.50 |
350 |
|
2 |
6.35 |
18.00 |
0.37 |
260 |
|
3 |
5.82 |
15.90 |
0.30 |
210 |
|
4 |
5.31 |
14.30 |
0.21 |
145 |
|
5 |
4.91 |
11.10 |
0.13 |
90 |
For human use, empty capsules ranging in size from 000 the largest to 5 the smallest. Generally, hard gelatin capsule are used to encapsulate between 65 mg to 1 gram.
Characteristic
- Usually use in the extemporaneous compounding of Rx.
- Made of gelatin, sugar, and water.
- Clear, colorless and essentially tasteless.
- Colored with various FD & C and D & C dyes and made opaque by adding agents such as titanium dioxide.
Combination of colorants and Opaquants to make them distinctive, many with caps and bodies of different colors.
Plasticizers:-
- The amount of plasticizers used to make the capsule to hard or soft.
- The plasticizers are used – Glycerin, Sorbitol.
Preservatives:-
- If included, is generally a mixture of Methylparaben (4part) and Propylparaben (1part) to the extent of 2%.
Flavors:-
- If added, should not exceed 2%.
- Generally the flavors are used- Ethyl vanillin or essential oils.
Sugar:-
- If included, may be up to 5% to give the gelatin shell desirable chewable characteristics.
Additives:-
- Diluents:-
- The diluents have to be added to bring the medicament up to a desired bulk.
- The quantities of diluents are related to the dose of the medicament and the capsule size.
- Protective sorbents:-
- Sometimes some inert materials are included to prevent the absorption of moisture by hygroscopic substances.
- Materials like – oxides and carbonates of Mg or Ca.
- Glidants:-
- Glidants become essential when the powders are filled by automated machinery requiring their regular flow in the capsule bodies.
- Glidants like– Talc, Stearates.
- Anti-dusting compounds:-
- These are the compounds which prevent the flow of dust particle of the drug in the air to causes health hazards.
- Anti-dusting compounds like- inert edible oils.
Gelatin
- It is obtained by the partial hydrolysis of collagen obtained from skin, white connective tissue and bones of animals.
- Available in the form of a fine powder, a coarse powder, shreds, flakes, or sheets.
- Stable in air when dry but when become moist – subject to microbial decomposition.
- HGC contain 13 to 16 % of moisture.
- Extreme dryness- capsules may become brittle and crumble.
Manufacture of Hard Gelatin Capsule
- Manufactured into 2 sections, the capsule body and the shorter cap.
- The 2 parts overlap when joined, with the cap fitting snugly over the open end of the capsule body.
- Shells are produced by chemical dipping of pins or pegs of the desired shape and diameter into a temperature-controlled reservoir of melted gelatin mixture.
- The pegs made of manganese bronze, are affixed to plates, each capable of holding up to about 500 pegs.
- Each plate is mechanically lowered to the gelatin bath, the peg submerge to the desired depth and maintained for the desired period to achieve the proper length and thickness of coating.
- The plate and the pegs are slowly lifted from the bath and the gelatin dried by a gentle flow of temperature-and humidity-controlled air.
- When dried, each capsule part is trimmed mechanically to the proper length and removed from the pegs, the capsule bodies and caps are joined.
Capsules parameter as per I.P.
|
Product |
Dose (m.g.) |
Conversion (m.g.) |
Drug content (%) |
Dissolution (%) |
|
amoxicillin |
250 |
285 |
90-110 |
80 |
|
Ampicilline Trihydrate |
250 |
287 |
92.5-104.5 |
75 |
|
Cephalexin Monohydrate |
250 |
270 |
90-110 |
75 |
|
Doxycycline |
100 |
116 |
90-120 |
65 |
|
Rifampicine |
150 |
165 |
92.5-107.5 |
70 |
Filling Hard Capsules Shells
- Use Punch Method
- powder is placed on a sheet of a clean paper or porcelain plate,
- using spatula – formed into a cake having a depth of approximately one-fourth to one-third the length of the capsule body,
- then empty capsule body is held between the thumb and forefinger and punched vertically into the powder cake repeatedly until filled,
- Feton capsule filling
- with empty capsule in the loader tray, the tray placed on top of the filler unit,
- the loader inserts the capsules into the filling unit and is removed, and the top plate is lifted to separate the caps from the bodies,
- the powder is placed on the unit and the capsule bodies filled,
- the top plate is returned to the unit and the caps placed on filled capsule bodies,
Process Capsule Filling
- Milling /Sieving of all Ingredients.
- Blending Powder Blender / Empty Capsules.
- Capsule Filler.
- Capsule cleaner.
- Capsule injection screen.
- Capsule check-weighing system/reject.
- Finished capsules.
ProFill 100
– The ProFill 100 Capsule Filling Machine utilizes an advanced design for fool-proof manual filling of two-piece capsules.
With the ProFill 100 machine, there is no need for expensive capsule filling equipment and electrical/vacuum connection.
Capsule Filling Machine:-
Manual and Semi-Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
Finishing:-
The filled the sealed capsules necessitate finishing operation before inspection, bowling or packing in strips and labeling. The following steps are involve in the finishing process-
- Pan polishing.
- Cloth dusting.
- Inspection (ROTOSORT).
Evaluation of capsules:-
- Uniformity of weight.
- Content of active ingredients in capsules.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf