Aceclofenac – Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetic, Uses, Doses, Adverse Effect, Precautions and Drug Interaction
Generic Name
Summery
analog of diclofenac. It is used for the relief of pain and inflammation in
rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
It is reported to have a higher anti-inflammatory action or
at least comparable effects than conventional NSAIDs in double-blind studies.
Aceclofenac potently inhibits the cyclo-oxygenase enzyme
(COX) that is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are
inflammatory mediators that cause pain, swelling, inflammation, and fever.
It was patented in 1983 and approved for medical use in 1992.
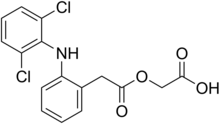
Structure
Molecular
Weight
Molar mass: 354.1847 g/mol
Chemical
formula
Formula: C16H13Cl2NO4
IUPAC
Name
[[[2-[(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)amino]phenyl]acetyl]oxy]acetic
acid.
Pharmacology
Indication
Pain & Inflammation
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pharmacodynamics
enzyme, a key enzyme involved in the inflammatory cascade.
COX-1 enzyme is a constitutive enzyme involved in
prostacyclin production and protective functions of gastric mucosa whereas
COX-2 is an inducible enzyme involved in the production of inflammatory
mediators in response to inflammatory stimuli.
Aceclofenac displays more selectivity towards COX-2 (IC50 of
0.77uM) than COX-1 (IC50 of >100uM), which promotes its gastric tolerance
compared to other NSAIDs.
The primary metabolite, 4′-hydroxyaceclofenac, also
minimally inhibits COX-2 with IC50 value of 36uM.
Mechanism
of Action
Although the mode of action of aceclofenac is thought to
mainly arise from the inhibition of synthesis of prostaglandins (PGE2).
Aceclofenac also inhibits the production of inflammatory
cytokines, interleukins (IL-1β, IL-6), and tumor necrosis factors (TNF).
It is also reported that aceclofenac also affects the cell
adhesion molecules from neutrophils.
Aceclofenac also targets the synthesis of glycosaminoglycan
and mediates chrondroprotective effects.
Absorption
Aceclofenac is rapidly and completely absorbed from the
gastrointestinal tract and circulates mainly as unchanged drug following oral
administration.
Peak plasma concentrations are reached around 1.25 to 3 hours
post-ingestion, and the drug penetrates into the synovial fluid where the
concentration may reach up to 60% of that in the plasma.
There is no
accumulation in regular dosing, with similar maximum plasma concentration
(Cmax) and time to reach peak plasma concentration (Tmax) after single and
multiple doses
Volume
of Distribution
Protein
Binding
Highly protein-bound (>99%)
Metabolism
4′-hydroxyaceclofenac is the main metabolite detected in
plasma however other minor metabolites include diclofenac,
5-hydroxyaceclofenac, 5-hydroxydiclofenac, and 4′-hydroxydiclofenac
Route
of Elimination
Urine
70-80% as glucuronidated and hydroxylated forms of aceclofenac.
About 20% of the dose is excreted into feces
Half
Life
Approximately 4 hours
Clearance
Approximately 5 L/h
Doses
every 12 hours.
Adult – 100mg
Tablet to be taken twice after meal.
Adverse
Effects
Gastro-intestinal disorders (dyspepsia, abdominal pain,
nausea),
Skin rash,
Loss of Appetite,
Visual Disturbance,
Urticaria,
Symptoms of enuresis,
Headache,
Dizziness, and drowsiness
Precautions
Allergies – Avoid
if you have a known allergy to Aceclofenac or other NASIDs.
Asthma – Aceclofenac
is not recommended in asthma.
Bleeding – if you
have any bleeding disorder, Aceclofenac is not recommended.
Pregnancy – not recommended
to pregnant women.
Breast Feeding –
not recommended for breast feeding women.
Cardiac Surgery –
Not recommended after and before coronary artery bypass surgery.
Impaired Kidney
Function – Not Recommended.
Impaired Liver
Function – mild liver falure 100mg once daily, contraindicated in severe liver
failure.
Drug
Interaction
Abacavir – Decrease the excretion rate of Abacavir.
Abciximab – The risk or severity of bleeding and hemorrhage
can be increased.
Acebutolol – Decrease the antihypertensive activities of
Acebutolol.
Acemetacin – The risk or severity of adverse effects can be
increased.
Acenocoumarol –
The risk or severity of bleeding and hemorrhage can be increased.
Aceclofenac – Pharmacodynamics, Pharmacokinetic, Uses, Doses, Adverse Effect, Precautions and Drug Interaction PDF Notes