Introduction to the Nomenclature of Organic Chemicals
Mainly two nomenclature system are proposed for the naming
of organic compounds.
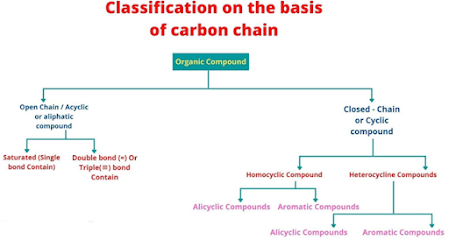
Classification
on the basis of carbon chain
1. Common
naming system.
a) On the basis of
source.
Example:
CH4 | Marsh gas (marshy place) |
CH3COOH | Acetic acid (vinegar) |
HCOOH | Formic acid (Red ant) |
CH3OH | Methyl alcohol ( wood spirit) |
b) On the basis of
hydrocarbons (Radical independent).
No. of Carbon Atoms Prefix |
1C form. |
2C acet |
3C propion |
4C butyr |
5C valer |
• Three carbon with
one double bond—Acryl.
• Four carbon with
one double bond—
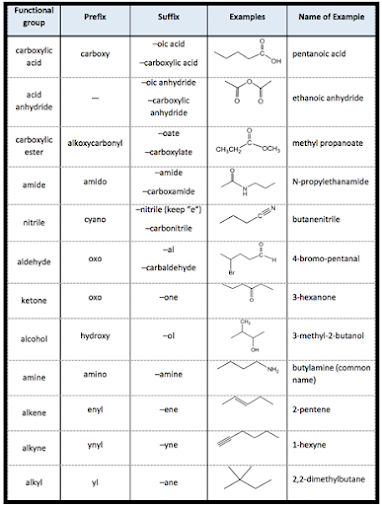
Functional |
–CHO aldehyde |
–COOH IC acid |
–COOR alkyl–ate |
–COX alkyl halide |
–CONH2 amide |
–CN Onitrile |
Radical dependent-
Sr.no Number of Bond Suffix |
1) Single |
2) Double |
3) Triple(≡) bond yne suffix |
For saturated hydrocarbon—CnH2n+2- Suffix used as -ane.
• If unbranched
hydrocarbon then use prefix (n)
• When one
methyl group is attached to the second C-atom of the continuous chain then iso
prefix is used.
• When Two
methyl group is attached to the second C-atom of the continuous chain then neo
prefix is used.
Note—when one
hydrogen group are removed from the alkane then radical is form and called
monovalent radical or alkyl. -CH3—methyl -C2H5—ethyl For unsaturated
hydrocarbon…
• Double bond (CnH2n)—suffix
— ene
• Triple bond (CnH2n-2)—suffix
— yne
Note—unsaturated radical.
Ex -CH2=CH— vinyl. -CH2-CH=CH2 — Allyl.
If any functional group are attached to the radical then
direct functional suffix are used to radical. Name= prefix of R + Suffix of
Functional |
-OH alcohol |
–NH2 Amine |
-O– ether |
–S– thio ether |
–X– halide |
–CN Cyanide |
–CO– ketone. |
IUPAC
NAMING SYSTEM.
Rule—
A) Selection of
longest continuous parent carbon chain. B)
Numbering in selected parent carbon chain.
Priority
order for selection of carbon chain
(Functional group > multiple bond>number of carbon
atom>substituents)
Functional group-
Multiple bond—
Sr.no Number of Bond Suffix |
1) Single bond (-) ane suffix |
2) Double |
3) Triple(≡) bond yne suffix |
No of carbon
Number of |
1C meth |
2C eth |
3C prop |
4C but |
5C pent |
6C hex |
7C hept |
8C oct |
Substituents means
Substituents Prefix |
–R alkyl |
–NH2 amino |
–o–N=O nitrite |
-OCH2CH3 ethoxy |
-CH2-Cl Chloro |
-S- thio |
-X Halo |
Numbering of selected carbon chain— Priority order.
Functional group>multiple bond>substituents.
Procedure of naming.
(Secondary prefix—– primary prefix—– word)
(root—– primary suffix——- Secondary suffix. )
➢ Secondary prefix means —
substituents with locants
➢ Primary prefix means—cyclic
group(cyclo).
➢ Word root means—number of
carbon chain.
➢ Primary suffix means– – ane,
-ene, – yne.
➢ Secondary suffix means—principle
fuctional groups.
➢Number and alphabets are
seperated by hyphen (-).Di,tri,iso,neo and cyclo are neither seperated by comma
nor by hyphen .
➢ First latter of naming is
always capital letter and space required between naming.
➢ If more than one substituents
then use alphabetical order of substituent names.
Examples.
Heterocyclic rings which are used during the naming…