Surface and Interfacial Phenomenon

Surface and Interfacial Phenomenon
Learning Objectives of Surface and Interfacial Phenomenon
- At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
– Explain the terms surface and interfacial tension and Surface and Interfacial Phenomenon
– Describe the difference between surface and interface
– Explain the relationship between the cohesive and adhesive forces with surface and interfacial tension
– Explain the application of surface and interfacial tension
– Describe the method of determination of surface tension by capillary rise method
– Describe the method of determination of surface and interfacial tension by tensiometer
– Explain the concept of surface free energy and its importance in pharmaceutical preparations
– Describe work of cohesion, adhesion and spreading coefficient for different types of interfaces
– Explain the classification of surface active agents and their applications in pharmacy
– Describe the adsorption at solid interfaces
– Explain the differences between physical and chemical adsorption
– Describe the Freundlich adsorption isotherm and its Applications
– Describe the mechanism of adsorption on solid/gas and solid/liquid interfaces
– Explain Langmuir adsorption isotherms and its applications
– Describe multimolecular layer adsorption
– Explain different types of adsorption isotherms
– Explain the concept of HLB and its applications in pharmacy
– Describe the concept of required HLB in the preparation of pharmaceutical formulations
– Explain soluble monomolecular film and its applications
– Describe the adsorption at solid-liquid interface
– Explain contact angle and wetting phenomenon
– Explain the electrical properties of interfaces and the effect of electrolytes
Introduction to Surface and Interfacial Phenomenon
- Interface is the boundary that forms between two phases like solid and liquid
- The term surface is normally used to denote interface when one of the phases is gas
- Solid- liquid interfaces are important in pharmacy in the area of adhesion of granules to form a tablet, flow of granules through hopper during tableting

Surface and Interfacial Tension-General Principle
- Surface Tension is defined as the force, in dynes, acting on the surface of the liquid at right angles to any line of length of surface 1 centimeter
- Units of surface tension are Dyne/cm in CGS system and Newton’s/ meter in MKS system.
- Surface tension is responsible for the following processes:
– Spherical globules in emulsions
– Nearly spherical shape of falling water droplets
– Spherical shape of mercury particles on a flat surface
– Rise of liquid in capillary tube
– Lower meniscus of water in glass tubes
- In a liquid, molecules experience greater attraction from the neighbouring molecules and such intermolecular force of attraction between like molecules are called cohesive forces of attraction
- Surface tension denotes cohesive forces of interaction in a liquid
- An example of water in a beaker and the intermolecular forces of attraction can explain about the surface tension

- Interfacial tension is defined as the force per unit length existing at the interface between two immiscible liquids
- Units are dyne/cm (CGS system) and Newton/meter (MKS system)
- Interfacial tensions are less than the surface tensions
- Interfacial tension indicates the strength of the adhesive forces between immiscible liquids
- Internal factors – intermolecular forces of attraction is a measure of the magnitude of the surface tension
- External factors – presence of electrolyte causes a slight increase in the surface tension
– Surface active agent’s decreases surface tension
– Increase in temperature causes decrease in surface tension
Determination of Surface and Interfacial Tension
- Different methods to determine surface and interfacial tensions are:
– Capillary rise method
– The Du Nouy tensiometer
– Bubble pressure
– Drop weight (drop count)
Capillary Rise method
- When a capillary tube is placed in the liquid contained in a beaker, the liquid rises up the in the tube to a certain distance
- The rise of the liquid is because of the adhesive forces between the liquid molecules and glass
- Rise of the liquid will continue until the upward movement is just balanced by the downward force of gravity

Upward component
- Surface tension of the liquid (γ) at any point on the circumference is given by:
Upward component,
a = γ.Cosθ…………………(1)
Where, γ=surface tension of the liquid
θ=contact angle between the surface of the liquid and capillary wall
- The total upward force around the inside circumference (2πr) of the tube is:
Upward component,
a= γ. 2 πr Cosθ…………….(2)
Where r is the inside diameter of the capillary tube
- For water θ is zero, so, cos θ = 1 and equation (1) changes to upward component,
a= 2 πr. γ………….(3) Downward component
- Counteracting force is gravity and depends upon the weight of liquid in the capillary rise Downward component,
b=mass x acceleration
=volume x density x acceleration
=cross sectional area x height x density x acceleration
= πr2 x h x ρ x g……………(4)
- At equilibrium the opposing forces are equal i.e., a=b
2 πr. γ = πr2 x h x ρ x g…………..(5)
γ = 1/2rhρg…………….(6)
- Equation (6) is used to measure the surface tension by capillary rise method
The DuNouy Ring Method
- The method is widely used to measure surface and interfacial tension
- The force required to detach the platinum iridium ring immersed at the interface or surface is measured

Upward pull
Upward pull= dial reading in dynes………….(7)
Downward pull
- The weight of the liquid that is adhered to the ring, acts as the downward force
Downward pull= mg= γ .2 πr.2………….(8)
- At equilibrium:
Upward pull=downward pull
dial reading= γ .2πr.2
![]()
An error of 25% is possible, so a correction factor is applied
![]()
Surface Free Energy
- Surface tension maintains the surface area of a liquid to a minimum value
- Surface free energy is defined as the work required to increase the area of a liquid by 1 cm2
- Surface free energy is equal to the surface tension
Derivation of surface free energy
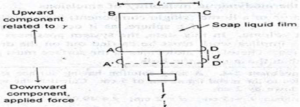
- A rectangular wire ABCD, the side of AD=L which is movable
- A drop of soap solution is placed to form a film within the frame
- The side AD remains stable initially on account of surface tension
- When force is applied (a hanging mass) downward, the film gets stretched as the movable bar AD goes down until the film breaks
- If the applied force is less than that is required for breaking, the film would retract on account of surface tension
- If force ‘f’ applied on AD (downward component), it shifts the movable wire to a distance ‘d’ to A’D’
- The work done ‘W’ is given by
W=f x d…………….(1)
- The above force acts against the surface tension (upward component), γ, of the liquid
- The force acting on the surface is:
f= γ x 2L……..(2)
- Substituting eq. (2) in equation (1) gives
W= γ x 2L x d…………(3)
- Since, 2L x d = ΔA, produced by extending the soap film, eq. (3) changes t
W= γ x ΔA…………(4)
or, ΔG= γ x ΔA
where, W= work done or surface free energy increase (ΔG), expressed in ergs (mJm-2)
Spreading Coefficient
- Spreading coefficient can be analysed by considering the cohesive and adhesive forces operating between two molecules
Work of cohesion
- It is the energy required to separate the molecules of the spreading liquid
- When a hypothetical cylinder is divided, two new surfaces are created

Work of cohesion= Wc=2γL………….(5)
Where, γL = surface tension of the liquid (L)
Work of adhesion

- It is the energy required to bring out the adhesion between the unlike molecules
- The work done is equal to:
Work of adhesion= Wa= γL + γs + γLs………(6)
where, γs= interfacial tension of sublayer
γLs=interfacial tension of liquid/solid surface
- Spreading of liquid occurs when adhesive forces (Wa) are stronger than the cohesive forces (Wc)
- The spreading coefficient is obtained by the equation:
S= Wa-Wc =(γL + γs – γLs)-2 γL
Or, S= γs(γL+ γLs)
- If, γs> (γL+ γLs), S is positive, indicating spreading
- If γs< (γL+ γLs), S is negative, indicating no spreading
- Spreading coefficient of substance can be increased by:
– The prescence of polar functional groups such as –COOH, -OH etc., in the structure
– Reducing the nonpolar chain length
Surface Active Agents
- Surface active agents are the substances which preferentially get adsorbed at the interface and exhibit self-association in the bulk of the liquid at a specific concentration
- These are polymer like substances which have both polar and non-polar groups so that they remain at the interface and reduce the interfacial tension
- They are also termed as amphiphiles
- Depending on the number and the nature of the groups they may be classified as:
-Predominantly lipophilic
-predominantly hydrophilic
-Well balanced
Surface Active Agents-Applications

- Pharmaceutical adjuvants like
-solubilizing agents
-wetting agents
-detergents
-suspending agents
-emulsifying agents
-foaming agents
- Influence on drug action
- Antibacterial activity
Adsorption at Solid Interfaces
- Adsorption of a gas or a liquid onto a solid surface is important in pharmacy
- Material used to adsorb gases or liquids is termed as adsorbent
- The substance that is attached to the surface of the solid is called adsorbate
- Depending on the nature of interactions, adsorption is classified into physical adsorption (physisorption) and chemical adsorption (chemisorption)
| Physical adsorption | Chemical adsorption |
| Reversible | Irreversible |
| Weak van der Waals forces | Strong chemical bonds |
| Nonspecific | More specific |
| Common at low temperature | Occurs at high temperature |
| Heat of adsorption is low | Heat of adsorption is high |
| Example –adsorption of gases on charcoal | Example-adsorption of oxygen on silver or gold |
- The combination of both types of adsorption is termed as ‘Sorption’
- Phenomenon opposite to adsorption is desorption
- In thermodynamic terms adsorption is a surface phenomenon
- Greater the surface area greater is the adsorption
- The relationship between the surface free energy and surface tension is given by:
W = ΔG =γΔA……………(4)
Where, W= work done to obtain division of particles
ΔA =increase in the surface area
ΔG= increase in the surface free energy
Adsorption at Solid/Gas Interface
- Adsorption of a gas onto a solid surface is important in pharmacy due to :
-removal of objectionable odours from the rooms
-prevention of obnoxious gases entering into the body
-estimation of surface area and particle size of powders
- In the study of adsorption, the amount of gas adsorbed per unit area or unit mass of solid is measured at different pressures of the gas
- Study is usally conducted at constant temperature and graphs are plotted, which are known as adsorption isotherms
Adsorption at Solid/Gas Interface-Freundlich Isotherm
- Freundlich isotherm gives the relationship between pressure of the gas and amount adsorbed at constant temperature
- The equation is:

where, x= weight of gas adsorbed per unit weight of adsorbent,
P= equilibrium pressure,
K and n = constants

- Converting equation (5) into logarithmic form


Adsorption at Solid/Gas Interface-Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm
- Langmuir adsorption isotherm can be represented by:

Where, y= mass of gas adsorbed per gram of adsorbent
ym= mass of gas that 1g of adsorbent can take up when a monolayer is complete
b= k1/k2 (constant)
p= pressure
- Inverting equation (1) and multiplying by ‘p’ gives:

Adsorption at Solid/Gas Interface- Multi-molecular Adsorption (BET equation)
• Sometimes gases adsorb as multi-molecular layers on solids
![]()
Where, P= pressure of the adsorbate, in mm Hg
y= mass of the vapour per gram
P0= vapour pressure at saturation
ym= amount of vapour adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent (surface is covered with monomolecular layer) b= constant, proportional to heat of adsorption and latent heat of condensation of subsequent layer
Adsorption at Solid/Gas Interface- Adsorption Isotherms
- Adsorption isotherms are the plots between the amount of gas adsorbed on a solid against the equilibrium pressure or concentration at constant temperature

Type I
- This isotherm represents an increase in the adsorption with increasing pressure followed by levelling off • Levelling off is due to saturation of entire surface by formation of monomolecular layer
- It represent Freundlich or Langmuir adsorption isotherm
Type II
- Occurs when gases undergo physical adsorption onto nonporous solids
- First inflection point represents, formation of monolayer, when pressure in increased multilayer formation occurs
- Isotherm is described by BET equation
Type III
- The heat of adsorption of gas in the first layer is less than the latent heat of condensation of subsequent layers
- In BET equation the constant ‘b’ is smaller than 2
Type IV
- Plot represents the adsorption of gases on porous solids
- First point of inflection extrapolated to zero represents the monomolecular layer adsorption
- Condensation within the pores of the solid and the multi-molecular layer is represented by further adsorption
Type V
- Seen rarely and indicates capillary condensation
- The adsorption reaches a limiting value before P0 is attained
Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB)
- HLB is an arbitrary scale that indicates the extent of hydrophilic lipophilic balance (HLB)

- The higher the HLB of an agent, the more the Hydrophilicity
- Spans (sorbitan ester) are lipophilic and have low HLB values (1.8-8.6)
- Tweens (polyoxyetylene derivative of span) are hydrophilic and have high HLB values (9.6-16.7)
- HLB scale is used to identify the optimum efficiency of a variety of surfactants
- Method 1
HLB= Σ(hydrophilic group number)-Σ(lipophilic group number) +7
- Method 2
![]()
Where, E= percent by weight of ethylene oxide chain
P=percent by weight of polyhydric alcohol groups
- Method 3
![]()
where, S= saponification number of the ester
A=acid number of the fatty acid
Required HLB (RHLB)
- Required HLB (critical HLB) is the hydrophilic-lipophilic value that is desired in order to prepare a stable emulsion of o/w or w/o type
- A blend of surface active agents are used in the preparation of emulsions and the blend is estimated based on the nature of the oil phase
- HLB of a mixture of two surfactants containing the fraction f, of A and (1-f) of B is an algebraic mean of the two HLB values
HLBmixture = f.HLBA + (1-f).HLBB
Soluble Monomolecular Films
- When a small drop of polar-short chain alcohol is added to water with an increasing concentration it completely covers the surface with a monomolecular film
Applications
-Stabilization of emulsions
– Wetting and detergency
– Membrane models
- The following parameters are evaluated:
-Surface tension
-Surface excess
-Concentration of amphiphiles in the bulk
- The number of molecules per unit area of the surface can be estimated using Gibbs equation:
![]()
Where, ᴦ= moles of solute adsorbed/unit area or surface excess
R= ideal gas constant
T=absolute temperature
γ =change in the surface tension
da2=change in the solute activity at a
- Surface excess is the amount of the amphiphiles per unit area of surface in excess of that in the bulk liquid
- For dilute solutions activity term can be replaced by solute concentration, c:
![]()
- Since the term integral dc/c is equal to d (ln c), the Gibbs equation can be written as

- Equation (2) and (3) is applicable to the absorption of surfactants
- From equation (3), surface tension is plotted ag
Adsorption at Solid/Liquid interface
- Solute present in a solution may often adsorb on the solid- liquid interface
- Adsorption phenomenon find applications in many ways:
-Reduced absorption
-Antidote in poisoning
-Purification and reduced toxicity
-reduced drug content
-Separation of substances in a mixture
Adsorption at Solid/Liquid interface-Wetting Phenomenon
- Wetting is an adsorption process in which an intimate contact of the solids with liquid phase is achieved • The importance of wetting phenomenon are:
– In the preparation of suspensions and emulsions
-Mixing of powders with binding agents in granulation process
-Film coating of tablets
-Dissolution of tablets or capsules
- Surfactants are used to aid in the wetting of powders
- Contact angle can be defined as an angle between the liquid droplets and surface over which it spreads
- Contact angle can take any value between 0 digree to 180 digree

- Contact angle can be estimated by placing a drop of liquid on a solid surface
- The forces acting at equilibrium:
γS= γLS + γL. Cos θ……………(4)
Whereθ is the contact angle
- Equation (4) can be written as:
− γSL + γS
Cos θ = ———- ………….(5)
γL
- Ideal wetting is Cos θ=1 or θ=0
Adsorption at Solid/Liquid Interface- Critical Surface Tension
- The surface tension obtained to Cos θ=1 is known as critical surface tension

Electrical Properties of Interfaces
- The electrical properties of interfaces finds applications in:
-Stabilization of colloidal dispersions
-Preparation of flocculated suspensions
-Stabilization of emulsions
- The origin of charge on interface can be accounted as:
– Electrolytes present on the surface may get adsorbed on the solid surface
– Functional groups present on the surface of the particles dissociated and impart charge
– Differences between the dielectric constants between the particles and dispersion medium
Electrical Properties of Interfaces-Electrical Double Layer
- The electrical double layer can be illustrated by:
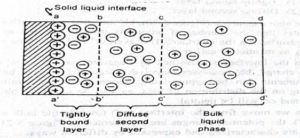
- The electrical double layer is consisting of
– Tightly bound layer
– Diffuse second layer
- The cations at the interface are potential determining ions
- The anions are termed as counter ions or gegenions
- Nernst potential, E (Electrothermodynamic potential) is defined as the difference in potential between the actual surface and the electroneutral region of the solution
- Zeta potential,ζ (electrokinetic potential) is defined as the difference in potential between the surface of the tightly bound layer and the electroneutral region of the solution
- Zeta potential is work required to bring a unit charge from infinity to the surface of the particles
- Zeta potential governs the degree of repulsions between the adjacent ions of like charges
- It is used to predict particle –particle interaction and an optimum zeta potential is desirable for the maximum stability

Surface and Interfacial Phenomenon Summary
- Surface tension – Force acting on the surface of the liquid at right angle
- Surface tension is the measurement of cohesive forces of attraction
- Interfacial tension is the measurement of adhesive forces of attraction
- Interfacial tension – Force acting at the interface of two liquids
- Applications of surface and interfacial tension – To know the properties of various liquids used the the pharmaceutical preparations
- Surface tension – Force acting on the surface of the liquid at right angle
- Interfacial tension – Force acting at the interface of two liquids
- Methods of determination – By capillary rise method and DuNouy tensiomete
- Surface free energy – The free energy associated with the surface of a compound
- Importance of surface free energy – Deals with the stability of different pharmaceutical formulations • Spreading coefficient – Differences between work of cohesion and work of adhesion
- A higher spreading coefficient signifies a lesser surface free energy
- Surfactants – Substances with both hydrophilic and lipophilic property
- Applications of surfactants – They are used as different adjuvants in pharmaceutical preparation • Material used to adsorb gases or liquids is termed as adsorbent
- The substance that is attached to the surface of the solid is called adsorbate
- The relationship between the surface free energy and surface tension is given by:
W = ΔG =γΔA
- Freundlich adsorption isotherm – Relationship between the pressure of the gas and amount adsorbed at constant temperature
- Langmuir adsorption isotherm – this isotherm explains about monomolecular layer adsorption
- Bet equation – Explains about multimolecular layer adsorption
- Adsorption isotherm – These are the plots of amount of gas or liquid adsorbed onto an unit mass of solid at an equilibrium pressure
- HLB scale – An arbitrary scaled notes Hydrophilicity and lipophilicity of surfactants and different pharmaceutical substances
- Application of HLB – Used to identify the optimum efficiency of a variety of surfactant
- Required HLB- It is the hydrophilic – lipophilic value that is desired to prepare a stable emulsion
- When a small drop of polar – short chain alcohol is added to water with an increasing concentration it completely covers the surface with a monomolecular film
- Wetting – An adsorption process in which an intimate contact of the solids with liquid phase is achieved
- Contact angle – It is defined as an angle between the liquid droplet and surface over which it spreads
- Nernst potential – Defined as the difference in potential between the actual surface and the electroneutral region of the solution
- Zeta potential – Defined as the difference in potential between the surface of the tightly bound layer and the electroneutral region of the solution
