Anti-Ulcer Drugs
Peptic ulcer

Objectives
At the end of this lecture, students will be able to
• Explain the pathophysiology of peptic ulcer
• Describe the symptoms
• Classify Anti-ulcer drug
Peptic ulcer
• Peptic ulcer very common disease of alimentary tract
• Peptic Ulcer(PU) is an ulcer of the GIT at an area exposed to the acid pepsin mixture (APM),i.e.the mucosa of the GIT
• This area is digested by pepsin (peptic digestion), hence the name
• A peptic ulcer is an ulcer (defined as mucosal erosions) of an area of the gastrointestinal tract that is usually exposed to the aggressive action of acid-peptic juices
• It causes inflammatory injuries in either the gastric or duodenal mucosa, with extension beyond the submucosa into the muscularis mucosa
• A peptic ulcer of the stomach is called a gastric ulcer & ulcer of duodenum is called a duodenal ulcer and of the esophagus is called an esophageal ulcer
Sign & Symptoms
• Dyspepsia (Indigestion)
• Abdominal pain
• Heart burn
• Bloating (swollen state)
• Nausea
• Anorexia
• Weight loss
• Melena (Black vomit)
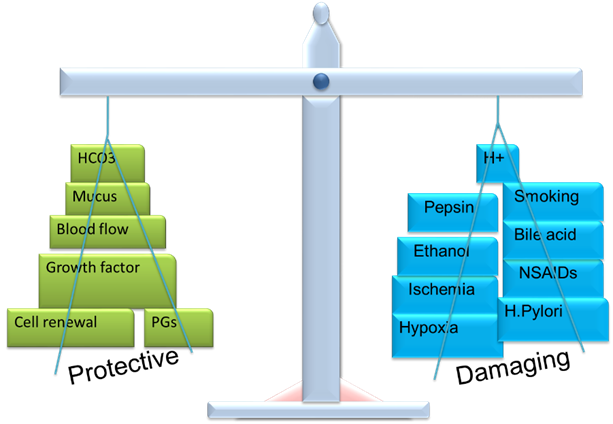
Pathophysiology of PUD
Gastro duodenal mucosal integrity is determined by protective (“defensive”) and Damaging (“aggressive”) factors
• Gastric and duodenal ulcers usually cannot be differentiated based on history alone, although some findings may be suggestive.
• Epigastric pain is the most common symptom of both gastric and duodenal ulcers.
• It is characterized by a gnawing or burning sensation and occurs after meals—classically, shortly after meals with gastric ulcer and 2-3 hours afterward with duodenal ulcer.
• Under normal conditions, a physiologic balance exists between gastric acid secretion and gastroduodenal mucosal defense.
• Mucosal injury and, thus, peptic ulcer occur when the balance between the aggressive factors and the defensive mechanisms is disrupted.
• Under normal conditions, a physiologic balance exists between gastric acid secretion and gastroduodenal mucosal defense.
• Mucosal injury and, thus, peptic ulcer occur when the balance between the aggressive factors and the defensive mechanisms is disrupted.
Secretion of HCl by gastric parietal cell and its regulation
Diagnostic tests
• Barium swallow: You drink a thick white liquid (barium) that coats your upper gastrointestinal tract and helps your doctor see your stomach and small intestine on X-rays
• Endoscopy (EGD): A thin, lighted tube is inserted through your mouth and into the stomach and the first part of the small intestine
• This test is used to look for ulcers, bleeding and any tissue that looks abnormal
• Endoscopic biopsy: A piece of stomach tissue is removed so it can be analyzed in a lab.
Classification of anti-ulcer drugs
1. Reduction of gastric acid secretion
(a) H2 antihistamines: Cimetidine, Ranitidine,Famotidine, Roxatidine
(b) Proton pump inhibitors: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole, Rabeprazole,Esomeprazole
(c) Anticholinergics: Pirenzepine, Propantheline,Oxyphenonium
(d) Prostaglandin analogue: Misoprostol
2. Neutralization of gastric acid (Antacids)
(a) Systemic: Sodium bicarbonate, Sodium citrate
(b) Nonsystemic: Magnesium hydroxide, Magnesim trisilicate, Aluminium hydroxide gel, Magaldrate, Calcium carbonate
3. Ulcer protectives: Sucralfate, Colloidal bismuth subcitrate (CBS)
4. Anti-H. pylori drugs: Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin,Metronidazole, Tinidazole, Tetracycline
Summary
• Peptic Ulcer(PU) is an ulcer of the GIT at an area exposed to the acid pepsin mixture (APM),i.e.the mucosa of the GIT
• The pathophysiological structure shows aggressors like increased acid and pepsin, an impaired defence system of the mucosa.
• Acute ulcers and erosions present clinically with gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Can stress really cause peptic ulcers?
- While stress can aggravate existing ulcers, it’s not the primary cause. Factors like H. pylori infection and certain medications play a more significant role.
- Is surgery the only option for severe peptic ulcers?
- No, surgery is usually considered when other treatments fail. Most ulcers respond well to medications and lifestyle changes.
- Are there specific foods that can worsen peptic ulcers?
- Yes, spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can irritate ulcers. It’s advisable to avoid these to promote healing.
- How long does it take for peptic ulcers to heal?
- The healing time varies, but with proper treatment, many ulcers improve within a few weeks.
- Can peptic ulcers recur after successful treatment?
- Yes, they can. It’s essential to continue with prescribed medications and maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent recurrence.