Penicillins
Objectives
At the end of this session, students will be able to:
• Classify Penicillins
• Describe the mechanism of action of Penicillins
• Outline the pharmacokinetic profile of Penicillin
• Discuss the clinical uses of Penicillins
β-Lactam antibiotics
• All of the drugs in this group contain a β-lactam ring in their structure
• Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
Penicillin
• Obtained from Penicillium notatum
• At present obtained from Penicillium chrysogenum
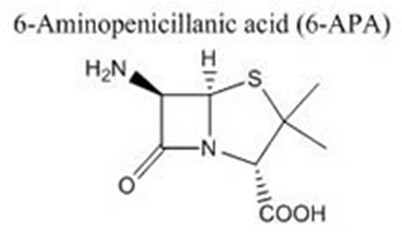
• Consists of sulfur containing thiazolidine ring fused with β-lactam ring having a side chain at C-6
• 6-amino pencillanic acid (6-APA)- active moiety
• Has intact β-lactam ring and amino group at C-6 joined at thiazolidine ring
Mechanism of action of penicillin
• Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis
• Bacterial cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan
• Peptide chains are cross linked by pentaglycine bridge
• Process of trans bridging – transpeptidation
• Catalysed by penicillin binding protein (PBP)
• Penicillin competes and inhibits PBPs
• Forms imperfect cell wall
• Osmatic drive of fluid
• Bacetrialbdeath by swelling and lysis
• Bactericidal action
Resistance to penicillin
By any of the following mechanism
• Inactivation of β-lactam ring by β-lactamase
• Modification of PBPs
• Reduction in penicillin permeability to reach PBPs
• Activation of antibiotic efflux mechanism
Classification of Penicillins
• Based on antimicrobial spectrum
• Some are stable to gastric acid
• Some are acid labile (give parenterally)
• Some are resistant to β-lactamase
• Others are β-lactamase sensitive
Narrow spectrum penicillin
Extendend spectrum penicillin
Pharmacokinetics
Narrow spectrum penicillin
• Penicillin V and G- natural penicillin
• β-lactamase sensitive
• Penicillin G – acid labile
• Easily absorbed
• Wide distribution – except eye, prostrate and CNS
• Excreted through kidneys
Extended spectrum penicillin
• β-lactamase sensitive
• Aminopenicillin – acid stable
• Carboxypenicillin and Ureidopenicillin – acid labile
• Goodbbioavailability
• Excreted through kidneys
Antimicrobial spectrum
Narrow spectrum penicillin
• Penicillin G and V – Effective against gram positive and gram negative bacteria
• Semisynthetic – Cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, methicillin and nafcillin
• Spectrumbof action similar to natural penicillin
Extended spectrum penicillin
• Retains antimicrobial spectrum of penicillin G
• Extended spectrum against gram negative organism
• Amoxycillin – for eradicating H.pylori in duodenal and gastric ulcers
• Piperacillin- antipseudomonal penicillin
Clinical uses
• UTIs, typhoid fever, bacillary dysentry
• Amoxycillin – for eradicating H.pylori in duodenal and gastric ulcers
• Ampicillin – for meningitis by Listeria monocytogenes
• Endocarditis
• Septicemia
• Cellulitis
Summary
• β-lactam antibiotics are the group of drugs that contain a β-lactam ring in their structure and they act by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis
• They include – penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams and cabapenems
• Penicillins are the drug initially obtained from fungus, now obtained by semisynthetic process
• They used in the treatment of UTIs, endocarditis, septicemia