Diazotization Titrations

Objectives
By the end of this lecture, students will be able to:
• Explain the principle involved in Diazotisation titrations
• Outline the method of preparation and standardization of sodium nitrite standard solution
• Brief the applications of diazotization titrations
Diazotization Titrations
• Carried out for the estimation of drugs containing primary aromatic amino group
• Several drugs contain primary amino group or
• Can be converted to have such groups by simple reactions
• Like hydrolysis, reduction, etc
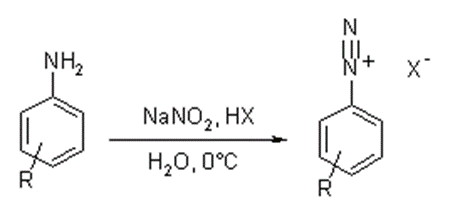
• Resulting amino group is diazotized by reaction with sodium nitrite solution in cold acid solution
• Nitrous acid formed diazotizes the compound
• End point can be determined by using external indicator method using starch iodide paper
• Alternatively, potentiometric method or dead stop end point technique can be used
Principle
• General reaction of diazotization,
• Addition of sodium nitrite to hydrochloric acid causes formation of nitrous acid
• Nitrous acid formed diazotizes the aromatic amino group
• After end point, excess nitrous formed is shown by instant formation of blue color with starch iodide paper
• Starch iodide paper is prepared by immersing a filter paper in starch mucilage and potassium iodide solution
• Color change of indicator paper is because of the reaction
• KI + HCl à KCl + HI
• 2HI + 2HNO2 à I2 + 2NO + 2H2O
• Iodine formed reacts with starch mucilage to give the blue color
• End point can also be determined by dead stop end point technique
• Here a potential of 30-50 mV is applied across two platinum electrodes
• Automatic pipette is used for the delivery of nitrite solution
• At the end point delivery of nitrite solution stops automatically
Preparation and Standardization of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
Preparation of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• 7.5 g of sodium nitrite is dissolved in sufficient water to produce 1000 ml
Standardization of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• About 0.5 g of sulphanilamide (previously dried at 105 0C for three hours) is transferred to a suitable beaker
• 50 ml of water and 20 ml of HCl is added, stirred until it dissolves
• Cooled to 15 0C
• Contents of beaker are titrated against 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• Each ml of 0.1M sodium nitrite solution = 0.01722 g of sulphanilamide
Diazotization Titration
• Specified amount of drug is dissolved in about 50 ml of water and 20 ml of HCl
• Solution is stirred and cooled to about 15 0C
• Mixture is titrated against 0.1M sodium nitrite solution
• End point is determined by
• Using external indicator- starch iodide paper
• Electrometric technique by using platinum electrodes
Types of Diazotization Titrations
Direct titrations
• Here, direct titration of amine in acid against sodium nitrite solution
Reverse method
• Here, solution of amine and sodium nitrite are run into a solution of acid
• Method is used when diazonium salts are insoluble
• For example, naphthylamine sulphonic acids
Special method
• Aminophenols are readily oxidized by nitrous acid to quinones
• For such substances, titration is carried out in the presence of copper sulfate
• It forms diazo oxide
• Diazo oxides are more stable and undergo diazo coupling reaction
Applications of diazotization titrations
1. Direct titration with sodium nitrite solution
• Benzocaine
• Dapsone
• Primaquine phosphate
• Procaine
• All sulpha drugs containing free aromatic amino group like sulfacetamide, sulfadiazine, sulfamethoxazole, etc
2. Conversion of amino group by chemical reactions
A. By reduction
• Metronidazole
• Secnidazole
• Chloramphenicol
• These drugs contain nitro group
• Can be reduced by using any reducing agent to get primary amino group
• Primary aromatic amino group can be diazotized by sodium nitrite
B. Hydrolysis
• Paracetamol (acetyl derivative)
• Phthalyl sulphathiazole (phthalyl derivative)
• Succinyl sulphathiazole (succinyl derivative)
• These drugs are derivatives of amino groups
• Like acetyl or phthalyl or succinyl derivative
• After hydrolysis to free amino group can be titrated with sodium nitrite
• Isocarboxazid- acid solution of the drug liberates benzylhydrazine which can be diazotized to give benzylazide
Reagents and Equipment Required
To perform Diazotization Titrations, specific reagents and equipment are necessary. These include diazotizing reagents, a titrant solution, a pH meter, and a spectrophotometer. The choice of reagents and equipment depends on the specific analysis being conducted.
Procedure for Diazotization Titrations
The procedure for Diazotization Titrations is systematic and involves several steps, including sample preparation, diazotization, titration, and data analysis. Careful execution of each step is crucial to obtaining accurate results.
Factors Affecting Diazotization Titrations
Several factors can influence the outcome of Diazotization Titrations. pH, temperature, and the choice of reagents play a significant role in the precision of the analysis. It is essential to maintain consistent conditions to ensure reliable results.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Diazotization Titrations offer high precision and specificity, but they also have limitations. They can be time-consuming, and the reagents used may be hazardous. Understanding these pros and cons is vital for efficient utilization.
Conclusion
Diazotization Titrations are a powerful analytical tool that offers precise results in the assessment of various compounds. Their applications extend across multiple industries, contributing to the quality control and safety of products we encounter daily. To master this technique, it is essential to understand the principles, procedures, and factors that influence the accuracy of Diazotization Titrations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are Diazotization Titrations used for? Diazotization Titrations are used for quantifying a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds, especially in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and environmental industries.
- What precautions should be taken when performing Diazotization Titrations? Safety precautions, including wearing protective clothing and ensuring proper ventilation, are essential to avoid accidents and exposure to hazardous reagents.
- How do Diazotization Titrations compare to other titration techniques? Diazotization Titrations offer high specificity but can be time-consuming. Comparing them with other titration methods helps determine the most suitable technique for a particular analysis.
- What is the significance of case studies in Diazotization Titrations? Case studies demonstrate the practical applications of this technique in real-world scenarios, providing insights into its importance in various industries.
- How is the field of Diazotization Titrations evolving in the future? Advances in technology and instrumentation are driving innovations in Diazotization Titrations, making them more precise and efficient for analytical chemists.
Summary of diazotization titrations
• Carried out for the estimation of drugs containing primary aromatic amino group
• Resulting amino group is diazotized by reaction with sodium nitrite solution in cold acid solution
• End point can be determined by using external indicator method using starch iodide paper
• Addition of sodium nitrite to hydrochloric acid causes formation of nitrous acid
• Nitrous acid formed diazotizes the aromatic amino group
• Starch iodide paper is prepared by immersing a filter paper in starch mucilage and potassium iodide solution
Also, Visit: B. Pharmacy Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy