Introduction to Dosage Forms
Contents
• Introduction to dosage forms
• Classification of pharmaceutical dosage forms, definitions
with examples.
Learning
Objectives
At the end of this
lecture, student will be able to
• Explain the
importance of dosage forms
• Define various
dosage forms
• Classify dosage
forms with examples
• Identify
different solid dosage forms
• Identify
different liquid dosage forms
• Define various
dosage forms
• Classify liquid
dosage forms
• Differentiate
between syrups and elixirs
• Differentiate
between gargles and mouthwashes
• Differentiate
between suspensions and emulsions
• Define various
semi-solid dosage forms
• Identify
different semi-solid dosage forms
• Differentiate
between ointments and creams
Pure Drug
1. Un-palatable
2. Obnoxius taste, odour
3. Dirty colour
4. Difficult to handle
Definitions
1. Drug – agent,
intended for use in the diagnosis, mitigation, treatment, cure or prevention of
disease in man or in animals
2. Excipients-
additives are used to
-Give a particular shape
-To increase its efficacy
– To increase its stability
– For palatability
– For elegance
3. Dosage form:
Drug + Excipients
NEED FOR
DOSAGE FORM
• Protection
• Clarity
• Masking- taste/ smell
• Solubility
• Modify drug release
• For topical administration
• For insertion – body cavities.
• For introduction – blood stream/ body tissues.
• For inhalation
Classification
(According to Physical State)
SOLID
DOSAGE FORMS
Unit Dosage Forms
• Tablets
• Capsules
• Powders
• Pills
• Suppositories
• Pessaries
Bulk Dosage Forms
• Internal
– Effervescent Granules or Powders
• External
– Dusting powder
– Insufflations
– Dentifrices
– Snuffs
LIQUID
DOSAGE FORMS
1. Monophasic
• Internal
– Syrups
– Liniments
– Elixirs
– Pediatric drops
• External
– Lotions
– Linctus
– Gargles
– Mouthwash
– Throat paints
– Sprays
– Eye lotions
– Eye drops
– Nasal drops
– Douches
– Enemas
2. Biphasic
– Emulsions
– Suspensions
SEMI-SOLID
DOSAGE FORMS
• Ointments
• Creams
• Pastes
• Jellies
GASEOUS
DOSAGE FORMS
• Aerosols
Classification
(According to the route of administration)
1. Oral route
2. Topical route
3. Parenteral route
4. Rectal route
5. Nasal route
6. Ophthalmic /Ocular route
7. Vaginal route
8. Otic route
Solid Dosage Forms
Tablets
• Solid unit dosage forms
• Compression or moulding methods.
Eg. Paracetamol tablets (Analgesic and Anti pyretic)
Tablet Compression
Machine
Tablet Shapes
Types of Tablets
• Coated tablets
-Film coated tablets
-Sugar coated tablets
-Enteric coated
tablets
• Buccal & sublingual tablets: Buccal- cheek,
Sublingual- Below the tongue
-Lozenges
• Effervescent tablets: Before administration, dissolve in
water effervescence.
• Chewable tablet: To be chewed
Capsules
• Solid unit dosage forms – drugs – in a tasteless hard or
soft soluble shell made of gelatin.
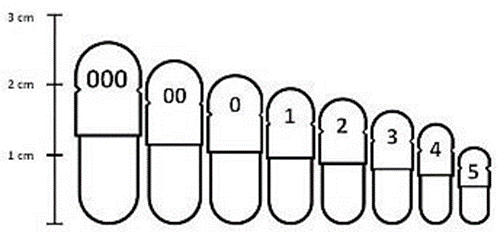
Hard Gelatin Capsule
Sizes of Hard gelatin
capsules
• Sizes from 000 to 5
• 000 is the largest and 5 the smallest
Soft Gelatin Capsules
Pills
• Small, round – solid dosage forms
Lozenges
• Solid dosage forms- medicaments + flavored base
• They dissolve or disintegrate slowly in the mouth.
Lollipops
• Sugar-based lozenge on a stick
• The lollipop provides almost immediate relief as the drug
starts being absorbed in the mouth and starts to work within minutes
• Fentanyl Actiq (Cephalon) is a raspberry lollipop that
contains Fentanyl citrate
• It has an off-white color
• Actiq is the first product specifically designed to aid in
controlling breakthrough pain in cancer patients
• It is indicated only for the management of breakthrough
cancer pain in patients with malignancies who are already taking and are
tolerant to opioids.
Powders
• Solid dosage forms – internal or external use
• Crystalline or amorphous forms
Suppositories
• Solid dosage forms
• Conical, bullet or ovoid shaped
• Insertion into the body cavities-such as rectum, vagina,
urethra, nose and ears.
• Melt or dissolve in the cavity fluids
• URETHRA-
URETHRAL BOUGIES
• NOSE- NASAL
BOUGIES
• EAR- AURINARIA
OR EAR CONES
Types of
Suppositories
Pessaries
• Solid dosage forms
• Conical or ovoid in shape
• Insertion into the vagina
Dusting
Powder
• Dusting powders – bulk powders
• External application to the skin.
• Mixtures of 2 or more than 2 ingredients. E.g. starch,
talc, kaolin, zinc oxide etc.
• 2 types
i) Medical D.P
ii) Surgical D.P
Insufflations
• Finely divided powders
• Introduction into body cavities such as ears, nose, and
tooth sockets
• Insufflator is used
Nebulizer
and Inhaler
Dentifrices
(Tooth Powder)
• Solid dosage forms
• Cleaning the surface of the teeth.
• Applied with the help of fingers or a tooth brush.
• Contain an abrasive, detergent, sweeteners and
colour.
Snuffs
• Finely divided solid dosage forms
• Inhaled into the nostrils
• Antiseptic, bronchodilator and decongestant action.
Effervescent
Powders/Granules
• Solid dosage forms
• Internal use
• Medicament + citric acid + tartaric acid + sodium
bicarbonate.
• Before administration, the granules are dissolved in
water-effervescence.
E.g. ENO granules
Monophasic Liquid Dosage Forms for Internal use
Syrups
• Sweet, viscous, saturated solution of sucrose
• The concentration of sugar is 66.7%w/w
• Vehicles- bitter drugs.
• Medicated syrups and Flavoured syrups
E.g. Simple syrup,
Ginger syrup, Orange syrup
• 66.7 % w/w: Self
preservative, High osmotic pressure, Survival of microorganisms is difficult
• Above 66.7 % w/w:
Crystallization
• Below 66.7 % w/w:
Microbial contamination
Elixirs
• Clear, pleasantly flavoured, sweetened,
hydroalcoholic
• Potent drugs such as antibiotics, antihistaminics and
sedatives.
• Non-medicated elixirs- flavours and vehicles.
E.g. Piperazine
citrate elixir
Linctuses
• Viscous, liquid preparations
• Relief of cough.
• Demulcent, sedative or expectorant action.
• Linctuses should be taken in small doses, sipped and
swallowed slowly
E.g. Codeine linctus
Paediatric
Drops
• Liquid dosage forms.
• For pediatric patients
• Administration –with a dropper.
E.g. Phenylephrine and Chlorpheniramine paediatric
drops
Monophasic Liquid Dosage Forms for External/Topical use
Liniments
• Liquid or semi liquid preparations
• External application -skin.
• Applied to the skin with friction and rubbing of the skin.
• Should not be applied to the broken skin.
E.g. Camphor liniment
Lotions
• Liquid preparations
• External application to the skin, without friction.
• Contain alcohol & glycerin
E.g. Body lotions
Monophasic Liquid Dosage Forms for use in the oral cavity
Mouthwashes
• Aqueous solutions
• Pleasant taste and odour
• Cleans and deodorises the buccal cavity.
• Should be diluted with water before use.
E.g Sodium Chloride mouthwash
Gargles
• Aqueous solutions
• Relieve soreness in mild throat infections.
• Brought into close contact with the mucous membranes of
the throat-retained for few seconds and spit out.
• Concentrated form – dilute with warm water before
use.
E.g. Potassium chlorate and phenol gargle
Throat
Paints
• Viscous liquid preparations
• Mouth and throat infections.
• Glycerin is used as the vehicle
• Applied with a brush.
• E.g. Mandl’s paint (Compound iodine paint)
Throat
Spray
• Liquid preparations of drug
• Vehicle may be water, alcohol or glycerin.
• Applied to the nose or throat with an atomiser or
nebuliser (large droplets).
• E.g. Atropine spray
Monophasic Liquid Dosage Forms instilled/ used in body cavities
Nasal Drops
• Aqueous solutions
• Instilled into the nose with a dropper.
• Antiseptic, local analgesic and decongestant property.
• E.g. Oxymetazoline nasal drops (Nasivion) and Otrivin
Eye Drops
• Sterile aqueous or oily solutions
• Instillation into the eye.
• Sterile, isotonic, free from foreign particles.
• Glass containers (containing a glass dropper with a rubber
teat) or plastic containers.
•Antiseptic, anaesthetic, anti-inflammatory, mydriatic or
miotic
E.g Ciprofloxacin eye drops (antiseptic)
Eye Lotions
• Aqueous solutions
• Washing the eyes.
• Concentrated form – diluted with warm water immediately
before use.
•Isotonic, free from foreign particles
E.g. Sodium Chloride eye lotion (antiseptic)
Douches
• Medicated solutions
• Rinsing body cavities such as nose, vagina or urinary
bladder.
• VAGINAL DOUCHE- VAGINA
• IRRIGATIONS: URINARY BLADDER
• NASAL DOUCHE: NOSE
• Irrigations & Vaginal douches- sterile in nature
E.g. Potassium Permanganate vaginal douche
Irrigations
Procedure for
administering Irrigations
Enemas
• Aqueous / oily solutions / suspensions
• Introduction into the rectum
• Purgative, sedative, anthelmintic and anti-inflammatory
effects.
•X-ray examination of the lower bowel.
E.g Barium sulphate enema
Barium Enemas
Biphasic Liquid Dosage Forms
Emulsions
•Biphasic heterogenous systems- 2 immiscible liquids
•2 immiscible liquids – water and oil.
• Mixed with each other by the addition of an emulsifying
agent.
• Emulsions are of 2 types
• O/W and W/O
E.g Liquid paraffin emulsion (laxative)
• Common emulsions are mayonnaise, egg , milk
Suspensions
• Biphasic heterogenous systems
• Finely divided solid particles suspended or dispersed in a
liquid vehicle.
• Oral administration: E.g Gelusil, Digene (antacids)
• External application: Calamine lotion (protective)
• Parenteral administration: Vaccines
• For biphasic preparations the labeling: “SHAKE WELL BEFORE USE” is mandatory
Semi Solid Dosage Forms
Ointments
•Semisolid preparations
• External application to the skin and mucous membrane
• Greasy in nature
• Medicated ointments
• Ophthalmic ointments – eye – sterile and free from
irritation.
E.g Neosporin ointment (Anti-bacterial)
Creams
• Semisolid preparations
• External application
• Less greasy/ not greasy when compared to ointments
E.g. Candid Cream (Anti- fungal)
Gels
• Semi- solid preparations
• Transparent or translucent
• Non greasy
• External application.
• Lubricating surgical gloves, rectal thermometers.
E.g. Hair styling gels, Toothpastes
Pastes
• Semi solid preparations
• Solid content is more
• Non greasy
• External application.
E.g. Toothpastes
Other Dosage Forms
Aerosols
• Pressurized dosage forms of medicament
• Liquid droplets or solid drug particle is dissolved or
suspended in a gas (which is called propellant).
• The different parts of an aerosol container are:
– Container
– Valve
– Actuator
– Dip tube.
Parts of an Aerosol Container
Uses of Aerosols
1) Topical use. E.g. Local anaesthetics, local analgesics,
anti-inflammatory drugs. E.g. Iodex spray
2) Various body cavities. E.g. Nasal spray
3) Deodorants, perfumes, cosmetics, hair sprays, shaving
lotions.
4) Disinfectant sprays, room fresheners and insect killers.
E.g Baygon cockroach spray
Poultice
• Paste like preparations
• Used externally to reduce inflammation because they retain
heat well.
• Heated and spread thickly on a dressing and applied hot to
the affected area.
Applications
• Liquid or viscous preparations
• Application to the skin.
• Can be suspensions or emulsions.
E.g. Calamine and lime application (Lime- calcium hydroxide)
Draught
• Liquid oral preparation
• Taken as a single dose.
• Dispensed in small volumes.
E.g. Paraldehyde draught (sedative)
Mixtures
• Liquid preparation for oral administration
• Medicament is dissolved or suspended in a suitable
vehicle.
• Supplied only for a small number of doses
• Should be used within a short period.
Cachet
• Solid unit dosage form
• Dry powder – enclosed in a shell
• Shell is rice flour + water – moulded and dried
• Wafer capsule.
• For administering drugs with an unpleasant taste
• Large dose can be enclosed
• Before administration – immersed in water for a few
seconds, placed on the tongue – swallowed with the help of water.
Collodion
• Liquid preparation
• External application
• The vehicle is volatile and evaporates on application
• Leaves a flexible, protective film on site of application.
• Used for minor cuts and abrasions, corn removal etc.
E.g Salicylic acid collodion (Corn remover)
Inhalations
• Liquid preparations
• Contain volatile substances
• Used to relieve congestion and inflammation of the
respiratory tract.
E.g. Eucalyptus oil – added to boiling water and the vapour
is inhaled.
• Effective in relieving nasal congestion.
Summary
1. Drug-
Therapeutic action
2. Excipients –
Non therapeutic ingredients
3. Dosage form-
Drug + Excipients
4. Classification of
dosage forms
– Physical
state: Solid, Liquid, Semi-solid & Gaseous
– Route of
administration: Oral, Topical, Parenteral, Rectal, Vaginal, Nasal, Ophthalmic
5. Solid dosage
forms: Tablets, Capsules, Pills, Suppositories, Pessaries and Powders
6. Tablets- Solid
unit dosage forms prepared by compression or moulding methods.
7. Capsules-
Solid unit dosage forms in which the drug is enclosed in a gelatin shell
8. Pills- Small,
round – solid dosage forms
9. Suppositories-
Solid dosage forms meant for insertion into the body cavities such as rectum,
urethra, nose and ears
10. Pessaries-
Solid dosage forms meant for insertion into the vagina
11. Powders-
Solid dosage forms which are crystalline /amorphous forms
12. Liquid dosage
forms- Monophasic and Biphasic
13. Differences
between monophasic and biphasic preparations- One phase/ two phase
14. Monophasic liquid
dosage forms- Internal use, external use, in oral cavity and in body
cavities.
15. Biphasic liquid
dosage forms- Emulsions and Suspensions
16. Emulsions –
Liquid + liquid (Immiscible)
17. Suspensions –
Insoluble solid + liquid
18. Ointments:
Greasy preparations for external application
19. Creams: Less
greasy preparations for external application
20. Gels:
Transparent or translucent preparations which are non-greasy and for external
application
21. Pastes:
Preparations with high solid content nad are meant for external application
22. Aerosols:
Pressurized packages containing a propellant
23. Applications: Viscous preparations for
external application
24. Draught:
Liquid orals taken as a single dose
25. Mixtures:
Liquid orals supplied for small doses
26. Collodions:
Volatile preparations for external application
27. Inhalations:
Liquid preparations meant to be inhaled