Nucleic acids
Objectives
At the end of this
lecture, student will be able
• Explain the chemistry of nucelosides and nucleotides
• Describe the double helix structure of DNA
• Describe the structure of RNA
• Compare the structural features of DNA and RNA
Content
• Nucleic acids
– Nucleotide
– Nucleoside
• Structure of DNA
• Structure of RNA
Nucleic
acids
• Macromolecules formed by repeating units of nucleotides
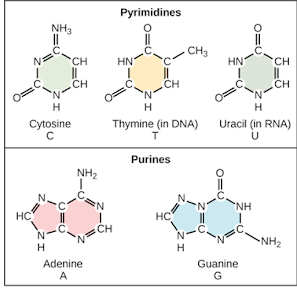
• Nucleotides – Purine or pyrimidine base linked to sugar
phosphate
• In DNA
Purine – adenine or guanine
Pyrimidine – thymine or cytosine linked to deoxy sugar
phosphate
• In RNA
Purine – Adenine or guanine
Pyrimidine – Uracil or cytosine linked to ribose sugar
phosphate
• Nitrogenous base – Purines and pyrimidines
• Nucleoside – Nitrogenous base + sugar (without phosphate
group)
• Nucleotide – Nitrogenous base + Sugar + Phosphate group
• Polymerization of nucleotides by reaction between
phosphate groups of one molecule with suger molecule of another – Long polymer
– Polynucleotide
Structure
of nitrogenous bases
Structure
of nucleoside and nucleotide
Nucleosides
• Bases covalently attached to 1’ – position of pentose
sugar ring
• RNA – sugar is ribose
• DNA – sugar is 2’ – deoxy ribose
• -OH group in 2’ position is replaced by a hydrogen
Structure
of nucleoside
Nucleotide
• Nucleoside with one or more phosphate group
• Bound covalently to 3’, 5’ or 2’ position
• If sugar – deoxyribose – deoxynucleotide
• Chemically phosphate esters
Phosphodiester
bonds
• Covalent linkage of a phosphate group between 5’ hydroxyl
group of one ribose and 3’ hydroxyl of next
DNA double
helix
• 2 separate chain of DNA wound around each other
• Has helical path – results in double helix
• Negatively charged sugar phosphate backbone of the molecule
are on outside
• The base of each strand stack one above the other in the
center
• Between backbones strands major and minor grooves –
helical patch exist
• Strands joined together by hydrogen bonds between bases on
opposite strand
• Two strands are complementary
• G pairs with C with 3 hydrogen bonds
• A pairs with T with 2 hydrogen bonds
Structure
of DNA
Ribonucleic
acid – RNA
• RNA occurs as a single stranded molecule
• No helical structure
• Forms globular conformation
• Local regions of helical structures are formed by
intramolecular hydrogen bondings
• Bases stack with in single nucleic acid chain
• Occur in regions where one part is complementary to other
• Nuclear RNA are small
• Ribosomal RNA are large
DNA vs RNA
Summary
• Nucleic acids are macromolecules formed by repeating units
of nucleotides
• Nucleotides consists of purine or pyrimidine base linked
to sugar phosphate
• DNA consists of purine (adenine or guanine) and pyrimidine
– (thymine or cytosine) linked to deoxy sugar phosphate
• RNA consists of purine (adenine or guanine) and pyrimidine
(uracil or cytosine) linked to ribose sugar phosphate
• Nucleosides are combination of nitrogenous base + sugar (without
phosphate group)
• Nucleotide are combination of Nitrogenous base + Sugar + Phosphate
group
• Polymerization of nucleotides by reaction between
phosphate groups of one molecule with suger molecule of another – Long polymer
– Polynucleotide