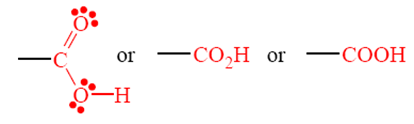Nomenclature of Organic
Compounds
Contents
• IUPAC Nomenclature of alkanes
• IUPAC nomenclature of cycloalkanes
• IUPAC nomenclature of
• Alkenes
• Dienes
• Alkynes
• Alkyl halides
• Alcohols
• Carboxylic acids
• Esters
• Acid halides
• Amides
• Identification of structures of the above classes
Learning
Objectives
At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
• Identify the structure of a given compound belonging to
the classes – alkanes and cycloalkanes
• Name above class of compounds according to IUPAC
• Identify the structure of a given compound belonging to
the classes
• Alkenes
• Dienes
• Alkynes
• Alkyl halides
• Alcohols
• Name above class of compounds by IUPAC
• Identify the structure of a given compound belonging to
the classes – carboxylic acids, esters, acid halides, and amides
• Give nomenclature of those compounds
Introduction
to Nomenclature
• Common (trivial) names
• IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry)
names
• 4 parts of IUPAC name
• Prefix
• Locant
• Parent name
• Suffix
Alkanes
• Saturated hydrocarbons
• Homologous series & homologs
• General molecular formula CnH2n+2
Unbranched
or Normal Alkanes
Structural
Formula of Alkanes
Branched
Alkanes
• Iso structural unit
• Neo structural unit
Alkyl
Group Nomenclature
Unbranched alkyl
groups
• Letter R indicates any alkyl group
• Branched alkyl
groups
• 1°, 2°, 3°
hydrogens
Nomenclature
of Alkanes
• Locate longest continuous chain
• Substituent – lowest possible number
• Designate the substituent
• 2 or more substituent – arranged alphabetically
• Similar substituents – prefix di, tri, tetra…
• Hyphen and comma
• 2 chains of same length – choose with more substituent
• Branching at equal distance
Nomenclature
of Cycloalkanes
• CnH2n
• Saturated hydrocarbons with a ring of carbon atoms in the
molecule
• Prefix – cyclo
• Examples
• One substituents
• Two substituents
• More than 2 substituents
Nomenclature
of Alkenes
• Unsaturated hydrocarbons, olefins
• General molecular formula CnH2n
• Replace suffix -ane by -ene
• Examples
• Rule 1
• Rule 2
• Rule 3
• Rule 4
• Rule 5
Nomenclature
of Dienes
• Dienes and its types
• Rules
• General formula CnH2n-2
• Terminal & internal alkyne
• Replace -ane by -yne
• Rule 1
• Rule 2
Nomenclature
of Alkyl Halides
• Alkyl halides or halo alkanes
• Rule 1
• Rule 2
Nomenclature
of Alcohols
• Classification
• Common names
• IUPAC names
• Locate and number
• One substituent
• More than one substituent – alphabetical order
• Branching at equal distance
• Glycols or diols
Nomenclature
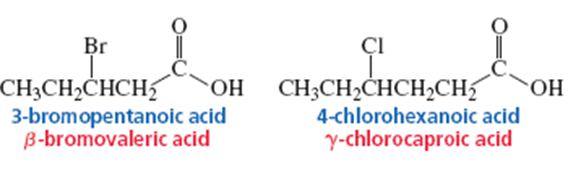
of Carboxylic Acids
• Carboxylic acid
• Acyl group
• Carboxyl group – carbonyl group + hydroxyl group
• Systematic and common names
• Alkanoic acid
• Examples
Nomenclature
of Esters
• Functional derivative of carboxylic acid
• Examples
Nomenclature
of Acid Halides
• Functional derivative of carboxylic acid
• Alkyl halide
• Examples
Nomenclature of Amides
• Functional derivative of carboxylic acid – amide
• Examples
• Substituent on nitrogen
Summary
• Non-systematic names of organic compounds – trivial names
or common names
• Systematic nomenclature of organic compounds – IUPAC names
• Alkanes –
hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds
• Branched chain
alkyl groups – indicated using the prefix iso, neo
• Cycloalkanes –
saturated hydrocarbons with a ring of carbon atoms in the molecule
• IUPAC names of
cycloalkanes – prefix ‘cyclo’ to the names of alkanes
• Alkenes –
hydrocarbons that contain double bond
• Functional group of alkenes – double bond
• Functional group suffix of alkenes – ene
• Dienes –
hydrocarbons that contain 2 double bonds, suffix – diene
• Alkynes –
hydrocarbons that contain triple bond
• Functional group of alkynes – triple bond
• Functional group of alkynes – yne
• Alkyl halides –
named as substituted alkanes
• Functional group of alkyl halide – X
• IUPAC name of alkyl halide – halo alkane
• Alcohols –
named using functional group suffix
• Functional group of alcohol – OH
• IUPAC name of alcohol – alkanol
• Functional group of
carboxylic acid – COOH
• IUPAC name of carboxylic acid – alkanoic acid
• Functional derivatives of carboxylic acid – esters, acid
halides, amides
• IUPAC name of acid
chloride – given by using the acid name and replacing “ic acid” with “yl
chloride”
• IUPAC name of ester
– name of the group R’ attached to the carbonyl group stated first followed
by the name of the acid with ‘ic’ acid replaced by ‘ate’
• IUPAC name of
amides – given by using the acid name, replacing “oic acid” or “ic acid”
with “amide”