Structure and Uses of Aliphatic Amines

Structure and Uses of Aliphatic Amines
Learning Objectives
At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
• Explain the basicity of amines
• Compare the basicity of ammonia with aliphatic and aromatic amines
• Write the structure and uses of aliphatic amines
What Are Aliphatic Amines?
Aliphatic amines are organic compounds derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups. Unlike aromatic amines, aliphatic amines have an open-chain structure, making them highly flexible and reactive.
Classification of Aliphatic Amines
Primary Amines
Primary amines have one alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom. They are the simplest form of aliphatic amines and serve as essential building blocks in organic synthesis.
Secondary Amines
Secondary amines possess two alkyl or aryl groups connected to the nitrogen atom. These compounds are widely used in the production of pharmaceuticals and dyes.
Tertiary Amines
Tertiary amines are characterized by three alkyl or aryl groups bonded to the nitrogen atom. They find applications in the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
Chemical Structure of Aliphatic Amines
The general formula for aliphatic amines is R-NH2, where R represents an alkyl or aryl group. This formula highlights the open-chain nature of these compounds, distinguishing them from their aromatic counterparts.
Physical Properties
Aliphatic amines are typically colorless, volatile liquids with a fishy odor. They have lower boiling points compared to their aromatic counterparts. The solubility of aliphatic amines in water varies depending on their size, with smaller amines being more soluble.
Common Sources of Aliphatic Amines
Aliphatic amines are found in various natural sources, including fish, plants, and bacteria. Additionally, they are synthesized in laboratories to meet industrial demands.
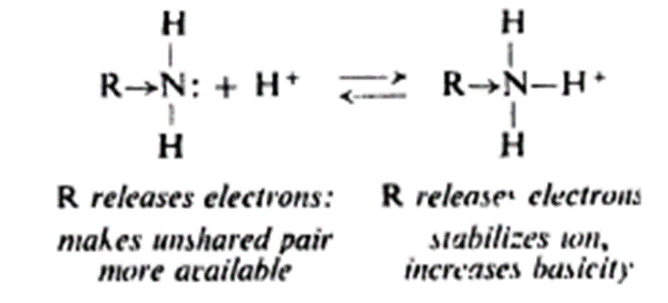
Aliphatic amine
• Aliphatic amine more basic than ammonia
• Basicity of amines – Kb – basicity constant
• Electron releasing group disperses positive charge of substituted ammonium ion
• Alkyl group pushes electrons towards nitrogen
Synthesis of Aliphatic Amines
Several methods are employed to synthesize aliphatic amines, with the choice of method depending on the specific compound needed. Some common methods include:
Gabriel Synthesis
Gabriel synthesis is commonly used to prepare primary amines. It involves the reaction of an alkyl halide with phthalimide followed by hydrolysis.
Reductive Amination
Reductive amination is a versatile method for the synthesis of secondary and tertiary amines. It involves the reaction of carbonyl compounds with ammonia or primary amines.
Hoffmann Degradation
Hoffmann degradation is a useful method for converting primary amides to primary amines. It involves the use of bromine and sodium hydroxide.
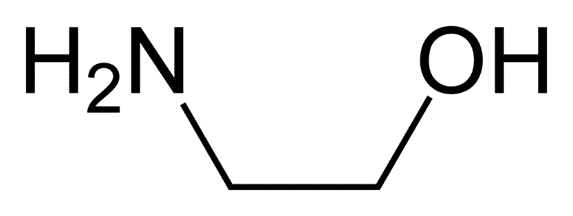
Ethanolamine
Structure
• 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine
• Has both primary amine and primary alcohol
Uses
• As gas stream scrubbing
• As buffer, pH regulator in cosmetics
• Injectable sclerosant
Ethylenediamine
Structure
• Strongly basic amine
Uses
• Precursor to chelation agents, drugs, and agrochemicals, polymers
• Ingredient in the common bronchodilator drug aminophylline
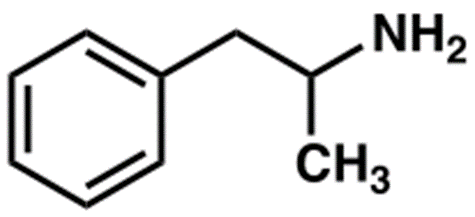
Amphetamine
Structure
• Alpha-methylphenethylamine
Uses
• Potent CNS stimulant
• For depression and chronic pain
Summary
• Basicity of amines – Kb – basicity constant
• Aliphatic amines – more basic than ammonia
• Aromatic amines – weakly basic than ammonia
• Ethylenediamine is Precursor to chelation agents, drugs, and agrochemicals, polymers
• Amphetamine is Potent CNS stimulant
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1: What is the difference between aliphatic and aromatic amines?
Answer: The key difference lies in the structure. Aliphatic amines have an open-chain structure, while aromatic amines have a closed-ring structure known as an aromatic ring. This structural dissimilarity impacts their chemical properties and reactivity.
FAQ 2: How are primary amines synthesized?
Answer: Primary amines can be synthesized through methods such as Gabriel synthesis, which involves the reaction of an alkyl halide with phthalimide followed by hydrolysis. Another common method is reductive amination, which utilizes carbonyl compounds and ammonia or primary amines to form primary amines.
FAQ 3: What are the key applications of aliphatic amines in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Aliphatic amines find applications in pharmaceuticals as intermediates for synthesizing drugs. They are essential in the production of various pharmaceuticals, including analgesics, antihistamines, and antiviral drugs.
FAQ 4: Are aliphatic amines harmful to the environment?
Answer: The impact on the environment depends on how they are used and managed. Improper disposal and waste management of aliphatic amines can have adverse environmental consequences. It’s important to follow proper handling and disposal procedures to minimize potential harm.
FAQ 5: What safety precautions should be taken when handling aliphatic amines?
Answer: When working with aliphatic amines, it’s crucial to follow safety protocols. This includes wearing appropriate protective gear such as gloves and eye protection, working in well-ventilated areas, and adhering to safety guidelines to minimize the risk of exposure, which can be harmful.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf