Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity

Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
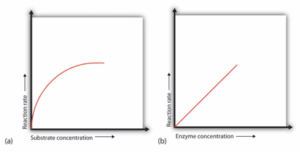
1. Concentration of enzyme:-
As the concentration of enzyme is Increased, The velocity of the Reaction also proportionally Increases:
Ex:- This property is used to determine the serum enzymes for the diagnosis of diseases.

2. Concentration of substrate:-
As the substrate concentration increases gradually the Enzyme Reaction also Increases but up to a limited Range after that it becomes constant.
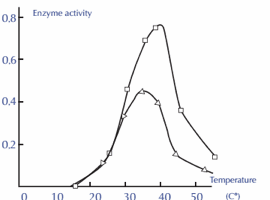
3. Effect of temperature:-
The velocity of an Enzyme Reaction Increases with an Increase in Temperature up to a maximum and then declines. A Bell-shaped Curve is usually observed. The optimum temperature for most of the enzymes is between 400c-450C.
When the Enzyme is Exposed to a Temperature above 500c denaturation will take place. The majority of the Enzymes Become inactive at higher Temperatures above700c.
4. Effect of ph:-
Each enzyme has an optimum PH at which the velocity is maximum. Below and above this pH, The Enzyme activity is much lower, and at Extreme pH, The Enzyme Becomes Inactive. Most of the Enzymes show optimum activity around Neutral pH (6-8).

5. Effect of inhibitors:-
The presence of enzyme inhibitors reduces the enzyme action.
Heavy metals are the inhibitors for enzyme activity.
6. Enzyme activators:-
The presence of activators in certain concentrations increases the enzyme activity i.e. cysteine HCL increases the proteolytic activity of papain.
7. Effect of time:-
Under Ideal and optimal conditions the time required for an Enzyme Reaction is less.
Strategies for Optimizing Enzyme Activity
To maximize enzyme efficiency, researchers employ various strategies, including:
- Temperature Control: Maintaining optimal temperatures for enzyme activity while avoiding denaturation.
- pH Adjustment: Adjusting pH levels to match the enzyme’s optimal range for enhanced activity.
- Substrate Optimization: Ensuring sufficient substrate concentration without reaching saturation to maximize reaction rates.
- Enzyme Engineering: Modifying enzyme properties through genetic or chemical methods to improve stability, specificity, and activity.
- Inhibitor Screening: Identifying and characterizing inhibitors to develop strategies for mitigating their effects on enzyme activity.
FAQs on Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1. What are enzymes, and why are they important? Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are crucial for maintaining cellular functions and facilitating various biochemical processes.
2. How does temperature affect enzyme activity? Temperature influences enzyme activity by altering the kinetic energy of molecules. Moderate temperatures enhance enzyme activity, while extreme temperatures can denature enzymes, rendering them inactive.
3. What is the optimal pH for enzyme activity? Each enzyme has an optimal pH range at which it operates most efficiently. Deviations from this pH range can disrupt enzyme structure and function, affecting catalytic activity.
4. How does substrate concentration impact enzyme activity? Increasing substrate concentration initially increases the rate of enzymatic reactions, but this relationship levels off as the enzyme becomes saturated with substrates. Further increases in substrate concentration do not enhance the reaction rate.
5. What are inhibitors, and how do they affect enzyme activity? Inhibitors are molecules that interfere with enzyme activity, either by competing with the substrate for binding at the active site (competitive inhibitors) or by binding elsewhere on the enzyme (non-competitive inhibitors), altering its conformation and reducing catalytic activity.
For detailed PDF Notes click on download button
