Flash Distillation

Flash Distillation
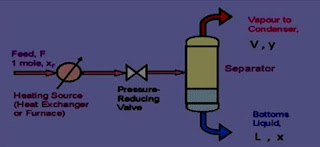
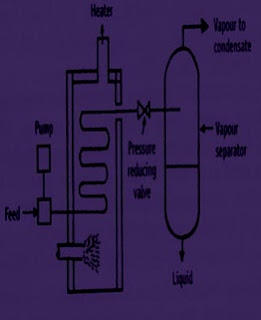
Flash distillation is defined as a process in which the entire liquid mixture is suddenly vaporized (flash) by passing the feed from a
high-pressure zone to a low-pressure zone. Flash distillation is also known as equilibrium distillation, i.e., separation is attempted when the liquid and vapour phases are in equilibrium. This method is frequently carried out as a continuous process.
Principle
• When a hot liquid mixture is allowed to enter from a high-pressure zone into a low-pressure zone, the entire liquid mixture is suddenly vaporised. This process is known as flash vaporisation. During this process, the chamber gets cooled.
• The individual vapour phase molecules of high boiling fraction get condensed, while low boiling fraction remains as vapour.
Working
• The feed is pumped through a heater at a certain pressure. The liquid gets heated, which enters the vapour-liquid separator through a pressure-reducing valve. Due to the drop in pressure, the hot liquid flashes, which further enhances the vaporisation process.
• The sudden vaporisation induces cooling. The individual vapour phase molecules of high boiling fraction get condensed, while low boiling fraction remains as vapour. The mixture is allowed for a sufficient time so that vapour and liquid portions separate and achieve equilibrium.
• The vapour is separated through a pipe from above and liquid is collected from the bottom of the separator. By continuously feeding into the still, it is possible to obtain continuous flash distillation.
• The operating conditions can be adjusted in such a way that the amount of feed exactly equals the amount of material removed.
Therefore, vapour and liquid concentrations at any point remain constant in the unit.
Uses: Flash distillation is used for separating components, which boil at widely different temperatures. It is widely used in the petroleum industry for refining crude oil.
Advantages: Flash distillation is a continuous process.
Disadvantages: Flash distillation is not effective in separating components of comparable volatility. It is not an efficient distillation when nearly pure components are required, because the condensed vapour and residual liquid are far from pure.
FAQs
How does Flash Distillation differ from traditional distillation?
Flash Distillation is a rapid process involving sudden pressure drops, making it quicker than continuous distillation methods.
What industries benefit the most from Flash Distillation?
Petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries find Flash Distillation particularly advantageous for substance separation.
Is Flash Distillation environmentally friendly?
Yes, Flash Distillation’s minimal energy consumption and waste reduction contribute to its eco-friendly profile.
Can Flash Distillation be automated?
Automation technologies can be integrated to streamline Flash Distillation processes, enhancing efficiency.
Are there safety concerns with Flash Distillation?
Proper pressure regulation and comprehensive training address safety concerns associated with Flash Distillation.
How can Flash Distillation contribute to research?
Flash Distillation aids in essential oil extraction and polymer synthesis, playing a vital role in scientific research.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf