Steam Distillation

Steam Distillation
Steam distillation is used for separating substances which are immiscible with water, volatile in steam & having high vapour pressure at the boiling temperature of water
It is a method of distillation carried with the aid of steam and used for the separation of high boiling substance from non-volatile impurities
It is the most common example of differential distillation
Principle
• A mixture of immiscible liquids begins to boil when the sum of their vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure.
• In case of a mixture of turpentine oil and water, mixture boils below the BP of water, though the turpentine boils at a much higher temperature than that of water.
• For example, the BP of turpentine is about 1600C. on mixing with water and heated the mixture boils at about 95.60C
• At this temperature, the VP of water is 86.24 kPa (647 mm Hg) and that of turpentine is 15.05 kPa (113 mm Hg)
• The sum of VPs is 101.31 kPa (760 mm Hg) which is normal AP.
• Thus high boiling substances can be distilled at a temperature much below its BP when steam is used
Construction
• It consists of a metallic ‘steam can’ fitted with a cork having two holes.
• Through one of the holes, a long tube is passed so as to reach almost the bottom of steam generator.
• This tube acts as a safety tube, so that in case the pressure inside the steam generator becomes too much, water will be forced out of it and the pressure will be relieved. Moreover, when steam start coming out from the safety tube; it indicates that the steam can is almost empty.
• Through another hole a bent tube is passed.
• Another end of the bent tube is connected to the flask containing non-aqueous liquid (for example, crude containing volatile oil) through a rubber bung. The tube should reach almost the bottom of the flask.
• Through the other hole of the rubber bung, a delivery tube is inserted which connects the flask and the condenser.
• The condenser is connected to a receiver flask using an adaptor.
Provisions are made to heat the steam can and flask.
Working of steam Distillation
The non- aqueous liquid is placed in the flask. A small quantity of water is added to it. Steam can is filled with water.
The steam generator and the flask are heated simultaneously, so that a uniform flow of steam passes through the boiling mixture. The mixture gets heated.
The steam carries the volatile oil and passes into the condenser, which is cooled by cold water.
The condensed immiscible liquid is collected into receiver.
Distillation is continued until all the non- aqueous liquid has been distilled. In the receiver, water and organic liquid form two separate layers, which can be easily separated using a separating flask.
Here’s how steam distillation works:
- Setup: The plant material, often chopped or crushed, is placed in a flask or a container with a heating element. Water is also added to the same container.
- Heating: The mixture is heated, causing the water to boil and turn into steam. As the steam rises, it passes through the plant material, extracting the volatile compounds.
- Vaporization: The volatile compounds in the plant material evaporate along with the steam. These compounds are carried with the steam as vapor.
- Condensation: The steam and vapor mixture is then passed through a cooling system, such as a condenser. In the condenser, the steam is cooled and condensed back into liquid form. This liquid is known as the “distillate.”
- Separation: Since oil and water do not mix, the distillate separates into two layers in a collection vessel. The upper layer contains the essential oil or volatile compounds, and the lower layer is water.
- Collection: The essential oil is collected from the upper layer, often through the use of a separatory funnel.
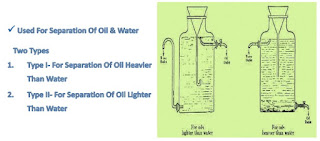
Florentine Receiver
Applications
• It is used for the separation of immiscible liquids (toulene and water)
• Extracting most of the volatile oils (anise, clove and
eucalyptus)
• Purification of liquid with high BP (essential oil of almond)
• Camphor can be distilled
• Aromatic water are prepared by this method
FAQs
1. Is steam distillation the only method for extracting essential oils?
No, while steam distillation is a popular method, essential oils can also be extracted through processes like cold-pressing and solvent extraction.
2. Can I perform steam distillation at home?
Yes, it’s possible to perform small-scale steam distillation at home with the right equipment, but it’s essential to follow safety precautions.
3. What are some plants commonly used in steam distillation?
Lavender, eucalyptus, peppermint, and rosemary are among the most commonly steam-distilled plants for essential oils.
4. Are there any potential hazards associated with steam distillation?
When not performed correctly, steam distillation can be hazardous due to the high temperatures involved. Safety measures and proper equipment are crucial.
5. Can steam distillation be used for non-botanical materials?
While it’s primarily used for botanicals, steam distillation has also been employed to extract volatile compounds from non-botanical sources, such as certain chemicals.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf