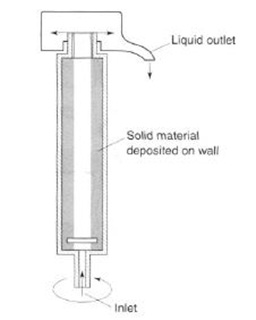
Tubular-bowl centrifuges (centrifugal sedimenters)
Used to separate solids and liquids
when the solid content is low. These consist of a cylindrical ‘bowl’
Around 100 mm in diameter and 1 m
long, which rotates at 300-1000 s-1
The product enters at the bottom
and centrifugal force causes solids to be deposited on the wall as it passes up
the bowl
The liquid overflows from the top
This type of centrifuge can also be
used to separate immiscible liquids
Rate of sediment can be control by
controlling the inlet rate
The uses of centrifugal sedimenters
include liquid/liquid separation
E.g. During antibiotic manufacture
and purification of fish oils, the removal of very small particles, the removal
of solids that are Compressible and which easily block the filter medium
The separation of blood plasma from
whole blood (need C =3000)
The separation of different
particle size fractions, and examining the stability of emulsions
Principle
• Super centrifuge is a
sedimentation centrifuge
• The separation is based on the
difference in the densities between two immiscible liquids
• Centrifugation is done in the
bowl of small centrifuge
• During centrifugation, the
heavier liquid is thrown against the wall, while the lighter liquid remains as an
inner layer
• The two layers are simultaneously
separated using modified weirs
Construction
• It consists of a long hallow
cylindrical bowl of small diameter
• It is suspended from a flexible
spindle at the top and guided at the bottom by loose-fit bushing
• It can be rotated on its
longitudinal axis
• Provision is made at the bottom
for the feed inlet using pressure system
• The liquid outlets are provided
at different heights at the top of the bowl, and modified weirs, are attached