OLFACTION: SENSE OF SMELL

Objectives
At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
• Describe the anatomy of olfactory receptor
• Explain the physiology of olfaction and olfactory transduction
OLFACTION: SENSE OF SMELL
• Originates in the nasal cavity, which also acts as a passage for respiration
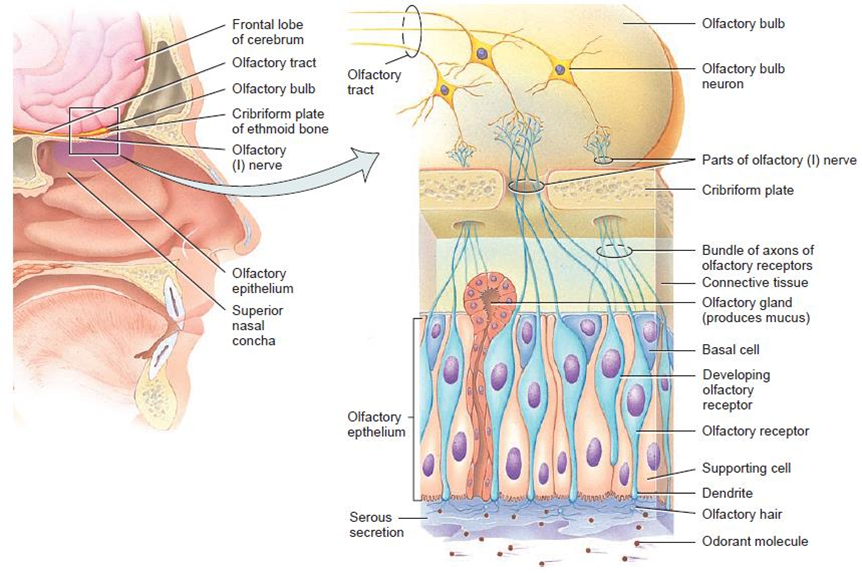
Anatomy of Olfactory Receptors
• Nose contains 10–100 million receptors for the sense of smell
• Contained within an area called the olfactory epithelium
Olfactory epithelium consists of three kinds of cells:
a) Olfactory receptors
b) Supporting cells
c) Basal cells
Olfactory receptors
• First-order neurons of the olfactory pathway
• Bipolar neuron with an exposed knob-shaped dendrite
• An axon projecting through the cribriform plate
• Ending in the olfactory bulb
• Olfactory hairs, cilia project from the dendrite
• Cilia responds to inhaled chemicals
• Produces a generator potential
• Initiates the olfactory response
Supporting cells
• Columnar epithelial cells of the mucous membrane lining the nose
• Provide physical support, nourishment, and electrical insulation for the olfactory receptors
• Detoxify chemicals that come in contact with the olfactory epithelium
Basal cells
• Stem cells located between the bases of the supporting cells
• Continually undergo cell division to produce new olfactory receptors
Olfactory (Bowman’s glands)
• Within the connective tissue; supports the olfactory epithelium
• Produce mucus
• Moistens the surface of the olfactory epithelium
• Dissolves odorants so that transduction can occur
Olfactory epithelium and olfactory receptors
Physiology of Olfaction – Olfactory pathway
• Olfactory receptors react to odorant molecules
• A generator potential (depolarization) develops and triggers one or more nerve impulses
• In some cases, an odorant binds to an olfactory receptor protein in the plasma membrane of an olfactory hair
• The olfactory receptor protein is coupled to a membrane protein called a G protein
• In turn activates the enzyme adenylate cyclase
Olfactory transduction
Olfactory Disorders
Anosmia: The Absence of Smell
Anosmia is a condition characterized by the complete loss of the sense of smell. Individuals experiencing anosmia find themselves unable to detect any odors, diminishing one of the essential facets of sensory perception.
Causes of Anosmia
- Nasal Issues: Blockages or abnormalities in the nasal passages can impede the flow of air carrying odor molecules.
- Neurological Factors: Conditions affecting the olfactory nerve or the brain’s olfactory processing centers can lead to anosmia.
- Trauma: Head injuries or trauma to the nasal region can disrupt the olfactory system.
Hyposmia: Diminished Smell Sensitivity
Hyposmia refers to a reduced sensitivity to odors, where individuals experience a diminished sense of smell. While not a complete loss, it can significantly impact the quality of one’s olfactory experience.
Causes of Hyposmia
- Respiratory Infections: Conditions like sinusitis or upper respiratory infections can temporarily reduce smell sensitivity.
- Age-Related Changes: Aging can lead to a natural decline in olfactory function, contributing to hyposmia.
- Medications: Certain medications may interfere with the olfactory system, causing a decrease in smell sensitivity.
Summary
• Olfactory receptors are responsible for the sense of smell
• Cilia responds to inhaled chemicals; generates potential; initiates the olfactory response; activates the enzyme adenylate cyclase
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can olfactory disorders be treated? Olfactory disorders can have varied causes, and treatment options depend on the underlying factors. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized advice.
- How does the olfactory system contribute to memory? The olfactory system is closely linked to the brain’s memory center, triggering strong recollections when exposed to certain scents. This phenomenon is often utilized in therapeutic practices.
- Are there any natural ways to enhance olfactory health? Maintaining overall health, staying hydrated, and avoiding exposure to harmful substances are simple yet effective ways to promote optimal olfactory function.
- What is the significance of the olfactory system in animal behavior? In the animal kingdom, the olfactory system plays a critical role in survival, influencing behaviors such as mating, hunting, and territorial marking.
- How can olfactory technology impact daily life? Olfactory technology holds potential in various domains, including entertainment, healthcare, and even enhancing the virtual reality experience. The future may see innovative applications that reshape our interactions with the world.
- Can anosmia or hyposmia be temporary? Yes, certain causes of anosmia and hyposmia, such as respiratory infections or nasal blockages, can be temporary and may improve with appropriate treatment.
- Are there any preventive measures for olfactory disorders? Maintaining overall nasal and respiratory health, avoiding head trauma, and promptly addressing any respiratory infections can contribute to preventing olfactory disorders.
- Is there a cure for anosmia or hyposmia? The possibility of a cure depends on the underlying cause. While some cases may be reversible with appropriate treatment, others may require ongoing management strategies.
- How does anosmia or hyposmia impact mental health? The loss or reduction of the sense of smell can have psychological effects, leading to feelings of isolation or frustration. Seeking support and developing coping mechanisms is crucial.
- Can lifestyle changes help improve olfactory function? Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding exposure to substances that may harm the olfactory system can contribute to improved olfactory function.
Also, Visit:
B. Pharma Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy pdf