NSAIDs- Non Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory Drugs
INTENDED
LEARNING OUTCOMES
At the end of the
lecture, students will be able to
• Define NSAIDs.
• Understand the general mechanism of action of NSAIDs
• Categorize the NSAIDs according to their chemical structure
• Outline the synthesis of some NSAIDs
• Recognize the specific uses of the different NSAIDs
Contents
• NSAIDs-Non Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
• The general mechanism of action of NSAIDs
• NSAIDs classification according to their chemical
structure
• The synthesis of some NSAIDs
• The specific uses of the different NSAIDs
NSAIDS
• NSAIDS are the drugs which are used against Inflammation
by inhibiting the COX Enzyme.
Mechanism of Action of NSAIDS
Classification
1. SALICYCLIC ACID DERIVATIVES
• ASPIRIN
• DIFLUNISAL
• SALSALATE
• SULPHASALAZINE
2. P-AMINO PHENOL DERVIVATIVES
• PARACETAMOL
• PHENACETIN
3. PYRAZOLIDINE DIONE DERIVATIVES
• PHENYL BUTAZONE
• OXYPHENBUTAZONE
• SULPHIN-PYRAZONE
4. ANTHRANILIC ACID DERIVATIVES
• MEFENEMIC ACID
• FLUFENEMIC ACID
• MECLOFENAMATE
5. ARYL ALKANOIC ACID
DERIVATIVE
A. INDOLE ACETIC ACID: INDOMETHACIN
B. INDENE ACETIC ACID: SULINDAC
C. PYRROLE ACETIC ACID: TOLMETIN, ZORMIPIRAC
D. PHENYL ACETIC (PROPIONIC) ACID:
• IBUPROFEN, DICLOFENAC,
• NAPROXEN, CAPROFEN,
• FENOPROFEN, KETO-PROFEN,
• FLURBIPROFEN, KETOROLAC, ETODAOLAC
6. OXICAMS
• PIROXICAM
• MELOXICAM
• TENOXICAM
7. SELECTIVE COX-2
INHIBITORS
• CELECOXIB
• ROFECOXIB
• VALDECOXIB
8. GOLD COMPOUNDS
•AURONOFIN
•AUROTHIOGLUCOSE
•AUROTHIOGLUCAMIDE
• AUROTHIOMALATE SODIUM
9. MISCELLANEOUS
•NABUMETONE
•NIMESULIDE
•ANALGIN
10. DRUG USED IN GOUT
•ALLOPURINOLL
• PROBENECID
• SULPHINPYRAZONE
I.
Salicylates
• Salicylates not only posses antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory
properties
• But also other actions that have been proven to be
therapeutically beneficial because salicylates promote the excretion of
uricacid
• They are useful in the treatment of gouty arthritis
• More attention has been given to the ability of
salicylates (aspirin) to inhibit platelet aggregation, which may contribute to
heart attack and strokes, and
• Hence, aspirin reduces the risk of myocardial infarction
• In addition, a recent study suggested that aspirin and
other NSAIDs might be protective against colon cancer
ASPIRIN:
Chemical Formula:
C9H8O4
Chemical structure of
Aspirin
Properties:
Aspirin is a white crystalline powder, slightly soluble in water and soluble in
alcohol
Mode of action of
Aspirin
Aspirin inhibits the enzyme cycloxygenase and thromboxane
synthetase (TxA2) by binding irreversibly and interfering with the platelet
aggregation
Medicinal Uses:
• Relief of minor aches and mild-to-moderate pain in the
conditions such as arthritis and related arthritic condition — Anti Rheumatic
• Also used in myocardial infarction prophylaxis
• Analgesic
• Anti-pyretic
Dosage forms:
• Aspirin tablets I.P., B.P.,
• Dispersible aspirin tablets B.P.,
• Effervescent soluble aspirin tablets B.P.,
• Gastro-resistant aspirin tablets B.P.,
• Aspirin and Caffeine tablets B.P.,
• Co-codaprin tablets B.P.,
• Dispersible co-codaprin tablets B.P.
SODIUM
SALICYLATE:
Chemical Name:
Sodium Salicylate, Monosodium salicylate; Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-, monosodium
salt; B.P., U.S.P., Eur. P., Int. P., Ind. P.,
Chemical Structure of Sodium Salicylate:
Properties:
Sodium salicylate is a white crystalline powder, soluble in water, sparingly
soluble in alcohol.
Medicinal Uses:
• It is used for fever and for the relief of pain
• It also possesses anti-inflammatory actions similar to
aspirin
• Symptomatic therapy of gout
II. p-Amino
phenol derivatives
• These derivatives possess analgesic and antipyretic
action, but lack anti-inflammatory effects
• Acetanilide was introduced into the therapy in 1886 as an
antipyretic–analgesic agent
• However, it was subsequently found to be too toxic, having
been associated with methemaglobinemia and jaundice
• Phenacetin was introduced in the following year and was
widely used but was withdrawn recently because of its nephrotoxicity
• Acetaminophen (paracetamol) was introduced in 1893 and it
remains the only useful agent of this group used as an antipyretic and an
analgesic agent
Paracetamol
INN, BAN, Acetaminophen USAN
Chemical Name:
4′-Hydroxyacetanilide; Acetamide, N-(4- hydroxyphenyl)-
Chemical Structure of Paracetamol
Properties:
Paracetamol exist as white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water,
soluble in alcohol, and very slightly soluble in methylene chloride
Mechanism of action of Paracetamol:
• Paracetamol produce antipyresis by acting on the
hypothalamic heat-regulating centre and analgesia by elevating the pain
threshold NHCOCH3
Paracetamol Toxicity:
•Hepatic necrosis and death have been observed following
over dosage hepatic damage is likely in an adult who takes more than 10 g in a
single dose or if a 2-year old child takes more than 3 g
Medicinal Uses:
•It is a metabolite of acetanilide and phenacetin employed
as an antipyretic and analgesic
•It may be used effectively in a broad spectrum of arthritic
and rheumatic conditions linked with musculoskeletal pain, headache,
neuralgias, myalgias, and dysmenorrhea.
•It is particularly useful in aspirin-sensitive patients.
Paracetamol Dosage
forms:
• Paracetamol tablets I.P, B.P.,
• Paracetamol syrup I.P., Co-codamol tablets B.P.,
• Effervescent Co-codamol tablets B.P.,
• Co-dydramol tablets B.P., Co-proxamol tablets B.P.,
• Paracetamol capsules B.P.,
• Paediatric paracetamol oral solution B.P.,
• Paracetamol oral suspension B.P.,
• Paracetamol suppositoriesB.P.,
• Dispersible paracetamol tablets B.P.,
• Soluble paracetamol tablets B.P.
Phenacetin
INN, BAN, USAN
Chemical structure of
Phenacetin
Chemical Name: p-Acetophenetidide;
Acetamide, N-(4- ethoxyphenol) – ; Acetophenetidin; p-Ethoxyacetanilid; B.P. (1973),
U.S.P., Eur. P., Int. P., Ind. P.
Properties: It
exists as a white glistering powder with a bitter taste, sparingly soluble in water
and soluble in chloroform.
Medicinal Uses:
• It is an analgesic and an antipyretic with similar
effectiveness as an aspirin.
• It has a greater potential for toxicity (hemolytic anaemia
and methemoglobinaemia) than paracetamol.
• Irreversible kidney damage with prolonged ingestion of
phenacetin has been established which ultimately resulted in complete
withdrawal of this drug in many countries.
Pyrazolidine
dione derivatives
3,
5-Pyrazolidinediones
Phenyl butazone:
It is a pyrazole derivative
Phenylbutazone
INN, BAN, USAN
Chemical Name:
4-Butyl-1, 2-diphenyl-3, 5-pyrazolidinedione; 3, 5- Pyrazolidinedione,
4-butyl-1, 2-diphenyl- ;Butadione ; B.P., U.S.P., Eur. P., Int. P.,
Chemical structure of Phenyl butazone
Properties: Phenylbutazone
is a white crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water, sparingly
soluble in alcohol, and soluble in alkaline solutions.,
Medicinal Uses:
• Antipyretic analgesic, and anti-inflammatory actions,
because of its toxicity it is not used as a general antipyretic or analgesic.
• It is a usual practice reserved for use in the treatment
of osteoarthrosis, ankylosing spondylitis, arthritis, acute superficial
thrombophlebitis, painful shoulder, and Reiter’s disease, where less toxic
drugs have failed.
Phenazone
INN, BAN, Antipyrine USAN (Antipyrine)
Chemical structure of
Phenazone
Chemical Name: 2,3-Dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one;
1,2- Dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-3H-pyrazol-3- one; Antipyrine; Phenazone
B.P., Eur. P., Int. P., Antipyrine U.S.P.
Medicinal Uses:
• As antipyretic, it possesses local anaesthetic and styptic
actions and solutions containing 5% are used locally as ear drops.
• It has now been replaced by relatively more effective and
safer drugs.
IV.
Anthranilic acid derivatives
Mefenamic
Acid BAN
Chemical structure of
Mefenamic acid
Chemical Name: N-(2, 3-Xylyl) anthranilic acid; Benzoic
acid, 2-[(2, 3-dimethylphenyl) amino] – ; B.P.,
Medicinal Uses:
analgesic and anti-infl ammatory agent
Synthesis of Mefenamic acid:
• It may be prepared by the condensation of o-chlorobenzoic
acid with 2, 3-xylidine in the presence of potassium carbonate to give the
potassium salt of mefenamic acid, which on treatment with hydrochloric acid
yields the official compound mefenamic acid
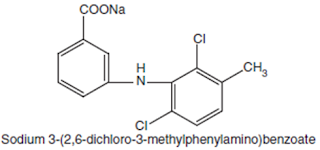
Meclofenamate
Sodium BAN, USAN, Meclofenamic Acid INN.
Chemical structure of
Meclofenamate Sodium
Chemical Name: Monosodium
N-(2, 6-dichloro-m-tolyl) anthranilate monohydrate; Benzoic acid, 2-[2, 6-(dichloro-
3-methylphenyl) amino]-, monosodium salt; U.S.P.,
Medicinal Uses:
It possesses analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. It is
used for the treatment of acute and chronic rheumatoid arthritis and
osteoarthritis.
V.
Arylalkanoic acids
a. Indole
acetic acid derivatives
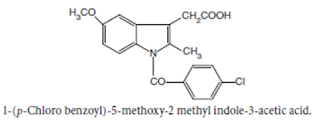
Indomethacin
BAN, USAN, Indomethacin INN
Chemical structure of
Indomethacin
Chemical Name:
1-(p-Chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2- methylindole-3-acetic acid ;
1H-Indole-3-acetic acid, 1-(4- chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methyl- ; BP ; USP
Properties: It is
a white or yellow crystalline powder, insoluble in water and sparingly soluble
in alcohol.
• Indomethacin is more effective than aspirin
Medicinal Uses:
• It is a non-steroid drug possessing anti-inflammatory,
antipyretic and analgestic properties.
• It is usually used for the treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis, ankylosing (rheumatoid) spondylitis, gouty arthritis and
osteoarthritis.
• It is not an ordinary simple analgesic and owing to its
reasonably serious untoward effects should be used with great caution
• The most frequent side effects are gastric distress and
headache
b. Indene
acetic acid derivatives
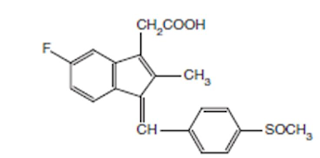
Sulindac
INN, BAN, USAN
Chemical structure of
Sulindac
Chemical Name:
cis-5-Fluoro-2-methyl-1-[(p-methylsulfinyl) benzylidene] indene-3-acetic acid ;
1H-Indene-3-acetic acid, 5-fluoro-2-methyl-1-[[4- (methylsulfinyl) phenyl]
methylene]-, (Z)-; USP
• It is a fluorinated indene with a structural resemblance
to indomethacin
Properties:
Suindac is a yellow crystalline powder, very slightly soluble in water, soluble
in methylenechloride, and dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides, sparingly
soluble in alcohol
Medicinal Uses:
• It is usually employed in the treatment of rheumatic and musculoskeletal
disorders;
• For severe and long-term relief of signs and symptoms of
acute painful shoulder, acute gouty arthritis and osteoarthritis
c. Pyrrole
acetic acid derivative
Tolmetin
Sodium BAN, USAN, Tolmetin INN
Chemical structure of
Tolmetin sodium
Chemical Name:
Sodium 1-methyl-5-p-toluoylpyrrole-2-acetate dihydrate; 1H-Pyrrole-2-acetic acid,
1-methyl-5-(4- methylbenzoyl)-, sodium salt, dihydrate; USP
Properties: It is
a light yellow, crystalline powder, soluble in water, slightly soluble in
alcohol.
Medicinal Uses:
• As an antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-infl ammatory
actions.
• It is employed in the treatment of rheumatic and
musculoskeletal disorders.
Zomepirac
Sodium BAN, USAN, Zomepirac INN
Chemical Structure of
Zomepirac Sodium
Chemical Name:
Sodium 5-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-1, 4-dimethylpyrrole-2- acetate dihydrate ;
1H-Pyrrole-2-acetic acid, 5-(4- chlorobenzoyl)-1, 4- dimethyl-, sodium salt,
dihydrate ; USP ;
• It is an analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug structurally
very similar to tolmetin sodium.
• It is normally used in mild to moderate pain, including
that of musculoskeletal disorders.
d. Phenyl
acetic (propionic) acid:
Diclofenac
Sodium BAN, USAN, Diclofenac INN
Chemical Structure of
Diclofenac sodium
Chemical Name: Sodium
[o-(2, 6-dichloroanilino) phenyl] acetate; Benzene-acetic acid, 2-[(2,
6-dichlorophenyl) amino]-, monosodium salt; Dichlorophenac sodium
Properties:
Diclofenac sodium is a white or slightly yellowish crystalline slightly
hygroscopic powder, sparingly soluble
in water, soluble in methanol and alcohol, slightly soluble in acetone.
Medicinal Uses:
in the treatment of rheumatic arthritis.
Ketorolac
Chemical Name: 5-benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic
acid
Chemical Structure of Ketorolac
Properties:
Colourless compound freely soluble in water
• A pyrrolizine carboxylic acid derivative structurally
related to INDOMETHACIN.
• It is an NSAID Ketorolac non-selective inhibits the
enzymes cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1) and COX-2
Medicinal Uses:
• Used principally for its analgesic activity
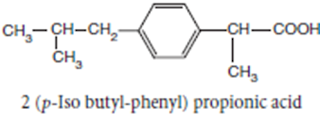
Ibuprofen
INN, BAN, USAN
Chemical Name: -p-Isobutylhydratropic acid; Benzeneacetic
acid, α- methyl-4-(2-methyl-propyl)
Chemical Structure of Ibuprofen
Properties:
Ibuprofen is a white crystalline powder or colourless crystals, practically
insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, methanol, methylene chloride, and
dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates
• Ibuprofen is a propionic acid derivate and nonsteroidal anti-
inflammatory drug (NSAID). Ibuprofen inhibits the activity of cyclo- oxygenase
I and II
Medicinal uses:
• Anti-inflammatory
• Analgesic
• Antipyretic
effects
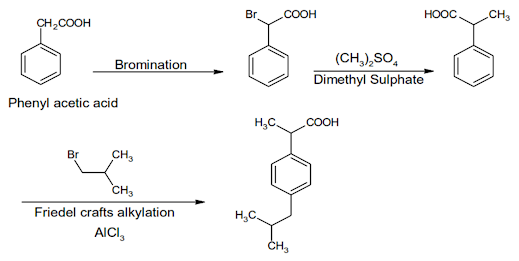
Ibuprofen Synthesis:
Naproxen INN, BAN, USAN
Chemical Structure of Naproxen
Chemical Name:
2-(6-Methoxy-2-naphthyl)-propionic acid; (+)-6-
Methoxy-α-methyl-2-naphthaleneacetic
acid ; 2-Naphthaleneacetic acid,
6-methoxy-α-methyl-, (+)- ; BP ; USP
Properties:
Naproxen is a white crystalline powder, practically insoluble in water, soluble
in ethanol and in methanol.
Medicinal Uses:
• It possesses analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic
actions
• It is used in the treatment of rheumatic arthritis,
dysmenorrhea, and acute gout
VI. OXICAMS
Piroxicam
INN, BAN, USAN,
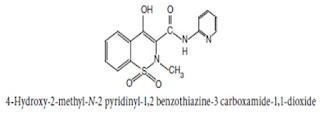
Chemical Structure of Piroxicam
Chemical Name:
4-Hydroxy-2-methyl-N-2-pyridyl-2H-1, 2-
benzothiazine-3-carboxamide 1, 1-dioxide ; 2H-1, 2- benzothiazine-3-
carboxamide, 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-2-pyridinyl-, 1, 1-dioxide
Properties and uses:
Piroxicam is a white or slightly yellow crystalline powder, practically
insoluble in water, soluble in methylene chloride, and slightly soluble in
ethanol.
Medicinal Uses:
• It is employed
for acute and
long-term therapy for
the relief of symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid
arthritis.
• It also possesses
uricosuric action and
has been used
in the treatment of acute gout
SUMMARY
• NSAIDS are the drugs which are used against Inflammation
by inhibiting the COX Enzyme
• Some NSAIDs are only used topically eg. Methyl salicylate,
sodium salicylate
• Along with anti-inflammatory action, most NSAIDs also possess
analgesic and anti-pyretic action.