PROTEIN BINDING
Contents
• Protein binding
• Effects of protein binding
• Types of plasma proteins
• Determination of protein binding
• Pharmacokinetic Importance of protein binding
• Disease and protein binding
Intended
learning outcomes
At the end of this
lecture, student will be able to:
• Explain the importance of protein binding of drug
molecules on biological action.
Binding of
drug to proteins may:
• Facilitate the distribution of drugs.
• Inactivate the drug by not enabling a sufficient concentration
at a receptor site
• Retard the excretion of a drug.
The
interaction of drugs to protein may cause:
• Displacement of body hormones or co-administered agent
• Change the configuration of protein to another structure
capable of binding a co-administered agent
• Inactivates the drug biologically by forming a drug-
protein complex
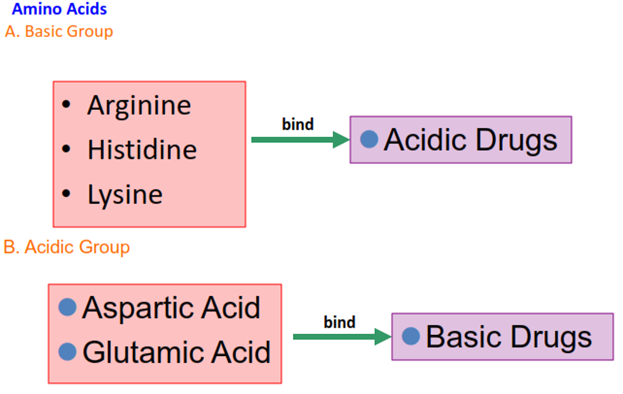
Two Important Plasma Proteins
1. ALBUMIN
2. ACIDGLYCOPROTEIN
ALBUMIN
• Albumin is the most important protein that binds to drug
molecule due to its high concentration compared with other proteins.
• It binds both acidic and basic drugs.
• Constitutes 5% of the total plasma.
∂1-ACIDGLYCOPROTEIN
• Also known as orosomucoid (∂1-globulin)
• Binds to numerous drugs
• Have greater affinity for basic than acidic drugs
molecules
• Binds mostly basic and highly lipophilic drugs.
Things to remember:
• Many drugs bind to the same receptor site but drugs with
higher affinity will replace those drugs with lower affinity by competition.
• Only free and unbound drugs exert therapeutic effect by
interacting with receptors.
Drugs may
bind to protein through:
• Self-Association
• Some drug may self-dissociate to form dimers, trimers or
aggregates of larger size
• Dimers or trimers – is a reaction product of two or three
identical molecules
• May affect solubility, diffusion, transport, therapeutic
action of drugs
Protein
binding is determined by:
• Dialysis
• Ultracentrifugation
• Ultrafiltration
• Sephadex-gel filtration
• Molecular filtration
• Electrophoresis
• Agar plate test
The Pharmacokinetic
Importance of Protein Binding
• Drug-protein binding influences the distribution
equilibrium of the drug
• Plasma proteins exert a buffer and transport function in
the distribution process
• Only free and unbound drug acts can leave the circulatory
system and diffuse into the tissue
Disease and Protein
Binding
• Protein binding will be affected by the presence of
diseases
Drugs showing
Decrease Extent of Protein Binding in the following diseases:
Liver | Renal |
Dapsone Diazepam Morphine Phenytoin Prednisolone Quinidine Tolbutamide Triamterene | Barbiturates Salicylates Cardiac Glycosides Sulfonamides Chlordiazepoxide Triamterene Clofibrate Diazepam Diazoxide Furosemide Morphine Phenylbutazone Phenytoin |
• When drugs bind to protein, Albumin concentration is
reduced
• The exchange of proteins between plasma and interstitial
compartment (normally proceeds at a rate of 5% plasma protein per our) will be
hampered.
• The diffusion of plasma to the interstitial fluid is
increased by:
• Inflammatory process
• Pregnancy
• Use of oral contraceptives
• Diabetes
• Septic shock
• Pulmonary Edema
• The reduced albumin concentration and binding capacity is
due to:
• Change in albumin molecule
• Presence of endogenous binding inhibitors such as free
fatty acids, and metabolic acidosis.
• Hypoalbuminemia may result in patients with cancer, burns,
cardiac failure, cystic fibrosis, enteropathy, inflammations, liver impairment,
malabsorption, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, sepsis and trauma.
Pathological
Conditions in which Plasma Concentration ∂1 – ACIDGLYCOPROTEIN is increased
Cancer | Carcinoma, Leukemia, Lymphoma, Malignant melanoma, myeloma |
Inflammation | Crohn’s disease, inflammatory polyarthritis, pneumonia, rheumatoid |
Myocardial Infarction | Trauma Burns, extensive tissue |
Displacement of Drugs
from their Plasma Protein Binding by Other Drugs given concomitantly
Drug | By |
Warfarin and other highly bound coumarin-type anticoagulants | Clofibrate Phenylbutazone Ethacrynic acid Mefenamic Acid Nalidixic Acid Oxyphebutazone Chloral hydrate |
Tolbutamide | Phenylbutazone Salicylates Sulfafurazole |
SUMMARY
• Albumin is the most important protein that binds to drug
molecule due to its high concentration compared with other proteins
• It binds both acidic and basic and constitute 5% of the
total plasma
• ∂1-acidglycoprotein also known as orosomucoid
(∂1-globulin) and binds to numerous drugs
• Have greater affinity for basic than acidic drugs
molecules Binds only basic and highly lipophilic drugs
• Effects of protein binding and its pharmacokinetic importance
is studied.