Hallucinogens
Contents
• Hallucinogens
• Types of hallucinogens
• Effect of hallucinogens
Objective
At the end of this
lecture, students will be able to:
• Discuss about the types of hallucinogens
• Understand the effect of hallucinogens
Hallucinogens
HALLUCINOGENS:
EFFECTS & SOURCES
May cause changes in:
• Consciousness
• Perception
• Thought
• Emotion
• Come from fungi, plants & animals (Colorado River
Toad)
Hollister’s criteria for hallucinogens
L. E. Hollister’s criteria for hallucinogens:
• Cause changes in thought, perception, and mood
• Little intellectual or memory impairment
• No stupor, narcosis, or excessive stimulation
• Minimal autonomic nervous system side effects
• No addictive cravings
History and use of hallucinogens
• Long history of use, lots of research on in 1900’s
• Religious ceremonies – successful Native American Indians,
Other groups
• Medicinal – not so successful
• Depression
• PTSD, OCD
• Alcoholism
• Drug addiction, Movement Cluster headaches, Recreational/Spiritual – 1960’s
Categories for hallucinogens
• Psychedelics
• Dissociatives
• Deliriants
Psychedelics
• Greek derivation:
• ψυχή (psychê) mind, soul + δηλος (dêlos) manifest, reveal
• Reveals a hidden part of the mind or soul
• Perception-altering effects
Examples:
• Lysergic Acid (LSD)
– from ergot fungus grown
on petri plate (originally on rye grain, morning glory
seeds)
• Psilocybin – from mushrooms
Dissociatives
• Pain relief, amnesia, catalepsy (no response to external
stimuli).
• Derealization (perception that outside world is a dream)
&/or
• Depersonalization (similar to out-of-body experience)
Examples:
• Ketamine – immoblizer, used in animal research with
anesthetics & analgesics, aka “date rape drug”
• Phencyclidine (PCP) – synthesized for use as anesthetic,
now used recreationally, aka “angel dust” “KJ” “illy” or “wet”
• Dextramethorphan (DXM) – cough suppressant found in
Robitussin, Mucinex DM, and Theraflu
• Nitrous oxide (NO) – used at dentist as
analgesic/anesthetic, aka “laughing gas”
Deliriants
Unable to focus or control actions
• Confusion
• Delusion
Examples:
• Diphenhydramine – Benadryl
• Dymenhydramate – Dramamine
• Uncured tobacco – high nicotine
• Atropa belladona – deadly nightshade plant
• Brugmansia – Angel’s trumpet plant
• Datura stramonium – Jimson weed
Unpredictable effects of hallucinogens
Sounds interesting, but:
• “Not all drugs produce the same effect and even the same
drug can produce different effects in the same individual on different
occasions.”
• So, you can’t necessary predict the outcome of taking a hallucinogen.
• Because they are illegal,quality and strength varies a lot
• In some cases, have long-termirreversible effects/brain
damage
• Mescaline – from some cacti (ex: peyote), small amounts in
some beans
TERATOGEN:
“terato-” = monster
“-gen” = to make
• Substances that are toxic to some part of a developing
embryo or fetus
• Common things that can harm fetal development
Nicotine and Cocaine:
• Both nicotine and cocaine are known to be addictive
• Developing fetuses become addicted too
• Both drugs constrict blood vessels
• This decreases oxygen delivery to the fetus
Results of Nicotine
and Cocaine Use
• Low birth weight babies, because they didn’t get enough
oxygen to grow
• Newborns going through withdrawal from drugs
• Most cannot adjust their own body temperatures
• Nicotine and other drugs can also cause “Neural tube
defects”
• A neural tube defect is a problem with the formation of
the brain and/or spinal cord
• The most common neural tube defects are spina bifida and
myelomeningocoel
Some poisonous fungi when taken orally produce
hallucinations
• Genera Amanita
• Genera Psilocybe
• Genera Gonocybe
Amanitas
• Produce hallucinogenic effect and are extremely toxic
• Amatoxins, bufotenine, phallotoxins, ibotenic acid
• Fly agaric –Amanita muscaria – mixture of isoxazole
alkaloids isobetic acid and muscimol
• Within 2 hours the pharmacological effects starts with
initial period of excitation followed by muscular
twitches, a slow pulse rate, impaired breathing, delirium and coma
• Panther cap – A. pantherina
Mexican
mushrooms
• Species of
Psilocybe and conocybe – P. mexicana, C. cyanopus
• Onset of symptoms is rapid – inability to concentrate and
occurrence of hallucinogens
• Active constituents
– tryptamine derivatives – psilocybin and psilocin – compound related to
serotonin
• Highest amount of psilocybin – PSILOCYBE CUBENSIS
Puffballs
• Species –
Lycoperda – constituents produce auditory hallucinations and a state of half
sleep – ½ hr after consumption
Lysergic
acid derivatives
• Lysergic acid and LSD (Diethylamide derivative) – non
peptide portion of ergot alkaloids
Morning
glory seeds
• Rivea corymbosa – seeds
• Ipomoea tricolor, I. purpurea, I. hederacea (Japanese
morning glory)
• Peyote
• Certain cacti – proto alkaloids – hallucinogen property
• Cactus –
Lophophora willaiamsii – peyote or mescal buttons – cactus stem – cut into
slices of about 20-0 mm in diameter – mescaline
Alkaloids of peyole
Indian Hemp
• Cannabis sativa –
European hemp
• Dried flowering and fruiting tops of cannabis sativa and
C. indica
• Cultivation is
regulated – many countries – license
• Hemp products –
Ganja, Bhang, Charas
• Ganja –
contains NMT 10 % of fruits, foliage leaves and stems
• Bhang –
consists of larger leaves and twigs of both male and female plants – used in
India for smoking with either tobacco or opium or datura
• Resin is scrapped off and forms ingredients of numerous
smoking
Charas – obtained
by rubbing the tops between the hands, beating them on cloths or carpets or by
wearing leather aprons walk through the field
Constituents –
cannabinol, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol, cannabigerol and cannabichromene
Other
higher plants
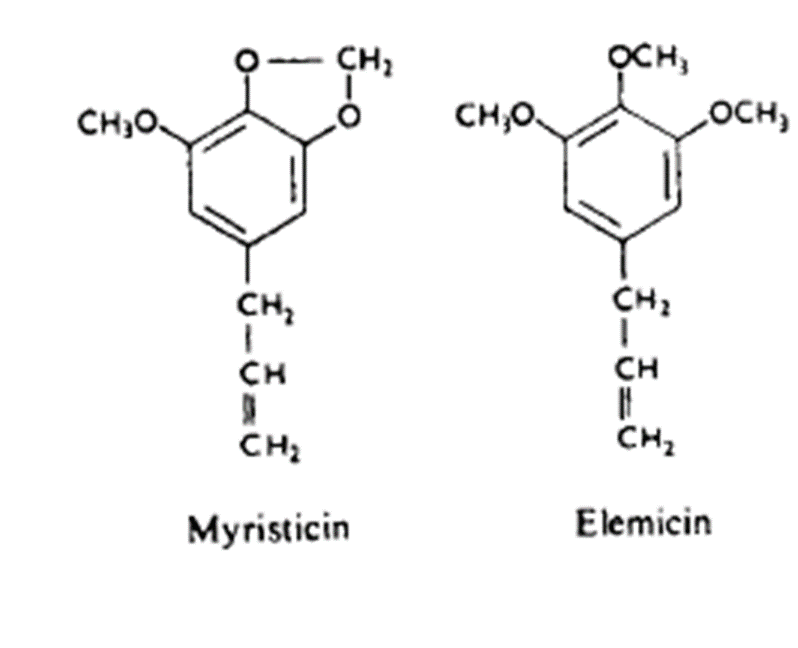
Nutmeg and mace –
psychotropic agent – myristicin and elemicin
Parsley – apiol,
dillapiol of dill – has similar compounds
Virola spp
• Family –
myristcaceae
• Blood red bark
resin – tryptamine – N, N- dimethyl tryptamine (DMT), 5 hydroxy – DMT,
5-methoxy DMT, 2-methyl-1,2,3,4 –tetrahydro-b- carboline