Beta receptor blocking agents
ß – Blocker
Intended
learning outcomes
At the end of the
lecture the students will be able to
• Categorize Beta receptor blocking agents
• State the specific uses for the various Beta receptor
blockers
• Outline the synthesis of Propranolol
Contents
• Categorize Beta receptor blocking agents
• The specific uses for the various Beta receptor blockers
• The synthesis of Propranolol
ß-Adrenoceptor blocking agents
• β-Adrenoceptor blocking agents or antagonists usually
inhibit the actions of catecholamines at the β-adrenergic receptor sites
competitively.
• They are also frequently termed as β-adrenoreceptor or
β-adrenergic blocking agents.
• These agents normally retard the cardiac activity by
preventing β-adrenoceptor stimulation.
• The effect on the heart may be viewed through different
angles, viz : minimising its rate and force of contraction, reducing its
reaction to stress and exercise and lastly, reducing the rate of conduction of
impulses through the conducting system.
• All these remarkable characteristics are vital for their
numerous applications in the therapeutic armamentarium, e.g., in the treatment of angina pectoris and
cardiac arrhythmias.
• These are also used in the control and treatment of hypertension.
Mechanism
of Action of β-Adrenergic Receptor Blockers
• β adrenergic receptor antagonists slow the heart rate and
decrease the myocardial contractility, these prolongs the systolic conduction
and disturbs the ventricular fibres.
• Dimensions of the ventricle is decreased, oxygen
consumption is decreased, and thereby decreases the heart rate and aortic
pressure.
• In blood vessels, these drugs reduces the noradrenaline
release from the sympathetic terminals and decrease the renin from kidney due
to the blockade of β receptors
Classification: Beta-receptor
blocking agents
a. β-Blockers with
membrane stabilizing activity and intrinsic sympathomimetic property:
i.Oxprenalol
ii.Pindalol
b. Specifi c
β-blockers:
i.Timolol
ii.Nodalol
c. β-blockers with
membrane stabilizing activity
i.Propranolol
d. β-blockers with
cardio selective action
i. Acebutolol
ii. Atenolol
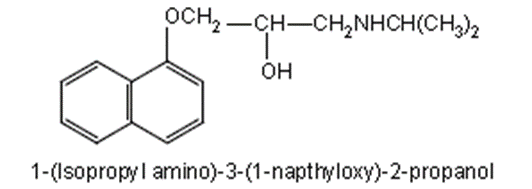
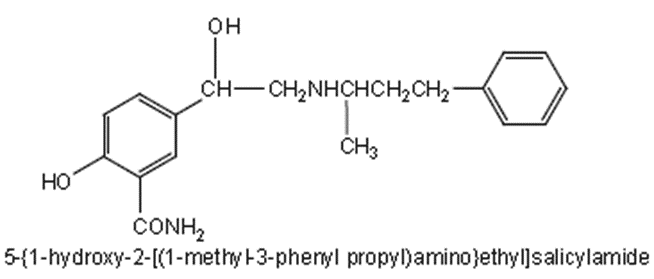
Propranolol:
Synonym: Inderal,
Ipran, Manopralol, Beetacap
Properties: It is
a white or almost white powder, soluble in water and in ethanol. Medicinal
uses:
• Currently, it is approved for hypertension associated
cardiac arrhythmia, angina pectoris, due to coronary atherosclerosis and
prophylaxis of migraine headache.
• It is a nonselective β-adrenergic antagonist and it has
equal affinity for β1 and β2 receptors.
Synthesis of
Propranolol
Propranolol is an effective antihypertensive agent
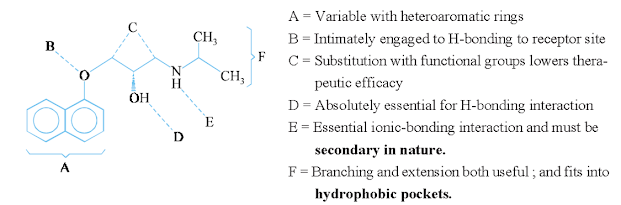
SAR of beta
blockers
1. The ‘branched and bulky N-alkyl functional moieties’,
such as : tert-butyl, iso-propyl etc., proved to be extremely vital for
attributing the β-antagonist activity, thereby suggesting a possible
interaction taking place with a hydrophobic pocket strategically located in the
binding site.
2. It is, however, feasible to afford a variation of the
aromatic ring system as well as heteroaromatic rings into the drug-molecules
e.g., timolol, pindolol etc.
3. The probable substitution of the two methylene moieties
present in the ‘side-chain’
enhances the metabolic
stability at the
expense of therapeutic potency
(lowering of activity).
4. The ‘alcoholic function’ on the side-chain is an absolute
necessary requirement for its activity
5. Isosteric
replacement of the
ethereal linkage (—O—)
with such moieties as : CH2, S or
NCH3 is found to be more or less
detrimental; however, a tissue-selective β-blocker has been synthesized by
replacing NH for O.
6. The introduction of relatively longer alkyl substituents
in comparison to ‘isopropyl’ or ‘tertbutyl’ are found to be much less
therapeutically potent and efficient.
7. The addition of an arylethyl functional moiety, for instance:
CH(CH3)— CH2—C6H5 or CH(CH3)2—CH2—C6H5 has proved to be useful in having better
efficacious drug substances.
8. The ‘amine nitrogen’ should always be a secondary in
character with regard to the optimum activity.
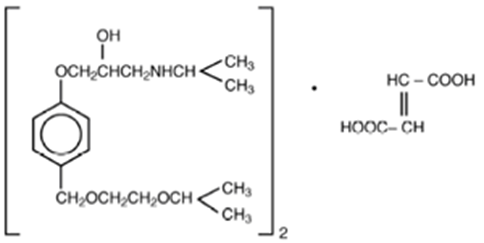
Metipranolol
Synonyms: Metipranolol,Trimepranol,Disorat
[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]-2,3,6-trimethylphenyl]
acetate
• A beta-adrenergic antagonist effective for both beta-1 and
beta-2 receptors.
• A non-cardioselective beta-blocker
• It is a propanolamine, an acetate ester, an aromatic ether
and a secondary amino compound
Medicinal Uses:
• As an antiarrhythmic
• As an antihypertensive
• As an antiglaucoma agent
• Beta-adrenergic antagonist
Atenolol
Synonyms: Atenex, Aten, Betacard
• Atenolol is
1-p-amidomethylphenoxy-3-isopropylamino-2-propanol
• Atenolol is a synthetic isopropylamino-propanol derivative
Properties: It is a white or almost white powder, sparingly soluble in water,
but soluble in ethanol.
Medicinal Uses:
• It is a β1 selective antagonist with low lipid solubility
• Mainly used in the treatment of essential hypertension
• Angina pectoris
• As an antiarrhythmic
Betaxolol
• Betaxolol is a selective beta1 receptor blocker used in
the treatment of hypertension and glaucoma.
• For the management of hypertension
Bisoprolol
• Chemically it is 1-(propan-2-ylamino)-3-[4-(2-propan-2-yloxyethoxymethyl)phenoxy]propan-2-ol
• Bisoprolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in the
treatment of hypertension
• Available as Fumarate salt
• Bisoprolol Fumarate is the fumarate salt of a synthetic
phenoxy-2-propanol-derived cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic receptor
antagonist with antihypertensive and potential cardioprotective activities.
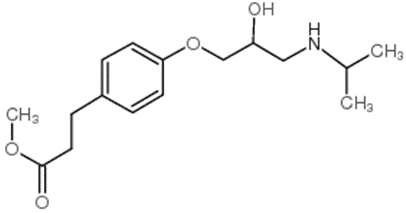
Esmolol
• Chemically: it
is chemically methyl 3-[4-[2-hydroxy-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propoxy]phenyl]propanoate
• Esmolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in
parenteral forms in the treatment of arrhythmias and severe hypertension
Metoprolol
Synonyms:
Betaloc, Lopresor, Metolar
Properties: It is
white, odourless powder, bitter in taste, soluble in water, alcohol, and
chloroform,but insoluble in acetone and ether.
Medicinal Uses:
• It is a β1 selective antagonist used in the treatment of
hypertension
Labetolol
Synonyms: Labesol,
Normadate
• Properties: It
is a white or almost white powder, sparingly soluble in water and alcohol, but
insoluble in methylene chloride
• Labetalol is a beta-Adrenergic Blocker.
• The mechanism of action of labetalol is as an adrenergic
beta-Antagonist.
Medicinal Uses:
• Labetalol is an antihypertensive agent with both alpha-
and beta-adrenergic receptor blocking activity
Carvedilol
Synonyms:
Cardivas, Carvedil, Carvipress
• A carbazole and propanol derivative that acts as a non-cardioselective
beta blocker and vasodilator.
Properties: It is
a white or almost white crystalline powder, insoluble in water and dilute
acids,but soluble in alcohol. It shows polymorphism.
Medicinal Uses:
• In treating hypertension and congestive heart failure
• It acts on both β and α-adrenergic receptors
• Only δ isomer is β–blocking, and both enantiomers have
α-blocking activity
• Antioxidant properties