6 – Thioguanine
6 Thioguanine
• 6 thioguanine comes under the category of Purine antagonist antimetabolite.
• It is thio analogue of naturally occurring purine base guanine.
• This unique composition makes it effective in disrupting cellular processes in cancer cells.
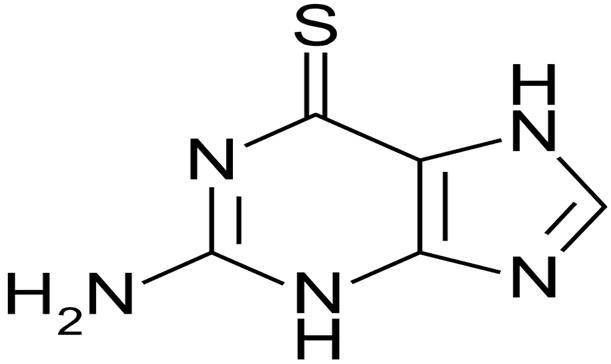
Structure of 6 – Thioguanine:
The IUPAC name of 6-thioguanine is 2-amino-3,7-dihydro-purine-6-thione. Its structure is characterized by the presence of a sulfur atom replacing an oxygen atom in the guanine molecule, giving it its distinct properties. The molecular structure can be visualized as follows:
IUPAC name: 2- amino-3,7 dihydro purine -6 – thione
Mechanism of Action of 6 – Thioguanine
• 6-Thioguanine interacts with enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase(HGPRTase) and gets converted into 6-thioguanosine monophosphate(TGMP).
• 6-thioguanosine monophosphate (TGMP) accumulates in the cells and inhibits the conversion of inosinic acid to xanthylic acid. This leads to the inhibition of synthesis of guanine nucleotide.
• TGMP is converted by phosphorylation to thioguanosine diphosphate (TGDP) and thioguanosine triphosphate (TGTP).
• The TGMP, TGDP and TGTP are collectively named 6-thioguanine nucleotides (6-TGN).
• 6-TGN are cytotoxic to cells by: (1) incorporation into DNA during the synthesis phase (S-phase) of the cell.
• Thus, the effect of this drugs against the tumor cell may be due to the both actions
1. Inhibition of purine synthesis
2. As well as through induction of cytotoxicity in the cell.
Therapeutic uses of 6 – Thioguanine:
• 6 -Thioguanine is given for the treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia (a type of cancer that begins in the white blood cells)
• It can be also used for the treatments of chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of 6-thioguanine varies depending on the type and severity of the leukemia being treated. It is typically administered orally in the form of tablets. The specific dosage and treatment regimen should be determined by a healthcare professional.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common Side Effects
Some common side effects of 6-thioguanine include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite. Patients may also experience low blood cell counts, which can increase the risk of infections and bleeding.
Precautionary Measures
To minimize side effects, it is important for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions carefully. Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor blood cell counts and liver function.
Drug Interactions
Potential Interactions
6-Thioguanine can interact with other medications, potentially altering their effects. For instance, combining it with other cytotoxic drugs can increase the risk of bone marrow suppression.
Recommendations
Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps avoid harmful interactions.
Clinical Studies and Efficacy
Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of 6-thioguanine in treating leukemia. It has been shown to induce remission in a significant number of patients with AML and CML, highlighting its importance in cancer therapy.
Potential New Uses
Ongoing research is exploring the potential use of 6-thioguanine in treating other types of cancer and diseases. Its unique mechanism of action makes it a promising candidate for various therapeutic applications.
Conclusion
6-Thioguanine is a critical drug in the fight against leukemia. Its unique mechanism of action, involving the inhibition of purine synthesis and induction of cytotoxicity, makes it highly effective. As research continues, the potential for new therapeutic uses remains promising, offering hope to many patients.
FAQs
What is 6-thioguanine? 6-Thioguanine is a purine antagonist antimetabolite used in the treatment of certain types of leukemia, such as AML and CML.
How does 6-thioguanine work? It works by inhibiting the synthesis of guanine nucleotides and incorporating into DNA, disrupting cancer cell division and function.
What are the side effects of 6-thioguanine? Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and low blood cell counts.
How is 6-thioguanine administered? It is typically administered orally in the form of tablets, with dosages determined by a healthcare professional.
What should I avoid while taking 6-thioguanine? Patients should avoid other medications that may interact with 6-thioguanine and follow their healthcare provider’s instructions carefully.
Also, visit B. Pharma Notes in PDF Free Download.