6-MERCAPTOPURINE

SAR of 6-Mercaptopurine
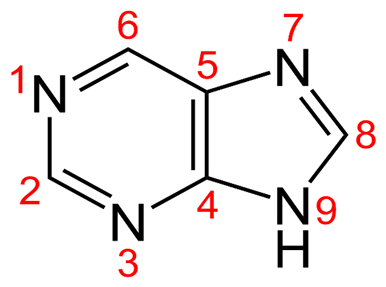
• 6-Mercaptopurine is a Purine Analogue with a Sulphur atom substituted at the 6th position of the purine nucleus.
• Structure of the basic purine nucleus with numbering:
• 6-Mercaptopurine falls under the anti-metabolite class of cytotoxic anti-cancer drugs.
• Apart from being an anti-cancer drug, it is also used for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
• It is used in the treatment of –
1. Acute lymphocytic leukemia
2. Chronic myeloid leukemia
3. Crohn’s disease
4. Ulcerative colitis
Mechanism of Action of 6-Mercaptopurine
Salvage Pathway for the synthesis of Purine nucleotides
De Novo synthesis of Purine Nucleotides
Conversion of IMP to AMP and GMP
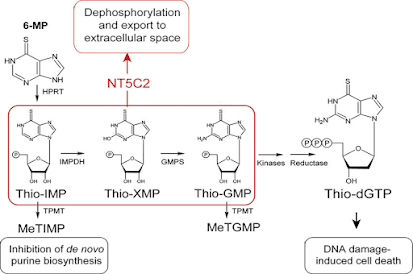
• 6-Mercaptopurine acts by competing with purine derivatives Hypoxanthine and Guanine in order to bind to the enzyme Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phosphoribosyl Transferase (HGPRT) (involved in the Salvage Pathway).
• It itself gets converted to Thio inosine monophosphate (TIMP).
• TIMP inhibits several reactions involving Inosine Monophosphate (IMP), including the conversion of IMP to AMP and XMP.
• TIMP can further get converted to Thioguanosine Monophosphate (TGMP).
• On incorporation of TGMP, a faulty nucleotide into DNA, the cell cycle gets arrested and apoptosis takes place.
• Further methylation of TIMP produces methyl thio inosine monophosphate (MTIMP).
• TIMP and MTIMP inhibit the enzyme Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Amidotransferase (PRPPAT), which is the first enzyme involved in the de-novo synthesis of purine nucleotides.
• Since this enzyme is the rate-limiting factor for purine synthesis, inhibition of the enzyme alters the synthesis and function of DNA and RNA, eventually inhibiting the cell from undergoing division and promoting cell death.