ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC AGENTS

ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC AGENTS
Anti-arrhythmics Agents are drugs that are used to treat abnormal heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation due to irregular electrical activity of the heart.
Classification of Anti-arrhythmic drugs
BASED ON MECHANISM
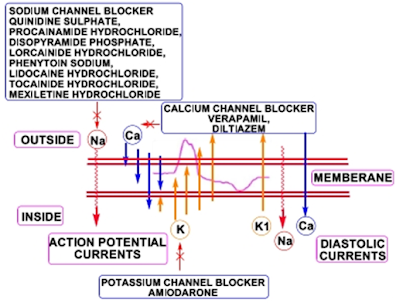
1. Sodium Channel Blocker
– Quinidine sulphate,
– Procainamide hydrochloride,
– Disopyramide phosphate,
– Lorcainide hydrochloride,
– Phenytoin sodium,
– Lidocaine hydrochloride,
– Tocainide hydrochloride,
– Mexiletine hydrochloride
2. Potassium Channel Blocker
– Amiodarone
3. Calcium Channel Blocker
– Verapamil
– Diltiazem
4. Beta-Adrenergic Blocker
– Sotalol
BASED ON PARENT NUCLEUS
1. Aryl phenyl ketone
– Amiodarone
2. Benzamide
– Procainamide hydrochloride
3. Imidazolidine
– Phenytoin sodium
4. Meta xylene
– Lidocaine hydrochloride
– Tocainide hydrochloride
– Mexiletine hydrochloride
5. Pheniramine
– Disopyramide phosphate
6. Sulfanilide
– Sotalol
7. Quinoline
– Quinidine sulphate
MECHANISM OF ANTIARRHYTHMIC AGENTS
QUINIDINE SULPHATE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl((3R,4S,7R)-3-vinylquinuclidin-7yl)methanol sulfuric acid
USES
1. Quinidine sulfate is a tested antiarrhythmic
2. It is very effective drug for treating supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias in short and long-term
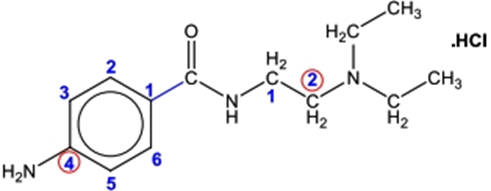
PROCAINAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
4-amino-N-(2-(diethylamino)ethyl)benzamide
USES
1. Procainamide used for the treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias in addition it act as platelet aggregation inhibitors
2. Procainamide is very effective suppressing agent of arrhythmias in ventricular origin, ventricular extrasystoles, paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia as well as ventricular fibrillation
DISOPYRAMIDE PHOSPHATE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
4-(diisopropylamino)-2-phenyl-2-(pyridin-2-yl)butanamide
USES
1. Disopyramide medication is used to treat serious irregular heartbeat, like persistent ventricular tachycardia
2. It is used to restore normal heart rhythm and maintain a regular, steady heartbeat.
3. Disopyramide is known as an anti-arrhythmic drug
SYNTHESIS OF DISOPYRAMIDE PHOSPHATE
PHENYTOIN SODIUM
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
5,5’-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione
USES
1. Phenytoin is used to prevent and control seizures
2. It works by reducing the spread of seizure activity in the brain
3. Phenytoin is known as an anticonvulsant or antiepileptic drug
LIDOCAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide
USES
1. Lidocaine is used on the skin to stop itching and pain
2. Lidocaine is used to treat minor discomfort and itching because of hemorrhoids
3. Lidocaine act like an local anesthetic that works by causing temporary numbness/loss of feeling in the skin and mucous membranes.
TOCAINIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
2-amino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)propanamide
USES
1. Tocainide is used to treat serious irregularity in heartbeat patterns.
MEXILETINE HYDROCHLORIDE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
1-(2,6-dimethylphenoxy)propan-2-amine
USES
1. Mexiletine medication is used to treat irregular heartbeat
2. It is used to restore normal heart rhythm and maintain a regular, steady heartbeat
3. Mexiletine is known as an anti-arrhythmic drug
LORCAINIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-(1-isopropylpiperidin-4-yl)-2phenylacetamide
USES
1. Lorcainide hydrochloride is a Class 1c antiarrhythmic agent
2. It is used to help restore normal heart rhythm and premature ventricular contractions, ventricular tachycardiac
3. Lorcainide is known as a Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome drug.
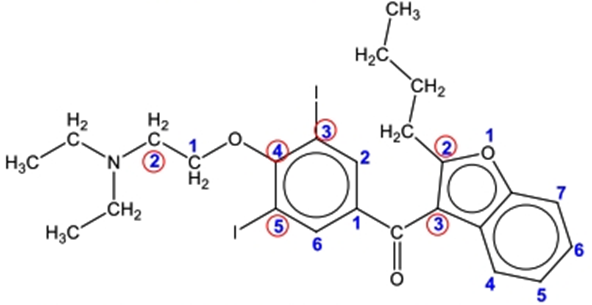
AMIODARONE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
(2-butylbenzofuran-3-yl)(4-(2-(diethylamino)ethoxy)-3,5diiodophenyl)methanone
USES
1. Amiodarone medication is used to treat certain types of serious irregular heartbeat
2. It is used to restore normal heart rhythm and maintain a regular, steady heartbeat.
3. Amiodarone is known as an anti-arrhythmic drug.
SOTALOL
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
IUPAC NAME
N-(4-(1-hydroxy-2(isopropylamino)ethyl)phenyl)methanesulfonamide
USES
1. Sotalol medication is used to treat a serious type of fast heartbeat called sustained ventricular tachycardia.
2. It is also used to treat certain fast/irregular heartbeats with severe symptoms like weakness and shortness of breath
3. Sotalol is is known as a both beta blocker and antiarrhythmic.
FAQ:
1. What are anti-arrhythmic agents?
- Anti-arrhythmic agents are medications used to treat abnormal heart rhythms, known as arrhythmias. They help regulate the electrical activity of the heart and restore a normal heart rhythm.
2. How do anti-arrhythmic agents work?
- These drugs work by affecting the electrical properties of cardiac cells. They can slow down or stabilize the heart’s electrical impulses, helping to prevent or control irregular heartbeats.
3. What are the main classes of anti-arrhythmic agents?
- Anti-arrhythmic agents are classified into four main classes: Class I (sodium channel blockers), Class II (beta-blockers), Class III (potassium channel blockers), and Class IV (calcium channel blockers). Each class has different mechanisms of action.
4. When are anti-arrhythmic agents prescribed?
- They are prescribed when a person experiences abnormal heart rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, or atrial flutter, and when these rhythms pose a risk to the patient’s health.
5. Are there any side effects associated with anti-arrhythmic agents?
- Yes, these medications can have side effects, which vary depending on the specific drug and individual patient factors. Common side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, nausea, and changes in heart rate.
6. How is the right anti-arrhythmic agent chosen for a patient?
- The choice of medication depends on the type of arrhythmia, its underlying cause, the patient’s overall health, and potential drug interactions. A healthcare provider will assess these factors to make an appropriate selection.
7. Can anti-arrhythmic agents cure arrhythmias?
- They can help control and manage arrhythmias, but they may not always cure the underlying cause. In some cases, other treatments like catheter ablation or surgery may be necessary.
8. How should anti-arrhythmic agents be taken?
- Patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions carefully. These medications are usually taken orally, but in some cases, they may be administered intravenously in a hospital setting.
9. Are there any lifestyle changes that can complement anti-arrhythmic treatment?
- Yes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be beneficial. This includes regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, stress management, and avoiding excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption.
10. Can anti-arrhythmic agents be taken alongside other medications? – It depends on the specific medications being used. Some drugs can interact with anti-arrhythmic agents, so it’s important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking.
Also, Visit: B. Pharmacy Notes | B. Pharma Notes | Study material Bachelor of Pharmacy