Chemical mediators of inflammation

Objective
At the end of this lecture, student will be able to
• List various chemical mediators of inflammation
• Describe the formation and functions of cell derived mediators
• Describe the formation and functions of plasma derived mediators
Chemical mediators of inflammation
• Endogenous compounds
• Released during inflammation
• Increases vascular permeability
• Edema, Destruction of inflammatory agents
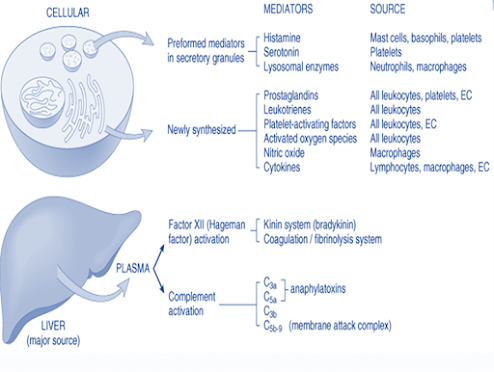
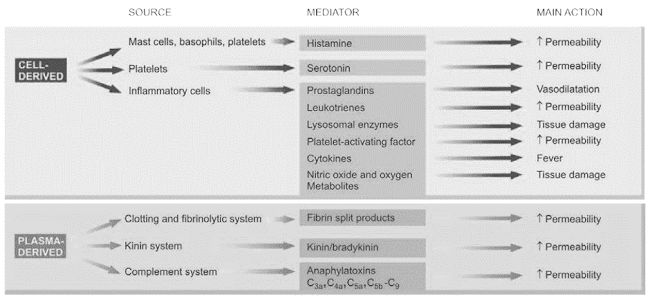
Cell-derived mediators of inflammation
• Vasoactive amines – Histamine, Serotonin, Neuropeptides
• Arachidonic acid metabolites
– Via COX pathway – Prostaglandins, Thromboxane A2, prostacyclin
– Via LOX pathway – 5-HETE, leukotrienes
• Lysosomal system
• Platelet activating factor
• Nitric oxide and oxygen metabolites
Plasma derived mediators of inflammation
• The kinin system
• The clotting system
• The fibrinolytic system
• The complement system
Vasoactive amines (Autocoids)
Amine autocoids
• Histamine
• 5 – HT / Serotonin
Released within 1 hour of inflammatory response
Histamine
• Stored in mast cells, basophills & platelets
Released due to – Heat/cold radiations
– Chemical irritant & immunological reactions
– Anaphyla toxins
Main actions of Histamine
• Vaso dilation
• ↑ permeability of venules
• Itching & pain
• Release of other cell derived mediators
• Broncho constriction
Serotonin
• Present in chromaffin cells of GIT
• In spleen, nervous system, mast cells & platelets
Actions
• Vasodilation
• ↑vascular permeability
• Less potent than histamine
Neuropeptides
• Tachykinin neuropeptides – substance P, neurokinin A, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) & somatostatin
• Produced in the central and peripheral nervous systems
Actions
• Increased vascular permeability
• Transmission of pain stimuli
• Mast cell degranulation
Arachdonic acid Metabolite
• Tissue injury – Phospholipase A2 activation
• Conversion of phospholipids into arachdonic acid
Metabolism of arachdonic acid follows 2 pathway
• COX (Cyclo-oxygenase) – Pathway
• LOX (Lipo- oxygenase) – Pathway
COX Pathway
LOX Pathway
Lysosomal components
Granules of Neutrophills
Primary granules
·
Myeloperoxidase
· Acid hydrolase
· Neutral proteases
Secondary granules
· Lactoferrin
· Lysozyme
· Alkaline phosphatase
· Collagenase
Granules of Monocytes & Tissue macrophages
• Cells on degranulation releases mediators like
• Acid proteases
• Collagenase
• Elastase
• Plasminogen activator
More involved in chronic inflammation
Platelet Activating Factor (PAF)
IgE-sensitised basophils or mast cells, other leucocytes, endothelium and platelets
• ↑ vascular permeability
• Vasodilatation in low concentration and vasoconstriction
• Broncho constriction
• Adhesion of leucocytes to endothelium
• Chemotaxis
Cytokines
• Group of polypeptide substances
• Produced by activated lymphocytes/ monocytes
• Interleukin 1 & 8
• Tumor necrosis factor
• Interferon
• Platelet factor
Actions:
• IL –I, TNF α & β – ↑ leucocyte adherence, Platelet aggregation, proliferation of fibroblast
• Interferon gamma – activation of macrophages & neutrophils
• IL-8 – Chemotactic of neutrophills
• PF – 4 – Chemotactic for neutrophills, monocytes & eosinophills
Nitric oxide & oxygen metabolites
• Released by activated macrophages from vascular endothelium
• Vasodilation
• Inhibiton of platelet aggregation
• Killing of micro organism
• O2 free radicals released from activated neutrophills & macrophages
• Endothelial damage
• ↑vascular permeability
• Tissue matrix damage
Plasma derived mediators
• Interlinked system
• Include
– Clotting system
– Kinin system
– Fibrinolytic system
– Complement system
• Hageman factor (Factor XII) – connects the other 4 system
Clotting system
• Results in formation of fibrinogen
• Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin & fibrinopeptide
– ↑ vascular permeability
– Chemotaxis of leucocytes
– Anticoagulant activity
Fibrinolytic system
• Activated by plasminogen
• Plasminogen activator – plasminogen – plasmin- breakdown of fibrin – fibrinopeptides or fibrin split products
Actions
– Activation of factor XII
– Splits complement fraction C3to C3a– permeability factor
– Degrade fibrin to form fibrin split products
Complement system
Involves 2 pathways
• Classic pathway through antigen-antibody complexes
• Alternate pathway via non-immunologic agents such as bacterial toxins, cobra venoms and IgA
Anaphylatoxins (C3a, C5a, C4a)
– Activate mast cells and basophils to release of histamine
– cause increased vascular permeability
– augments phagocytosis
• C3b – an opsonin
• C5a – chemotactic for leucocytes
• Membrane attack complex (MAC) (C5b-C9) is a lipid dissolving agent and causes holes in the phospholipid membrane
Chemical mediators of inflammation
Summary
• Chemical mediators are endogenous compounds released during inflammation which increases vascular permeability, bring about edema and destruction of inflammatory agents
• Chemical mediators of inflammation are derived from cell and plasma
• Cell-derived mediators include histamine, serotonin, leukotrienes, platelet activating factors, cytokinines, prostaglandins
• Plasma derived mediators include kinin system, cltting and fibrinolytic system and clotting system
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
1. What are chemical mediators of inflammation?
Chemical mediators of inflammation are signaling molecules produced by the body in response to injury or infection. They play a crucial role in initiating, amplifying, and resolving the inflammatory response.
2. What is the primary purpose of these chemical mediators?
The primary purpose of chemical mediators of inflammation is to coordinate the immune response, including the recruitment of immune cells, regulation of blood flow, and the resolution of inflammation after the threat is neutralized.
3. What are some common proinflammatory mediators?
Common proinflammatory mediators include histamines, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, cytokines (such as interleukins and TNF), and chemokines.
4. How do anti-inflammatory mediators work to resolve inflammation?
Anti-inflammatory mediators, like lipoxins, resolvins, and TGF-β, work by promoting the resolution of inflammation. They help reduce inflammation, prevent excessive immune cell recruitment, and aid in tissue repair.
5. Can inflammation be harmful in some cases?
Yes, while inflammation is a vital defense mechanism, chronic or excessive inflammation can lead to various diseases, including autoimmune conditions and chronic inflammatory disorders.
6. What is the role of prostaglandins in inflammation?
Prostaglandins are lipid compounds that play a crucial role in inflammation. They are involved in vasodilation, pain, fever, and regulating the immune response.
7. How do cytokines contribute to the inflammatory response?
Cytokines are signaling proteins that coordinate immune cell activities during inflammation. They can either promote or inhibit inflammation, depending on their type and role.
8. Are there natural ways to modulate inflammation using diet and lifestyle?
Yes, maintaining a healthy diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids) and adopting a lifestyle that includes regular exercise can help manage and reduce inflammation.
9. Can understanding chemical mediators lead to better treatments for inflammatory conditions?
Yes, understanding the roles of chemical mediators in inflammation is crucial for developing targeted treatments for various inflammatory conditions. Researchers continue to explore these pathways to develop more effective therapies.
10. What happens when the balance between proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators is disrupted?
When this balance is disrupted, it can lead to chronic inflammation or a weakened immune response, both of which can have adverse effects on health.