Transamination & Deamination of amino acids

Transamination of Amino Acid
The transfer of an amino group (-NH2) from an amino acid to a keto acid is known as transmission. This reaction involves reversible transfer of a pair of amino acids and a pair of keto acids catalyzed by a group of enzymes transaminases (Amino transferases). This process is predominantly in the liver.
Pyridoxal phosphate is the co-enzyme essential for transaminase activity. All the amino acids except lysine, proline hydroxy proline, and theramine can participate in the transmission reaction.
The keto acids participating in the transamination reaction are only three namely 2 -ketogluturic acid, oxaloacetic acid and pyruvic acid.
Significance:
- Trans amination divert the excess amino acids towards energy production.
- All the amino acids undergo of glutamate. In fact, glutamate is the only amino acid that under goes oxidative deamination to a significant to liberate free NH3 for urea synthesis in urea cycle.
- SGPT: (Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase): and SGOT (serum glutamate oxalo acetate transaminase). Have diagnostic importance the SGPT level is increases in liver diseases like viral hepatitis, jaundice. SGOT level is increases in myocardial infection.
- In the cells, all the amino acids reading available in a proportion for protein biosynthesis. Transamination is very important for the redistribution of amino group for protein biosynthesis and production of non-essential amino acids as per the requirement of the all.
Examples:
 1. Non-oxidative deamination:
1. Non-oxidative deamination:
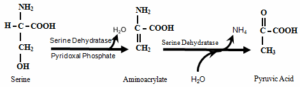
Some of the amino acids can be deaminated to liberate NH3 without undergoing oxidation. It is catalyzed enzymes such as: 1. Dehydratases.
2. Desulfhydrates:
Dehydratases enzymes deaminate amino acid containing hydroxyl group. E.g. Serine, threonine
Desulfhydrates enzymes deaminate amino acid containing sulphur. E.g. Cysteine
Example:
Decarboxylation of amino acids
Decarboxylation is the removal of carboxyl group (-COOH) from an amino acid to form amine with removal of CO2 is called as decarboxylation. These are catalyzed by the enzyme decarboxylase which requires pyridoxal phosphate as co-enzyme. Decarboxylase enzymes are available in liver, kidney and brain.
Significance:
Decarboxylation of amino acid leads to the formation of biologically important amines that is.
Deamination of amino acids
Deamination means removal of amino group from amino acid in the form of NH3. The ammonia liberated is diverted from urea synthesis. The remaining carbon skeleton of amino acid is catabolised to keto acid.
Diamination can be:
(1) Oxidative, (2) Non-oxidative
Significance:
- Deamination results in the liberation of ammonia for urea synthesis.
- The deamination results or serves synthesis of non-essential amino acids.
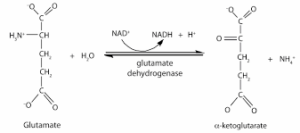
- Oxidative deamination:
It is the removal of amino group from an amino acid which results in liberation of NH3 and formation of keto acid by undergoing oxidation that is in aerobic condition. Oxidative deamination is catalyzed by the enzyme such as
- L-amino acid oxidases.
- D-amino acid oxidases.
- Glutamate dehydrogenase.
Example:
1. Tyrosine is decarboxylized to tyromine by the enzyme tyrosine decarboxylase causing devotion of B.P.
CO2 Tyrosine ————————— Tyromine ———————– Increase the B.P Tyrosine
Decarboxylase (PO4 – B6)
2. Histadine ————- Histamine ————— Affects B.P
(A.A) (Amine)
3. 3, 4, Dihydroxy phenyl alanine—-Dopamine—-Pressure of adrenaline and non-adrenaline
FAQs
- What is the significance of deamination in amino acid metabolism? Deamination removes amino groups from amino acids, generating ammonia for nitrogen excretion and keto acids for energy production or conversion into other biomolecules.
- How do transamination reactions contribute to amino acid metabolism? Transamination transfers amino groups between amino acids and keto acids, facilitating the synthesis of non-essential amino acids and the interconversion of amino acids.
- What are some clinical conditions associated with defects in deamination or transamination processes? Disorders such as aminoacidopathies, urea cycle disorders, and hepatic encephalopathy can result from impaired deamination or transamination reactions, leading to metabolic imbalances and health complications.
- How can dietary factors influence deamination and transamination reactions? Dietary intake of amino acids and micronutrients directly impacts deamination and transamination processes, as the body relies on exogenous sources of amino acids for metabolic needs and enzymatic cofactors for optimal enzyme activity.
- What are some future research directions in the field of amino acid metabolism? Ongoing research aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying deamination and transamination reactions, identify novel therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders, and develop diagnostic biomarkers for monitoring disease progression and treatment responses.
For detailed PDF Notes click on Download Button
