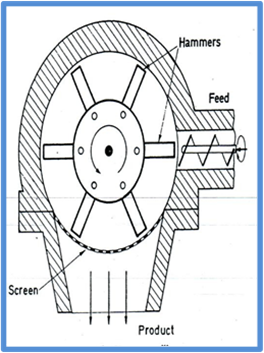
Hammer Mill
On the small scale, size reduction by Impact can be carried
out by the shattering of brittle substances with a hammer or with a pestle and
mortar.
Principle
A hammer mill is essentially a steel drum containing a
vertical or horizontal rotating shaft or drum on which hammers are mounted
The hammers are free to swing on the ends of the cross or
fixed to the central rotor
The rotor is spun at a high speed inside the drum while
material is fed into a feed hopper
The material is impacted by the hammer bars and is thereby
Shredded and expelled through screens in the drum of a selected size
Construction
The hammer mill consists of a central shaft to which four or
more hammers are attached
These are mounted with swivel joints, so that the hammers
swing out to a radial position when the shaft is rotated
The lower part of the casing consists of a screen through
which material can escape
The screen can be changed according to the particle size
required
Working
Material is fed into the mill grinding chamber through the
feed chute
It repeatedly is struck by ganged hammers which are attached
to a shaft rotators at high speed inside the mill chamber
The material is crushed or shattered by a combination of
repeated hammered impacts, collisions with the walls of the grinding chamber
and particle on particle impacts
Perforated metal screens or bar grates covering the
discharge opening of the mill retain coarse material for further grinding while
allowing properly sized materials to pass as finished product
Advantages
Easy to install, dismantle and clean
Scale up problems are minimum
Various types of feed stock can be handled using screen of
different sized
It occupies less space
It is versatile
Operated in a closed environment to avoid dust and explosion
hazard
The product can be controlled by variation of rotor speed,
hammer type, and size and shape of mesh
Operation is continuous. No surfaces move against each
other, so that there is little contamination of the product with metal abraded
from the mill
Disadvantages
The screens may get clogged
Product degradation due to heat building
Wearing of mill with abrasive materials
Unsuitable for sticky, fibrous and hard materials
Applications
Fine to moderate grinding of powders
Particle size may vary from 10 to 400 mm
Nonabrasive, brittle materials can be used as feed stock
Milling dry materials, wet slurries, ointments etc.