Para sympathomimetic agents
Intended learning outcomes
At the end of the lecture students will be able to
• SAR of Para
sympathomimetic agents
• Classify cholinergic
drugs
• Chemical structure,
medicinal uses of classified cholinergic drugs
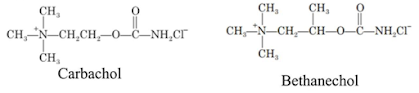
• Outline the synthesis
of Carbachol
• Write chemical structure,
medicinal uses of Indirect acting/ Cholinesterase inhibitors (Reversible &
Irreversible)
• Outline the synthesis
of Neostigmine
• Cholinesterase
reactivator: Pralidoxime chloride
Contents
• SAR of Para
sympathomimetic agents
• Classify cholinergic
drugs
• Drug profile of
cholinergic drugs
• Outline the synthesis
of Carbachol
• Drug profile of indirect
acting/ Cholinesterase inhibitors (Reversible & Irreversible)
• Outline the synthesis
of Neostigmine
• Cholinesterase reactivator:
Pralidoxime chloride
SAR of Para sympathomimetic agents
Onium Group
• Essential for affinity
and intrinsic activity
• It interact with the –vely
charged Aspartic acid residue of the receptor
• Trimethylammonium group
is optimal function moiety. (Exception is pilocarpine, arecoline, nicotine)
• Substitution with
larger alkyl groups decrease the activity.
Ester Group
• Essential for affinity,
forms H bond with threonine and asparagine residue at the receptor site.
• When methyl replaced by
higher homologues (i.e., the propionyl group), the resulting esters are less
potent the Ach.
• Aromatic Group possess
cholinergic antagonist activity
• NH2 Group (carbamic
acid ester group)
• It is more stable than
carboxylate esters to hydrolysis.
Ethylene Bridge
• Shortening or
lengthening of ethylene bridge decrease M activity
• α substation decrease both M (in greater
extent) and N Activity.
• β substation decrease both M (in greater extent)
and N Activity.